Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 5 (2022): 989 - 998
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF
NEOPENTYLGLYCOL ESTER AS BIOLUBRICANT BASE STOCK FROM PALM OIL FATTY ACIDS
(Sintesis
dan Pencirian Ester Neopentilglikol Sebagai Stok Asas Biopelincir
daripada
Asid Lemak Minyak Sawit)
Nurazira Mohd Nor1* and
Jumat Salimon2
1MaterOleo
Research Group, Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti Teknologi MARA, Cawangan Negeri Sembilan,
Kampus
Kuala Pilah, 72000 Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia
2Department
of Chemical Sciences,
Faculty
of Science and Technology,
Universiti
Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
*Corresponding author:
nurazira@uitm.edu.my
Received: 17 May 2022; Accepted: 6
August 2022; Published: 30 October 2022
Abstract
Palm
oil is one of the potential renewable resources in biolubricant production.
However, the direct application of palm oil
as a biolubricant base stock is restricted due to some performance limitations
such as low oxidative stability. It is due to the presence of oxidation
active site β-hydrogen in a glycerol backbone structure. This oxidative
drawback can be overcome by molecule structural redesign through a chemical
modification process such as esterification with polyhydric alcohol. The
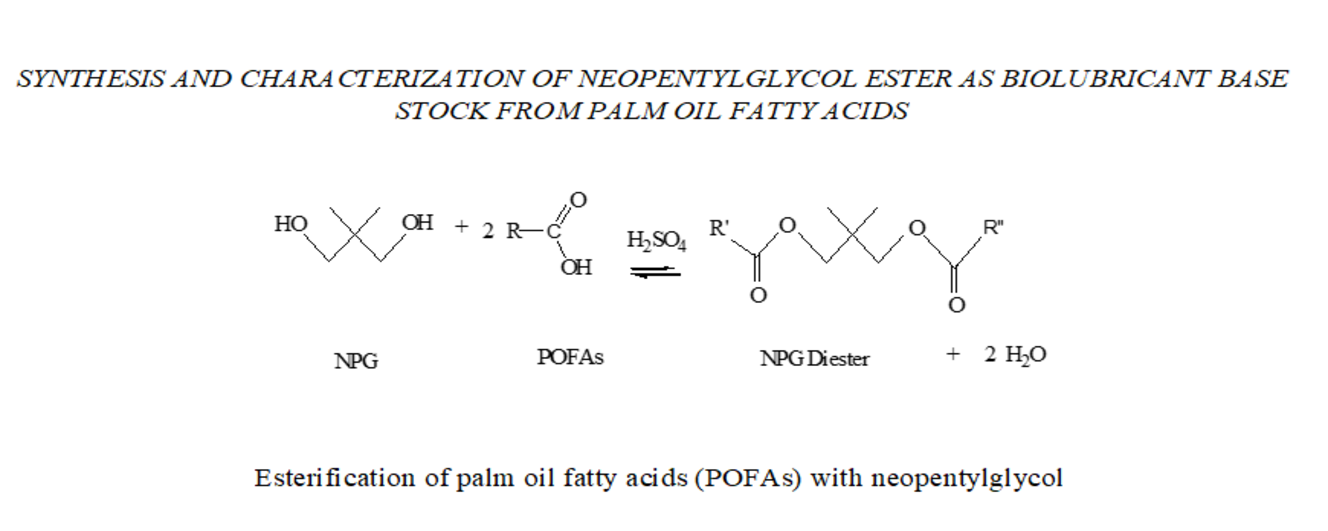
esterification of palm oil fatty acids (POFAs) with neopentylglycol (NPG) was
carried out in a mole ratio of 2:1, 1%
of sulphuric acid, reaction temperature of 145 °C and reaction time of 4.56 hours. Gas Chromatography
equipped with a Flame Ionization Detector (GC-FID) was used to determine the
ester composition in Neopentylglycol Diester (NPGDE). The structure of NPGDE
was confirmed by Fourier Transformation Infra-Red (FTIR), proton and carbon
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR and 13C-NMR)
spectroscopy. Results showed that the percentage yield of NPGDE
was 90% and NPGDE existed in liquid form at room temperature. NPGDE was
successfully synthesised with 100% composition of diesters. The existence of
the ester functional group is evidenced by FTIR at 1738 cm-1, the
chemical shift of 1H NMR at 2.29-2.33 ppm and 13C NMR at
173.71 ppm. Physicochemical properties analysis showed that NPGDE has oxidative
stability at 184 °C, pour point at 10 °C, flash point at 235 °C and
160-viscosity index which makes NPGDE plausible to be used in lubrication
applications.
Keywords: esterification, neopentylglycol,
oxidative stability, palm oil fatty acids
Abstrak
Minyak sawit merupakan salah
satu sumber boleh diperbaharui yang berpotensi untuk digunakan dalam
penghasilan biopelincir. Walau bagaimanapun, penggunaan minyak sawit secara
terus sebagai stok asas biopelincir adalah terhad disebabkan oleh had prestasi
seperti kestabilan oksidatif yang rendah. Ini disebabkan oleh kehadiran tapak
aktif pengoksidaan β-hidrogen dalam struktur tulang belakang gliserol.
Kelemahan oksidatif ini boleh diatasi dengan melakukan ubahsuai struktur
molekul melalui proses pengubahsuaian kimia seperti pengesteran dengan alkohol
polihidrik. Pengesteran asid lemak minyak sawit (POFAs) dengan neopentilglikol
(NPG) telah dijalankan pada nisbah mol 2:1, 1% asid sulfurik, suhu tindak balas
145 °C dan masa tindak balas 4.56 jam. Kromatografi gas dengan pengesan nyala pengionan
(GC-FID) digunakan untuk menentukan komposisi ester dalam Diester
Neopentilglikol (NPGDE). Struktur NPGDE disahkan dengan menggunakan
spektroskopi infra-merah transformasi Fourier (FTIR), resonans magnetik nuklear
proton dan karbon (1H-NMR dan 13C-NMR). Keputusan
menunjukkan bahawa peratusan hasil NPGDE ialah 90% dan NPGDE wujud dalam bentuk
cecair pada suhu bilik. NPGDE telah berjaya disintesis dengan 100% komposisi
diester. Kehadiran kumpulan berfungsi ester dibuktikan melalui FTIR pada 1738
cm-1, anjakan kimia 1H NMR pada 2.29-2.33 ppm dan 13C
NMR pada 173.71 ppm. Analisis sifat fizikokimia menunjukkan bahawa NPGDE
mempunyai kestabilan oksidatif pada 184 °C, takat tuang pada 10 °C, takat kilat
pada 235 °C dan indeks kelikatan 160 yang menjadikan NPGDE sesuai untuk
digunakan dalam aplikasi pelinciran.
Kata
kunci: pengesteran, neopentilglikol,
kestabilan oksidatif, asid lemak minyak sawit

References
1. Salimon,
J. and Salih, N. (2009). Oleic Acid
Diesters: Synthesis, characterization and low temperature properties. European Journal of Scientific Research, 32(2): 216-222.
2. Salimon, J.,
Salih, N. and Yousif, E. (2011). Chemically modified biolubricant
basestocks from epoxidized oleic acid: Improved low temperature properties and
oxidative stability. Journal of Saudi
Chemical Society, 15: 195-201.
3 Farhoosh,
R., Einafshar, S. and Sharayei, P.
(2009). The effect of commercial refining steps on the rancidity measures of
soybean and canola oils. Food Chemistry, 115: 933-938.
4. Erhan,
S. Z. and Asadauskas, S. (2000). Lubricant basestocks from vegetable oils. Industrial Crops and Products,11:
277-282.
5. Cerretani,
L., Bendini, A., Estrada, M. T. R., Vittadini, E. and Chiavaro, E. (2009).
Microwave heating of different commercial categories of olive oil: Part I.
Effect on chemical oxidative stability indices and phenolic compounds. Food
Chemistry, 115:1381-1388.
6. Moser,
B. R., Sharma, B. K., Doll, K. M. and Erhan, S. Z. (2007). Diesters from oleic
acid: Synthesis, low temperature properties and oxidative stability. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 84: 675-680.
7. Salimon,
J. and Salih, N. (2009). Substituted
esters of octadecanoic acid as potential biolubricants. European Journal of Scientific Research,
31(2): 273-279.
8. Nirmal,
V. P. and Dineshbabu, D. (2015).
Performance and emission of pongamia pinnata oil as a lubricant in diesel engine. International Journal of Innovative
Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 4(2):435-441.
9. Salih, N. and Salimon, J. (2021). A review on
eco-friendly green biolubricants from renewable and sustainable plant oil
sources. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 11(5): 13303-13327.
10. Nor, N. M. and Salimon, J. (2022). Synthesis of green- renewable
biolubricant base stock from Malaysia palm oil. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 26(3): 492-506
11. Masood, H., Yunus, R., Choong, T. S. Y., Rashid, U. and
Yap, Y. H. T. (2012). Synthesis and characterization of calcium methoxide as
heterogeneous catalyst for trimethylolpropane esters conversion reaction. Applied Catalyst A: General, 425-426:
184-290.
12. Wu,
X., Zhang, X., Yang, S., Chen, H. and Wang, D. (2000). The study of epoxidized
rapeseed oil used as a potential biodegradable lubricant. Journal
of the American Oil Chemists Society, 77: 561-563.
13. Fox,
N. J. and Stachowiak, G. W. (2007). Vegetable oil-based lubricants-a review of
oxidation. Journal of Tribology International, 40: 1035-1046.
14. Leung,
D. Y. C, Wu, X. and Leung, M. K. M. (2010). A review of biodiesel production
using catalyzed transesterification. Applied
Energy, 87:1083-1095.
15. Sripada,
P. K., Sharma, R. V. and Dalai, A, K. (2013). Comparative study of tribological
properties of trimethylolpropane-based biolubricant derived from methyl oleate
and canola biodiesel. Industrial Crops
and Products, 50: 95-103.
16. Wilson,
B. (1998). Lubricants and functional fluids from renewable sources. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology,
50: 6-15.
17. Nor, M. N., Derawi, D. and Salimon, J. (2017). Chemical
modification of epoxidized palm oil for biolubricant application. Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences,
21(6): 1423-1431.
18. Nor, M. N., Derawi, D.
and Salimon, J. (2018). The optimization of RBD palm oil
epoxidation process using d-optimal design. Sains
Malaysiana, 47(7):1359-1367.
19. Yunus, R., FakhrulRazi, T. L., OoiI, S. E., Iyuke. and
A. Idris. (2003). Development of optimum synthesis method for
transesterification of palm oil methyl esters and trimethylolpropane to
environmentally acceptable palm oil based lubricants. Journal of Oil Palm Research, 15: 35-41.
20. Sulaiman,
S. Z., Chuah, A. L. and Fakhru`I-Razi, A. (2007). Batch production of trimetylolpropane ester from palm oil as lubricant base stock. Journal
of Applied Sciences, 7: 2002-2005.
21. Salih,
N., Salimon, J. and Jantan, F. N. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of palm kernel oil based trimethylolpropane ester. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 25(17): 9751-9754.
22. Aziz, N. A. M., Yunus, R., Rashid, U. and
Syam, A. M. (2014). Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for
optimizing the palm-based pentaerythritol ester synthesis. Industrial Crops and Products, 62: 305-312.
23. Rajaendran, V., Salimon, J. and Yusop, R. M. (2016).
Synthesis and characterization of epoxidized neopentylglycol dioleate as an
intermediate of biolubricant. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 20(6): 1329-1337.
24. Nor, M. N., Derawi, D. and Salimon,
J. (2019). Esterification
and evaluation of palm oil as biolubricant base stock. Malaysian Journal of
Chemistry, 21(2): 28-35.
25. Nadkarni, R. A. (2007). Guide
to ASTM test methods for the analysis of petroleum products and lubricants.
ASTM International, West Conshohocken
26. Chowdhury, K., Banu, L .A., Khan, S. and Latif, A. (2007).
Studies on the fatty acid composition of edible oil. Bangladesh Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 42(3):
311-316.
27. Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M. and Kriz, G. S. (2010). Introduction
to Spectroscopy, 4th edition
United States, Thomson Learcning, Inc,
28. Denicol Motor Oils N.V (2020). Denicol compressor oil. https://pdf4pro.com/view/compressor-oil-iso-vg-32-46-68-100-150-denicol-5786bc.html.
[Access online 25 December 2020].
29. SubsTech: Substances and Technologies (2012). SubsTech hydraulic oil. http://www.substech.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=hydraulic_oil_iso_100. [Access online 25 December 2020].