Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 5 (2022): 965 - 975
ADSORPTION AND MOLECULAR DOCKING
STUDY
OF BISPHENOL A USING REUSABLE ZIF–8
(ZN) METAL–ORGANIC FRAMEWORKS IN AN AQUEOUS SOLUTION
(Penjerapan dan Kajian Penambatan Molekul Bisfenol A
Menggunakan Kerangka Logam–Organik ZIF–8 (Zn) yang boleh Digunakan Semula dalam
Larutan Air)
Afzan
Mahmad1, 3, Teh Ubaidah Noh2, Maizatul
Shima Shaharun3*, Zakariyya Uba Zango4
1Laboratory Department,
Universiti Kuala Lumpur, Royal College of Medicine Perak,
Malaysia
2Institute of Bioproduct Development, Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia, Malaysia
3Fundamental and Applied Sciences Department,
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Seri Iskandar, Perak,
Malaysia
4Department of Chemistry, Al-Qalam University, Katsina,
Nigeria
*Corresponding author:
maizats@utp.edu.my
Received: 24 May 2022; Accepted: 18
July 2022; Published: 30 October 2022
Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a derivative of phenol that
has been identified as a pollutant in water. This work aimed to evaluate the
experimental and molecular docking findings on the adsorption of BPA using
porous material metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) of zeolitic imidazolate
frameworks (ZIF–8 (Zn)). The commercial ZIF–8 (Zn) was characterized by field
emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), scanning electron microscopy
(SEM), and energy dispersive X–ray (EDX). The surface morphology of ZIF–8 (Zn) showed
cubic particles and zinc components (18.70 %) detected by EDX. The adsorption
of endocrine– disruptive chemicals of BPA was performed by batch adsorption
experiments and measured using ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometry.
ZIF–8 (Zn) was shown to achieve adsorption at BPA dosage (0.4 g), and pH 6 (25 oC)
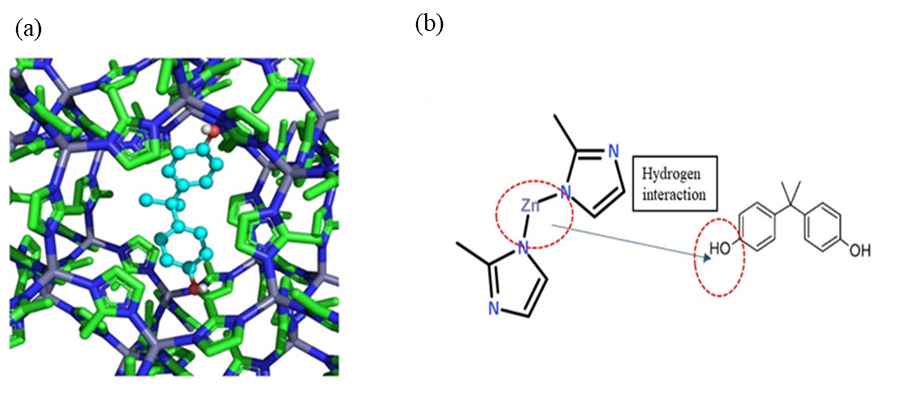
with high BPA removal (98.84%). Molecular docking simulation represented that
BPA was bound to ZIF–8 (Zn) via the inner pores. The mechanism interaction of
BPA and ZIF–8 (Zn) was via van der Waals interaction. The adsorption of BPA
onto ZIF–8 (Zn) fitted the Langmuir isotherm and the pseudo–second–order model.
The possible regeneration and reusability of ZIF–8 (Zn) show good suitability
for reusable adsorbent in BPA adsorption application from environmental
water.
Keywords: bisphenol A, adsorption,
ZIF–8, water pollutants, metal–organic frameworks
Abstrak
Bisfenol A (BPA) adalah terbitan
fenol yang telah dikenal pasti sebagai bahan pencemar di dalam air. Kerja
kajian ini bertujuan untuk menilai ekperimen dan kajian penambatan molekul pada
penjerapan BPA menggunakan kerangka kerja logam–organik (MOFs) bahan berliang
iaitu kerangka besi zeolitik
imidazolat (ZIF–8 (Zn)). ZIF–8 (Zn) secara komersil dicirikan oleh mikroskopi
electron imbasan pancaran medan (FESEM), mikroskopi electron elektron imbasan
(SEM), dan sinar–X serakan tenaga (EDX). Morfologi permukaan ZIF–8 (Zn) oleh
EDX menunjukkan zarah padu partikel kubik dan komponen zink (18.70 %) dikesan
oleh EDX. Penjerapan BPA yang mengganggu bahan kimia endokrin telah dilakukan
oleh secara eksperimen penjerapan kelompok dan diukur menggunakan
spektrofotometer ultraungu tampak (UV–Vis). ZIF–8 (Zn) yang ditunjukkan
mencapai penjerapan pada dos BPA (0.4 g), pH 6 (25 oC) dengan
penyingkiran BPA yang tinggi (98.84%). Simulasi penambatan molekul menunjukkan
bahawa BPA terikat kepada ZIF–8 (Zn) melalui liang dalam. Mekanisma BPA dan
ZIF–8 (Zn) adalah melalui interaksi van der Waals. Penjerapan BPA ke atas ZIF–8
(Zn) adalah sepadan dengan model Langmuir dan pseudo–tertib–kedua. Kemungkinan
penjanaan dan kebolehgunaan semula untuk ZIF–8 (Zn) menunjukkan kesesuaian yang
baik untuk bahan penjerap yang boleh diguna semula dalam aplikasi penjerapan
BPA daripada air persekitaran.
Kata kunci: bisfenol
A, penjerapan, ZIF–8, pencemaran air, kerangka besi logam–organik

References
1. Bhatnagar, A. and Anastopoulos, I. (2017).
Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: a review. Chemosphere,
168: 885-902.
2. Min Park, J. and Hwa Jhung, S. (2020). A
remarkable adsorbent for removal of bisphenol S from water: aminated
metal–organic framework, MIL–101–NH2. Chemical Engineering
Journal, 2020:125224
3. Ohore, O. E. and Songhe, Z. (2019).
Endocrine disrupting effects of bisphenol A exposure and recent advances on its
removal by water treatment systems. A review. Scientific African, 5:
e00135.
4. Goldinger, D. M., Demierre, A. L., Zoller,
O., Rupp, H., Reinhard, H. and Magnin, R. (2015). Endocrine activity of
alternatives to BPA found in thermal paper in Switzerland. Regulatory
Toxicology and Pharmacology, 71: 453-462.
5. Banaderakhshan, R., Kemp, P., Breul, L.,
Steinbichl, P., Hartmann, C. and Fürhacker, M. (2022). Bisphenol A and its
alternatives in Austrian thermal paper receipts, and the migration from
reusable plastic drinking bottles into water and artificial saliva using
UHPLC–MS/MS. Chemosphere, 286: 131842.
6. Ginter–Kramarczyk, D., Zembrzuska, J.,
Kruszelnicka, I., Zając–Woźnialis, A. and Ciślak, M. (2020).
Influence of temperature on the quantity of bisphenol A in bottled drinking
water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
19(9): 5710.
7. Ali, M., Jaghbir, M., Salam, M.,
Al–Kadamany, G., Damsees, R. and Al–Rawashdeh, N. (2018). Testing baby bottles
for the presence of residual and migrated bisphenol A. Environmental
Monitoring & Assessment, 191(1): 1-7.
8. Abraham, A. and Chakraborty, P. (2020) A
review on sources and health impacts of bisphenol A. Reviews on
Environmental Health, 35(2): 201-210.
9. Han, C. and Hong, Y. C. (2016). Bisphenol
A, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases: epidemiological, laboratory, and
clinical trial evidence. Current hypertension reports, 18:1-11.
10. Singh, N. (2016). Exposure to bisphenol–A
through excess use of polymer, with environmental toxicity. International
Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering, and Technology, 2:
454-457.
11 Adamakis, I. S., Malea, P. and Panteris, E.
(2018). The effects of bisphenol A on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa:
Leaf elongation impairment and cytoskeleton disturbance. Ecotoxicology and
Environmental Safety,157: 431-440.
12. Pettamanna, A., Raghav, D. and Nair, R. H.
(2020). Hepatic toxicity in Etroplus
suratensis (Bloch 1790): An economically important edible fish in Vembanad
fresh water Lake, Kerala, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and
Toxicology, 105(4): 565-571.
13. Samanidou, V. F. and Deliyanni, E. A.
(2020). Metal organic frameworks: Synthesis and application. Molecules,
25(4): 960.
14. Tibbetts, I. and Kostakis, G. E. (2020).
Recent bio–advances in metal–organic frameworks. Molecules, 25(6): 1291.
15. Wang, L. C., Ni, X. J., Cao, Y. H. and Cao,
G. Q. (2018). Adsorption behavior of bisphenol A on CTAB–modified graphite. Applied
Surface Science, 428: 165-170.
16. Hoseinpour, V. and Shariatinia, Z. (2021).
Applications of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) in bone tissue
engineering: A review. Tissue and Cell, 72: 101588.
17. Zango, Z. U., Sambudi, N. S., Jumbri, K.,
Ramli, A., Hanif Abu Bakar N. H., Saad B., Rozaini, M. N. H., Isiyaka, H. A.,
Osman, A. M., and Sulieman, A. (2020). An overview and evaluation of highly
porous adsorbent materials for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phenols
removal from wastewater. Water, 2020: 1-40.
18. Zango, Z. U., Sambudi, N. S., Jumbri, K.,
Ramli, A., Hanif Abu Bakar, N. H., Saad, B., Rozaini, M. N. H., Isiyaka, H. A.,
Osman, A. M. and Sulieman, A. (2020). A critical review on metal–organic
frameworks and their composites as advanced materials for adsorption and
photocatalytic degradation of emerging organic pollutants from wastewater. Polymers,
12: 264.
19. Ighalo, J. O., Rangabhashiyam, S., Adeyanju,
C. A., Ogunniyi, S., Adeniyi, A. G. and Igwegbe, C. A. (2022). Zeolitic
Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs) for aqueous phase adsorption – A review. Journal
of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 105: 34-48.
20. Peng, S., Hao, K., Han, F., Tang, Z., Niu,
B., Zhang, X. and Hong, S. (2015). Enhanced removal of bisphenol–AF onto
chitosan–modified zeolite by sodium cholate in aqueous solutions. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 130: 364-371.
21. Genç, N., Kılıçoğlu, Ö. and
Narci, A. O. (2016). Removal of bisphenol A aqueous solution using
surfactant–modified natural zeolite: Taguchi’s experimental design, adsorption
kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Environmental Technology,
38(4): 424-432.
22. Wang, H., Gao, J., Liu, W., Zhang, M. and
Guo, M. (2016). Recovery of metal–doped zinc ferrite from zinc–containing
electric arc furnace dust: Process development and examination of elemental
migration. Hydrometallurgy, 166: 1-8.
23. Peng, J., Li, Y., Sun, X., Huang, C., Jin,
J., Wang, J. and Chen, J. (2019). controlled manipulation of metal–organic
framework layers to nanometer precision inside large mesochannels of ordered
mesoporous silica for enhanced removal of bisphenol A from water. ACS
Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11(4): 4328-4337.
24. Bandura, L., Białoszewska, M.,
Malinowski, S. and Franus, W. (2021). Adsorptive performance of fly ash–derived
zeolite modified by β–cyclodextrin for ibuprofen, bisphenol A and caffeine
removal from aqueous solutions–equilibrium and kinetic study. Applied
Surface Science, 56: 150160.
25. Mahmad A., Shaharun M., Noh T. U., Zango Z.
U. and Faisal M. (2022). Experimental and molecular modelling approach for
rapid adsorption of bisphenol A using Zr and Fe–based metal–organic frameworks.
Inorganic Chemistry Communication. 142(2022): 109604.
26. Mahmad, A., Shaharun, M. S., Zango, Z. U.,
Noh, T. U. and Saad, B. (2021). Adsorptive removal of bisphenol a using
zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF–8). In: Abdul Karim, S. A., Abd Shukur, M.
F., Fai Kait, C., Soleimani, H., Sakidin, H. (eds) Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on
Fundamental and Applied Sciences. Springer Proceedings in Complexity.
Springer, Singapore.
27. Molavi, H., Hakimian, A., Shojaei, A. and
Raeiszadeh, M. (2018). Selective dye adsorption by highly water stable
metal–organic framework: long term stability analysis in aqueous media. Applied
Surface Science, 445: 424–436.
28. Oveisi, M., Mahmoodi, N. M. and Asli, M. A.
(2019). Facile and green synthesis of metal–organic framework/inorganic
nanofiber using electrospinning for recyclable visible–light photocatalysis. Journal
of Cleaner Production, 222: 669-684.
29. Yu, L., Cheng, J., Yang, H., Lv, J., Wang,
P., Li, J. R. and Su, X. (2021). Simultaneous adsorption and determination of
bisphenol compounds in water medium with a Zr(IV)–based metal–organic
framework. Microchimica Acta, 188(3): 83.
30. Zango, Z. U., Sambudi N. S., Jumbri, K., Abu
Bakar, N. H., Abdullah, N. A. F., Negim, E. S. M. and Saad, B. (2020).
Experimental and molecular docking model studies for the adsorption of
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons onto UiO−66 (Zr) and NH2−UiO−66
(Zr) metal−organic frameworks. Chemical Engineering Science, 220:
115608.
31. Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P.
and Ward, S. C. (2016). The Cambridge structural database. Acta Crystallographica Section B, 72: 171-179.
32. Zango, Z. U., Bakar, N. H. H. A., Sambudi, N. S.,
Jumbri, K., Abdullah, N. A. F., Kadir, E. A. and Saad, B. (2020). Adsorption of
chrysene in aqueous solution onto MIL-88 (Fe) and NH2-MIL-88 (Fe) metal-organic
frameworks: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics and docking simulation
studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(2): 103544.
33. Xiang, Y., Yan, H., Zheng, B., Faheem, A.,
Chen, W. and Hu, Y. (2021). E. coli@
UiO−67 composites as a recyclable adsorbent for bisphenol A removal. Chemosphere,
270: 128672.
34. Libbrecht, W., Vandaele, K., De Buysser, K.,
Verberckmoes, A., Thybaut, J., Poelman, H., Van Der Voort, P. (2015). Tuning
the pore geometry of ordered mesoporous carbons for enhanced adsorption of
bisphenol A. Materials, 8(4):
1652-1665.
35. Berhane, T. M., Levy, J., Krekeler, M. P.
S., and Danielson, N. D. (2016). Adsorption of bisphenol A and ciprofloxacin by
palygorskite–montmorillonite: Effect of granule size, solution chemistry, and
temperature. Applied Clay Science, 132-133: 518-527.