Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 734 - 741
THE ANTIBACTERIAL, ANTIFUNGAL, ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL AND TOTAL PHENOLIC
CONTENT OF MALAYSIAN ENDANGERED SPECIES Coscinium fenestratum FROM PAYA
BUNGOR PAHANG
(Potensi
Sifat Antibakteria, Antikulat, Antioksida dan Jumlah Kandungan Fenolik Cosinium
fenestratum Spesies Terancam Malaysia dari Paya Bungor Pahang)
Aiza Harun1*,
Noorshilawati Abdul Aziz2, Shaari Daud1
1Faculty
of Applied Sciences
2Faculty of Plantation and
Agrotechnology
Universiti
Teknologi MARA Cawangan Pahang, 26400 Bandar Jengka, Pahang, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: aizaharun@uitm.edu.my
Received: 21 January 2022; Accepted: 2 April 2022; Published: 25 August 2022
Abstract
Coscinium
fenestratum (family: Menispermaceae), which is
locally known as akar sekunyit, is one of the endangered species in
Malaysia. C. fenestratum is wildly grown in the forest reserve, Paya
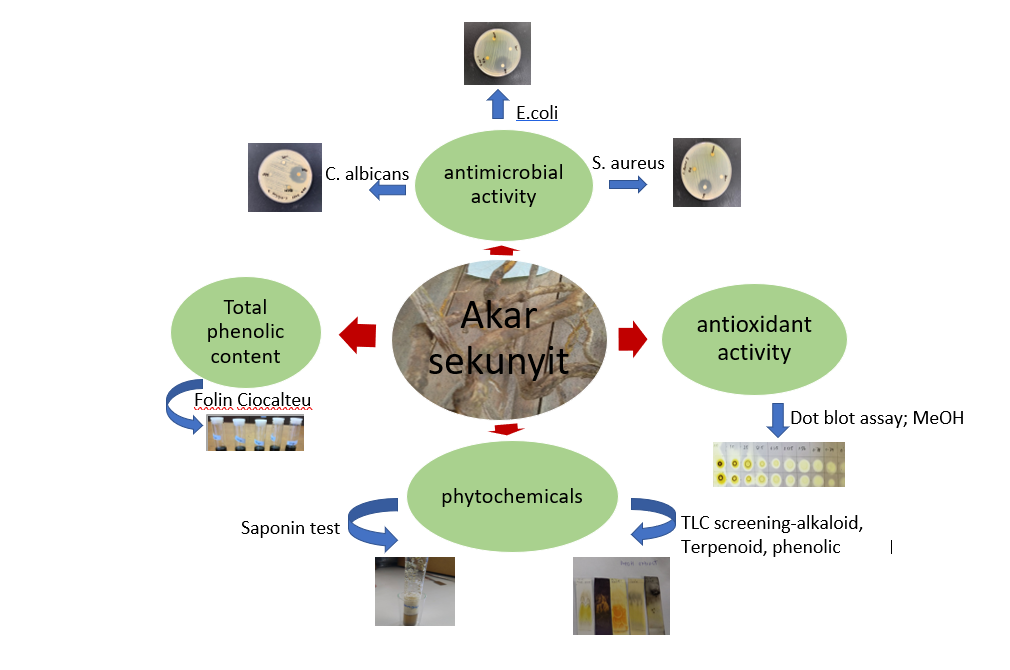
Bungor, Pahang. This study aims to investigate the potential of C.
fenestratum as an antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant agent as well
as its total phenolic content. Four types of extracts were prepared from the
consecutive soaking using hexane, dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate (EA),
and methanol. All types of extracts were assessed for their antibacterial and
antifungal activities using the disc diffusion method against Salmonella
thypi ATCC 10708, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 43300, Escherichia
coli UPMC 25922, Candida albicans ATCC 90028, and Aspergillus
brasiliensis ATCC 16404. The potency of this species as an antioxidant
agent was evaluated using semiquantitative staining dot blot assay against DPPH
(2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl). The total phenolic content was assessed using
the Folin-Ciocalteu method. The phytochemical screening for all types of
extracts revealed the presence of alkaloid, terpenoid, phenolic, and saponin.
All extracts with the concentration of 1,000 ppm demonstrated antibacterial and
antifungal activities against S. aureus ATCC 43300 and C. albicans
ATCC 90028 but none for the rest of the bacteria and fungi. The methanol
extract was more active with a moderate inhibition zone. The semiquantitative
staining dot blot assay against DPPH revealed that the lowest concentration of
methanol extract for DPPH inhibition was at the concentration of 0.012 mg/ml,
and the DCM extract showed that the DPPH inhibition was at 0.006 mg/ml.
However, the methanol extract of C. fenestratum had a higher total
phenolic content (TPC) with the value of 12.722 mg GAE/g sample compared to the
DCM extract at 8.627 mg GAE/g sample. Hence, both methanol extract and DCM
extract of C. fenestratum exhibited stimulating antimicrobial and
antioxidant properties with potent phenolic content.
Keywords: Coscinium fenestratum, antibacterial,
antifungal, akar sekunyit, antioxidant
Abstrak
Coscinium fenestratum (keluarga: Menispermaceae) yang dikenali sebagai akar
sekunyit adalah salah satu spesies terancam di Malaysia iaitu Pahang dan ia tumbuh secara liar di
hutan simpan Paya Bungor Pahang. Kajian ini bertujuan untuk menyiasat potensi C. fenestratum sebagai
agen antibakteria, antikulat dan antioksidan serta jumlah kandungan fenolik.
Empat jenis ekstrak telah disediakan daripada rendaman berturut-turut
menggunakan heksana, diklorometana (DCM), etil asetat dan metanol. Semua jenis ekstrak
telah dinilai untuk aktiviti antibakteria dan antikulat menggunakan kaedah
penyebaran cakera terhadap Salmonella thypi ATCC 10708, Staphylococcus
aureus ATCC 43300, Escherichia coli UPMC 25922, Candida albicans
ATCC 90028 dan Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 90028. Keupayaan spesies ini sebagai agen
antioksida dinilai daripada ujian bintik-bintik pewarnaan semikuantitatif
terhadap DPPH (2,2-difenil-1-pikrilhidrazil). Jumlah kandungan fenolik dinilai
menggunakan kaedah Folin-Ciocalteu. Pemeriksaan fitokimia untuk semua jenis
ekstrak mendedahkan kehadiran alkaloid, terpenoid, fenolik dan saponin. Semua
ekstrak dengan kepekatan 1,000 ppm menunjukkan aktiviti antibakteria dan
antikulat terhadap S. aureus ATCC 43300 dan C. albicans ATCC
90028, tetapi aktiviti itu tidak dapat dilihat untuk bakteria dan kulat yang
lain. Ekstrak metanol didapati sebagai ekstrak yang lebih aktif dengan zon
perencatan sederhana berbanding dengan ekstrak yang lain. Ujian bintik-bintik
pewarnaan separa kuantitatif terhadap DPPH mendedahkan bahawa kepekatan
terendah ekstrak metanol untuk perencatan DPPH adalah pada kepekatan 0.012
mg/ml dan ekstrak DCM menunjukkan perencatan DPPH pada 0.006 mg/ml. Walau
bagaimanapun, ekstrak metanol C. fenestratum mempunyai jumlah kandungan
fenolik yang lebih tinggi dengan nilai 12.722 mg sampel GAE/g berbanding
ekstrak DCM pada 8.627 mg sampel GAE/g. Oleh itu, adalah disahkan bahawa
kedua-dua ekstrak metanol dan ekstrak DCM C. fenestratum mempamerkan
sifat antimikrob dan antioksida yang baik dan sederhana dengan kandungan
fenolik yang memberangsangkan.
Kata kunci: Coscinium fenestratum, antibakteria, antikulat, akar sekunyit, antioksida
Graphical Abstract
References
1. Cook, N. C. and Samman, S. (1996).
Flavonoids-chemistry, metabolism, cardioprotective effects, and dietary
sources. Nutritional Biochemistry, 7: 66-76.
2. Rojsanga, P. and Gritsanapan,
W.(2005). Variation of berberine content in Coscinium fenestratum stem
in thailand market. Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
32(3-4): 66-70.
3. Danapur, V., Haleshi, C. and
Sringeswara A. N. (2020). Endangered medicinal plant Coscinium fenestratum (Gaertn.)
Colebr. - A review. Pharmacognosy Journal, 12(5): 1077-1085
4. Eamsiri, J., Chookaew, S., Pewlong,
W., Sajjabut, S. and Orpong, P. (2019). Effects of irradiation on antioxidant
and antimicrobial activities of Coscinium fenestratum (Goetgh.) Colebr. IOP Conf. Series: Journal of Physics: Conf. Series 1285 (2019) 012006.
5. Harun, A., Mat So’ad, S.Z., Mohd
Hassan, N. and Che Mohd Ramli, N.K. (2014). In-vitro antidermatophytic activity
of methanolic fractions from Entada spiralis Ridl. stem bark and its
bioautographic profile. Pertanika Journal Science & Technology 22(1): 113-121.
6. Daud, A. D., Azman, N. S., Alias, N.
I. A., Syaifudin, N., Harun, A. and Abdul Aziz, N. (2021). Phytochemical and
antibacterial properties on three medicinal plants for potent anti-soft rot
agents. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 25(1): 119-128.
7. Harun, A., Abdul Aziz, N., Mohd
Azenan, N. S., Muhammad Kamarazzaman, N. F and Mat So’ad., S. Z. (2020).
Antimicrobial efficacy, antioxidant profile and nine alternative active
constituents from petroleum ether and ethyl acetate extract of Entada
spiralis. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 25(5): 707-718.
8. Siddiqui, N., Rauf, A., Latif, A. and
Mahmood, Z.(2017). Spectrophotometric determination of the totalphenolic
content, spectral and fluorescence study of the herbal Unani drug Gul-e Zoofa
(Nepeta bracteata Benth). Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences,
12(4): 360-363.
9. Rubab,
M., Chelliah, R., Saravanakumar, K., Kim, J. R., Yoo, D., Wang, M. H. and Oh, D. H.
(2020). Phytochemical characterization, and antioxidant and
antimicrobial activities of white cabbage extract on the quality and shelf life
of raw beef during refrigerated storage. Royal Society of Chemistry,10: 41430-41442.
10. Nair, G. M., Narasimhan, S.,
Shiburaj, S. and Abraham, T. K.(2005). Antibacterial effects of Coscinium fenestratum. Fitoterapia,76:
585-587.
11. Singburaudom, N. (2015). The alkaloid
berberine isolated from Coscinium fenestratum is an inhibitor of
phytopathogenic fungi. Journal of Biopesticides, 8(1):28-36.
12. Goveas, S.W. and Abraham, A. (2013).
Evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of stem and leaf extracts
of Coscinium fenestratum. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Clinical
Research, 6(3): 218-221.
13. Mohd Azli,
N. A. N., Harun, A., Abdul Aziz, N. and Daud, S. (2021). Anti soft rot and
antioxidant behaviour of nine medicinal plants from Paya Bungor, Pahang. GADING
Journal of Science and Technology, 4(2): 20-26.
14. Keawpradub, N., Dej-adisai, S. and Yuenyongsawad., S. (2005).
Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Thai medicinal plants named
Khaminkhruea: Arcangelisia flava, Coscinium blumeanum and Fibraurea
tinctoria. Songklanakarin Journal of Science Technology, 27(2):
455-467.