Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 5 (2022): 1123 - 1134
CHARACTERIZATION AND
TENSILE PROPERTIES OF POLYLACTIC ACID BIOCOMPOSITE FILLED MICROCRYSTALLINE
CELLULOSE EXTRACTED FROM KENAF
(Ciri-Ciri Dan Sifat Tensil Poli(Asid Laktik) Biokomposit yang
Diisi Selulosa Mikrohablur yang Diekstrak daripada Kenaf)
Norhazirah Azhar 1, Adzrie Baharudin2,
Zuliahani Ahmad2,3 *, Rozyanty Rahman3,4, Luqman Musa3,4
,
Siti Nor Din2, Nor Mazlina Abdul Wahab2
1Malaysian Nuclear Agency, Bangi,
43000 Kajang Selangor
2Department of Polymer Technology,
Faculty of Applied Sciences
Universiti Teknologi MARA, 02600
Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
3Advanced Polymer Group,
Center of Excellence Geopolymer &
Department of Polymer Technology (CEGeoGTech),
Universiti Malaysia Perlis, 02600
Perlis, Malaysia
4 Faculty of Chemical Engineering &
Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Kompleks
Pusat Pengajian Taman Muhibah, 02600 Perlis, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: zuliahani@uitm.edu.my
Received: 17 November 2021; Accepted:
24 March 2022; Published: 30 October2022
Abstract
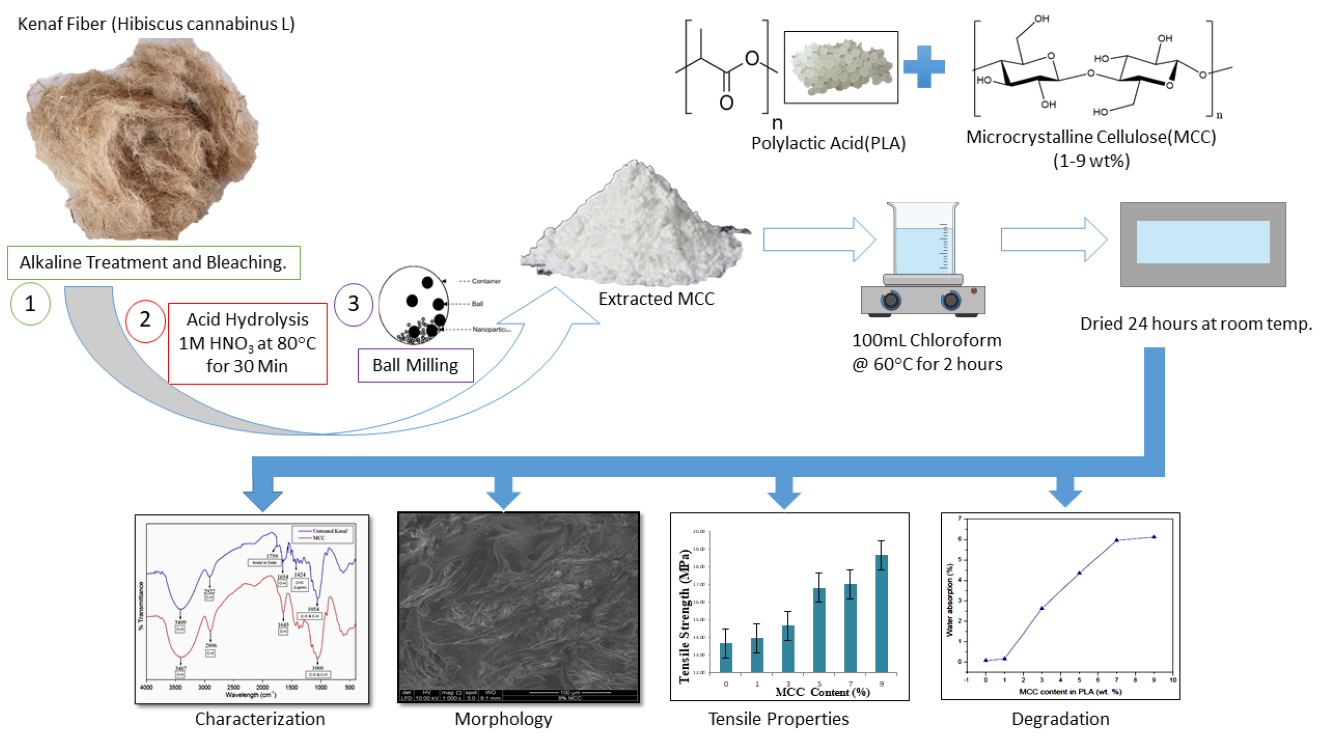
Microcrystalline
cellulose (MCC) was successfully extracted from kenaf bast fiber plant (Hibiscus
cannabinus L.) and incorporated into PLA biocomposite.
The kenaf bast fiber undergone alkali treatment and bleaching prior to acid
hydrolysis using 1M HNO3 in obtaining MCC. Several characterizations
on isolated MCC and PLA/MCC biocomposite conducted
such as Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and crystallinity
index. Further characterization was made on the PLA/MCC biocomposite
to study its mechanical and physical properties. FT-IR spectral indicated the
successive elimination of non-cellulosic constituents in MCC. Differential
scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis revealed the percentage of crystalline
region in the MCC obtained from kenaf bast fiber is higher at 88.53, making it
suitable to be used as reinforcement filler in PLA biocomposite.
Whilst tensile testing on various loading of PLA/MCC composites showed
increment in tensile strength and elastic modulus but decrement in percent
elongation. The optimum parameters were found at 9% MCC loading at 18.7 MPa in
tensile strength attributed to well mixing of PLA and MCC and 88.53
crystallinity index. The potential application of PLA/MCC biocomposite
to be used as food packaging.
Keywords: biocomposite, kenaf,
microcrystalline cellulose, polylactic acid
Abstrak
Selulosa mikrohablur (MCC) berjaya
diekstrak daripada tumbuhan gentian kulit kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.)
dan dimasukkan ke dalam biokomposit PLA. Gentian kulit kenaf menjalani rawatan
alkali dan pelunturan sebelum dihidrolisis asid menggunakan 1M HNO3
dalam mendapatkan MCC. Beberapa pencirian pada biokomposit MCC dan PLA/MCC
terpencil dijalankan seperti Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) dan indeks
kehabluran. Pencirian lanjut dibuat pada biokomposit PLA/MCC untuk mengkaji
sifat mekanikal dan fizikalnya. Spektrum FT-IR menunjukkan penghapusan
berturut-turut juzuk bukan selulosa dalam MCC. Analisis kalorimetri pengimbasan
pembezaan (DSC) menunjukkan peratusan kawasan kristal dalam MCC yang diperoleh
daripada gentian kulit kenaf adalah lebih tinggi iaitu 88.53, menjadikannya
sesuai digunakan sebagai pengisi tetulang dalam biokomposit PLA. Manakala ujian
tegangan ke atas pelbagai pemuatan komposit PLA/MCC menunjukkan peningkatan
dalam kekuatan tegangan dan modulus keanjalan tetapi penyusutan dalam peratus
pemanjangan. Parameter optimum didapati pada 9% pemuatan MCC pada 18.7 MPa
dalam kekuatan tegangan yang dikaitkan dengan pencampuran telaga PLA dan MCC
dan indeks sistaliniti 88.53. Potensi penggunaan biokomposit PLA adalah untuk
digunakan dalam pembungkusan makanan.
Kata kunci: biokomposit, kenaf, selulosa mikrohablur, poli(asid
laktik)
References
1.
Bhasney, S. M., Kumar, A. and Katiyar, V. (2020). Microcrystalline cellulose, polylactic
acid and polypropylene biocomposites and its
morphological, mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Composites
Part B: Engineering, 184: 107717.
2.
Bhasney, S. M., Bhagabati, P., Kumar, A. and Katiyar,
V. (2019). Morphology and crystalline characteristics of polylactic acid
[PLA]/linear low-density polyethylene [LLDPE]/microcrystalline cellulose [MCC]
fiber composite. Composites Science and Technology, 171:
54-61.
3.
Zuliahani, A., Nurul Nadhirah, R., Rozyanty, A. R.,
Nawawi, W. I. and Nor Hanani, A. B. (2016).
Crystallinity, tapping and bulk density of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)
isolated from rice husk (RH). In Applied Mechanics and Materials,
835: 272-276.
4.
Sadalage, P. S. and Pawar, K. D.
(2021). Production of microcrystalline cellulose and bacterial nanocellulose
through biological valorization of lignocellulosic biomass wastes. Journal
of Cleaner Production, 327: 129462.
5.
Nampoothiri, K. M., Nair, N. R. and
John, R. P. (2010). An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA)
research. Bioresource technology, 101(22): 8493-8501.
6.
Adel, A. M., Abd El-Wahab, Z. H., Ibrahim, A. A. and
Al-Shemy, M. T. (2011). Characterization of
microcrystalline cellulose prepared from lignocellulosic materials. Part II:
Physicochemical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2):
676-687.
7.
Ahmad, Z., Roziaizan, N.
N., Rahman, R., Mohamad, A. F. and Ismail, W. I. N. W. (2016). Isolation and
characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from rice husk (RH).
In MATEC Web of Conferences, 47: p. 05013.
8.
Khalil, H. A., Yusra, A. I., Bhat, A. H. and Jawaid, M. (2010). Cell wall ultrastructure, anatomy,
lignin distribution, and chemical composition of Malaysian cultivated kenaf
fiber. Industrial Crops and Products, 31(1): 113-121.
9.
Haafiz, M. M., Eichhorn, S. J.,
Hassan, A. and Jawaid, M. (2013). Isolation and
characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm biomass
residue. Carbohydrate polymers, 93(2): 628-634.
10.
Radzi, M. K. F. M., Muhamad,
N., Akhtar, M. N., Razak, Z. and Foudzi, F. M.
(2018). The effect of kenaf filler reinforcement on the mechanical and physical
properties of injection moulded polypropylene
composites. Sains Malaysiana, 47(2):
367-376.
11.
Sun, X., Lu, C., Liu, Y., Zhang, W. and Zhang, X.
(2014). Melt-processed poly (vinyl alcohol) composites filled with
microcrystalline cellulose from waste cotton fabrics. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 101: 642-649.
12.
Rosa, S. M., Rehman, N., de Miranda, M. I. G., Nachtigall, S. M. and Bica, C. I.
(2012). Chlorine-free extraction of cellulose from rice husk and whisker
isolation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 87(2): 1131-1138.
13.
Chaiwutthinan, P., Pimpan,
V., Chuayjuljit, S. and Leejarkpai,
T. (2015). Biodegradable plastics prepared from poly (lactic acid), poly
(butylene succinate) and microcrystalline cellulose extracted from waste-cotton
fabric with a chain extender. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 23(1):
114-125.
14.
Ibrahim, M. M., El-Zawawy,
W. K., Jüttke, Y., Koschella,
A. and Heinze, T. (2013). Cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose from rice
straw and banana plant waste: preparation and characterization. Cellulose, 20(5):
2403-2416.
15.
Aimi, M. N., Anuar, H., Maizirwan, M., Sapuan, S. M., Wahit, M. U. and Zakaria, S. (2015). Preparation of durian
skin nanofibre (DSNF) and its effect on the
properties of polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposites. Sains Malaysiana, 44(11):
1551-1559.
16.
Mukherjee, T., Sani, M., Kao, N., Gupta, R. K., Quazi, N. and Bhattacharya, S. (2013). Improved dispersion
of cellulose microcrystals in polylactic acid (PLA) based composites applying
surface acetylation. Chemical Engineering Science, 101:
655-662.
17.
Yussuf, A.
A., Massoumi, I. and Hassan, A. (2010). Comparison of polylactic
acid/kenaf and polylactic acid/rise husk composites: the influence of the
natural fibers on the mechanical, thermal and biodegradability
properties. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 18(3):
422-429.
18.
Rocca-Smith, J. R., Whyte, O., Brachais,
C. H., Champion, D., Piasente, F., Marcuzzo, E., ... & Karbowiak, T. (2017). Beyond
biodegradability of poly (lactic acid): physical and chemical stability in
humid environments. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5(3):
2751-2762.
19. Wan, L., Zhou, S. and
Zhang, Y. (2019). Parallel advances in improving mechanical properties and
accelerating degradation to polylactic acid. International Journal of
Biological Macromolecules, 125: 1093-1102.