Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 5 (2022): 944 - 952
THE EFFECTS OF SOAKING TIME ON THE
QUALITY AND PROPERTIES OF DURIAN (Durio zibethinus) SEED GUM: A MINI
REVIEW
(Kesan Masa Rendaman Terhadap Kualiti Dan Sifat Gam Biji
Durian
(Durio zibethinus): Ulasan Mini)
Nurul I’zzati Ramli1, Boon Yih Tien1,2*,
Boon Yih Hui3, Wang Kang Han4
1Department of Food Science and Technology,
Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan
Negeri Sembilan, Kampus Kuala Pilah,
72000 Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia
2*Alliance of Research and Innovation for Food (ARIF),
Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Negeri Sembilan,
Kampus Kuala Pilah,
72000 Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia
3Research and Development Centre, KL-Kepong Oleomas Sdn. Bhd,
Lot 1 & 2, Solok Waja 3, Bukit Raja Industrial
Estate, 41710 Klang, Selangor, Malaysia
4Faculty of Applied Sciences,
UCSI University, UCSI Height, 56000 Cheras, Kuala
Lumpur, Malaysia.
*Corresponding author: boonyihtien@uitm.edu.my
Received: 28 February 2022; Accepted:
19 May 2022; Published: 30 October 2022
Abstract
Durian (Durio zibethinus)
is one of the most notorious fruits in the world, especially in Southeast Asian
countries. It is well-known as the "King of Fruits" due to its rich
flavour and large size. The unique taste of
durian has created its own global demand, which continues to increase despite
its unpleasant odour. However, only one-third of the entire durian is
consumable, while the seeds and husks are ordinarily disposed of as waste. The
seed waste can be potentially converted into value-added products such as seed
gum. The high content of carbohydrates and starch in the seeds makes them
suitable for use as biopolymers. A natural hydrocolloid can be obtained from
durian seeds through a chemical extraction process. This review provides an
overview of the effects of different extraction parameters on the
physicochemical and functional properties of durian seed gum and discusses the
potential application of durian seeds as a food gum. The physical and chemical
properties of durian seed gum highly depend on the further extraction parameters
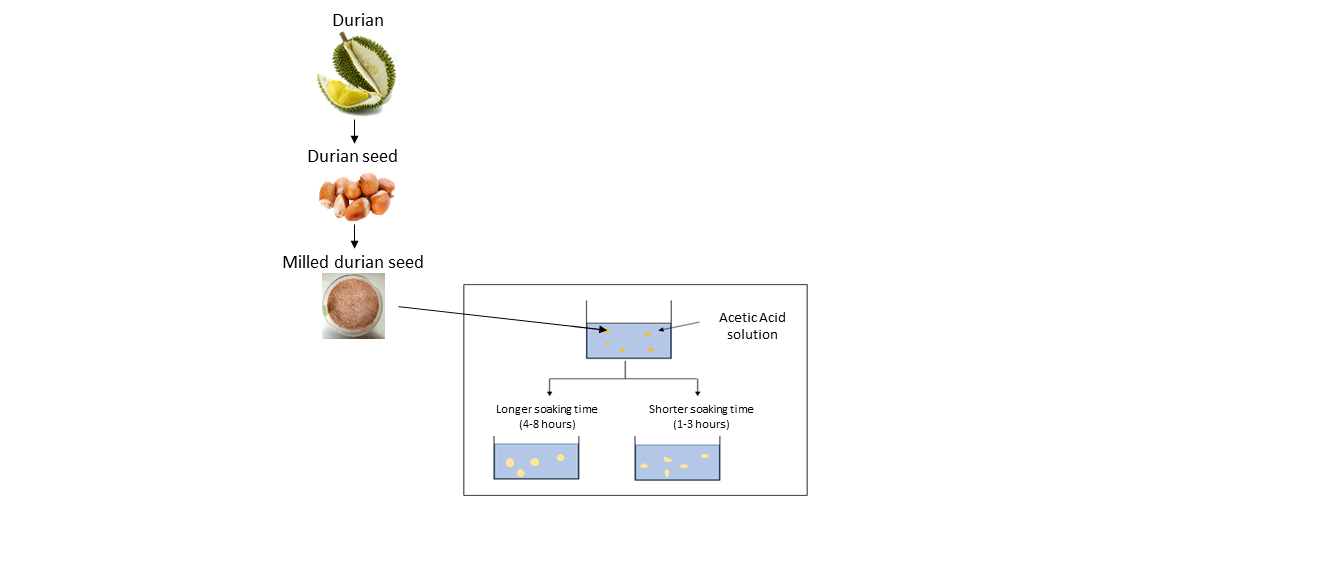
and processing of the gum. The findings showed that the soaking process has a
greater impact on the quality of the gum produced compared to the concentration
of acid used in terms of solubility and water-holding capacity. The
physicochemical properties of durian seed gum are comparable to those of
commercial food gum, but its anti-nutrient content and sensory evaluation in
food products must be further investigated to ensure its safety before
consumption.
Keywords: seed waste, chemical extraction, durian seed gum, physicochemical
properties
Abstrak
Durian (Durio
zibethinus) adalah salah satu buah-buahan yang terkenal di negara-negara
Asia Tenggara. Durian dikenali sebagai “Raja Buah” kerana ciri-cirinya yang
kaya dengan rasa dan mempunyai saiz yang besar. Keenakan dan rasanya yang unik
menyebabkan durian telah meraih permintaan yang tinggi di peringkat global
walaupun mempunyai bau yang kurang menyenangkan. Walau bagaimanapun, hanya satu
pertiga daripada keseluruhan buah durian yang dapat dimakan, iaitu bahagian
isinya, manakala biji dan kulitnya biasanya dibuang sebagai sisa kerana
dipercayai tiada nilai komersial. Biji durian berpotensi tinggi untuk diolah
menjadi produk nilai tambah seperti gam makanan kerana mengandungi karbohidrat
dan kanji yang tinggi. Objektif kajian ini adalah untuk menilai pengaruh
perbezaan parameter pengekstrakan terhadap sifat fiziko-kimia serta fungsi gam
biji durian dan menilai potensi penggunaan biji durian sebagai penstabil
makanan. Ciri-ciri fizikal dan kimia gam biji durian bergantung pada parameter
pengekstrakan dan pemprosesan yang lebih lanjut. Hasil kajian menunjukkan
bahawa proses rendaman mempunyai kesan yang lebih besar terhadap kualiti gam
yang dihasilkan dibandingkan dengan kepekatan asid yang digunakan dari segi
kelarutan dan kapasiti pengekalan air. Ciri-ciri fiziko-kimia gam biji durian
adalah setanding dengan gam makanan yang terdapat di pasaran, tetapi kandungan
anti-nutrien dan penilaian berderia dalam produk makanan perlu dikaji dengan
lebih mendalam untuk memastikan keselamatannya sebelum digunakan dalam
pemakanan.
Kata kunci:
sisa biji benih, pengekstrakan kimia, gam biji durian, sifat fizikokimia
References
1.
Glicksman, M.
(2020). Food Hydrocolloid (1st ed.). CRC Press Publisher.
2.
Syamila, M.,
Hikmah, A.R., Zaiton, H. and Radhiah,
O. (2020). Comparative study on the absorption and solubility properties of
durian seed gum and commercial guar gum. Retrieved from https://oarep.usim.edu.my/jspui/handle/123456789/6888.
3.
Ana, M.E.,
Carmen, S., María, L.E., Berta, E., Sandra, E. and Cristian, S. (2004).
Extraction methods and some physical properties of mesquite (Prosopis
chilensis (Mol) Stuntz) seed gum. Journal of
the Science of Food and Agriculture, 84(12):
1487-1492.
4.
Hamdani,
A. M., Wani, I. A., Bhat, N. A. and Masoodi, F. A. (2018). Chemical
composition, total phenolic content, antioxidant and antinutritional
characterisation of exudate gums. Food BioScience,
23: 67-74.
5.
Mirhosseini, H. and Amid, B.T. (2012). Effect of different
drying techniques on flowability characteristics and chemical properties of
natural carbohydrate-protein gum from durian fruit seed. Chemistry Central
Journal, 2013: 7
6.
Mirhosseini, H. and
Amid, B. T. (2012). Influence of chemical extraction conditions on the
physicochemical and functional properties of polysaccharide gum from durian (Durio zibethinus)
seed. Molecules, 17(6) :
6465-6480.
7.
Khalaf, A., Desa, S. and Baharum, S. (2019). Overview of selected native seeds in
agricultural wastes and its properties. Medico-legal
Update, 19(2): 324-330.
8.
Clemens,
R. and Pressman, P. (2017). Food gums: An overview. Nutrition Today, 52(1): 41-43.
9.
Phillips,
G. and Williams, P. (2020). Handbook of Hydrocolloids (3rd
ed.). Woodhead Publishing.
10.
Golkar, A., Taghavi, S. M. and Dehnavi, F. A.
(2018). The emulsifying properties of Persian gum (Amygdalus scoparia Spach) as compared with gum Arabic. International
Journal of Food Properties, 21(1):
416-436.
11.
Cornelia,
M., Siratantri, T. and Prawita,
R. (2015). The utilization of extract durian (Durio
zibethinus L.) seed gum as an emulsifier in vegan
mayonnaise. Procedia Food Science, 3: 1-18.
12.
Srianta, I., Hedrawan, B., Kusumawati, N. and
Blanc, P. J. (2012). Study on durian seed as a new substrate for angkak production. International Food Research Journal, 19(3): 941-945.
13.
Amin, A.
M., Ahmad, A. S., Yin, Y., Yahya, N. and Ibrahim, N. (2007). Extraction, purification,
and characterization of durian (Durio zibethinus) seed gum. Food Hydrocolloids, 21(2): 273-279.
14.
Navaratne, S. B and
Nawarathne, N. H. N. T. (2014). Determination of
suitability of durian seed gum extract (Durio
zebethinus) in replacing of xanthan gum in fruit
nectar. International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Research, 2(2): 86-89.
15.
Amid, B., Mirhosseini, H. and Kostadinovic,
S. (2012). Chemical composition and molecular structure of
polysaccharide-protein biopolymer from Durio
zibethinus seed: extraction and purification
process. Chemistry Central Journal, 6: 117.
16.
Sawasdikarn, J., Nilanon, W. and Suwannarat, Y.
(2017). Characterization of gum from durian seed an application in ice cream. International
Journal of Agricultural Technology,
13(7): 2661-2667.
17.
Sompie, M., Surtijono, S. E., Pontoh, J. H.
W., and Lontaan, N. N. (2015). The effects of acetic
acid concentration and extraction temperature on physical and chemical
properties of pigskin gelatin. Procedia Food
Science, 3: 383-388.
18.
Vieira, J. M., Mantovani, R. A., Raposo, M. F.
J., Coimbra, M. A., Vicente, A. A. and Cunha, R. L. (2019). Effect of extraction temperature on rheological behavior and antioxidant capacity of flaxseed gum. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 213: 217-227.
19.
Shad, M.
A., Nawaz, H., Hussain, M. and Yousuf, B. (2011). Proximate composition and
functional properties of rhizomes of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) from
Punjab, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 43: 895-904.
20.
Akdowa, E. P., Boudjeko, T., Woguia, A. L. and Njintang N. Y. (2014). Optimization of variables for
aqueous extraction of gum from grewia mollis powder. Journal of Polymers, 2014: 1-10.
21.
Batal, H. E. and Hasib,
A. (2013). Optimization of extraction process of carob bean gum purified from
carob seeds by response surface methodology. Chemical and Process
Engineering Research, 12: 1-8
22.
Marina, Z., Noriham, A., Noorlaila,
A. and Azmi, M. N. (2016). Influence of thermal processing on chemical
composition and antinutritional factors of durian (Durio zibethinus) seed. Retrieved from https://ir.uitm.edu.my/id/eprint/26756/.
23.
Selvi, D. T. and Saraswathy, S. (2017). Seed viability, seed deterioration
and seed quality improvements in stored onion seeds: A review. Journal of Horticultural
Science and Biotechnology, 93(1):
1-7.