Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 742 - 754
EFFECTS OF PROCESSING PARAMETERS ON THE QUALITY AND
PROPERTIES OF MANGO KERNEL FLOUR: A MINI-REVIEW
(Kesan Pemprosesan Parameter Terhadap Kualiti dan Sifat
Tepung Biji Mango: Ulasan Mini)
Amal Hanani
Binti Zikri1, Boon Yih Tien1,2*, Boon Yih Hui3,
Wang Kang Han4
1Department of
Food Science and Technology, Faculty of Applied Sciences
2Alliance of
Research and Innovation for Food (ARIF)
Universiti
Teknologi MARA, Kampus Kuala Pilah, 72000 Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan,
Malaysia
3Research and
Development Centre, KL-Kepong
Oleomas Sdn. Bhd, Lot 1 & 2, Solok Waja 3,
Bukit Raja
Industrial Estate, 41710 Klang,
Selangor, Malaysia
4Faculty of
Applied Sciences,
UCSI
University, UCSI Height, 56000 Cheras,
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: boonyihtien@uitm.edu.my
Received: 28 February 2022; Accept ed: 23 April 2022; Published: 25 August 2022
Abstract
Mango (Mangifera indica Linn) is a popular tropical fruits that is widely
available in the market. In order to reduce food waste, mango kernels are
usually treated as waste mango kernel flour due to their nutritional
composition and bioactive compounds. However, the processing method used during
the production of mango kernel flour has lowered its nutritional value and
affected the quality of the mango kernel flour. In addition, the
anti-nutritional found in the mango kernel influences the flour’s quality.
Hence, this review provides an overview of the effect of processing parameters
on the quality of mango kernel flour (in terms of nutritional, functional
properties, and bioactive compounds) and the application of mango kernel flour
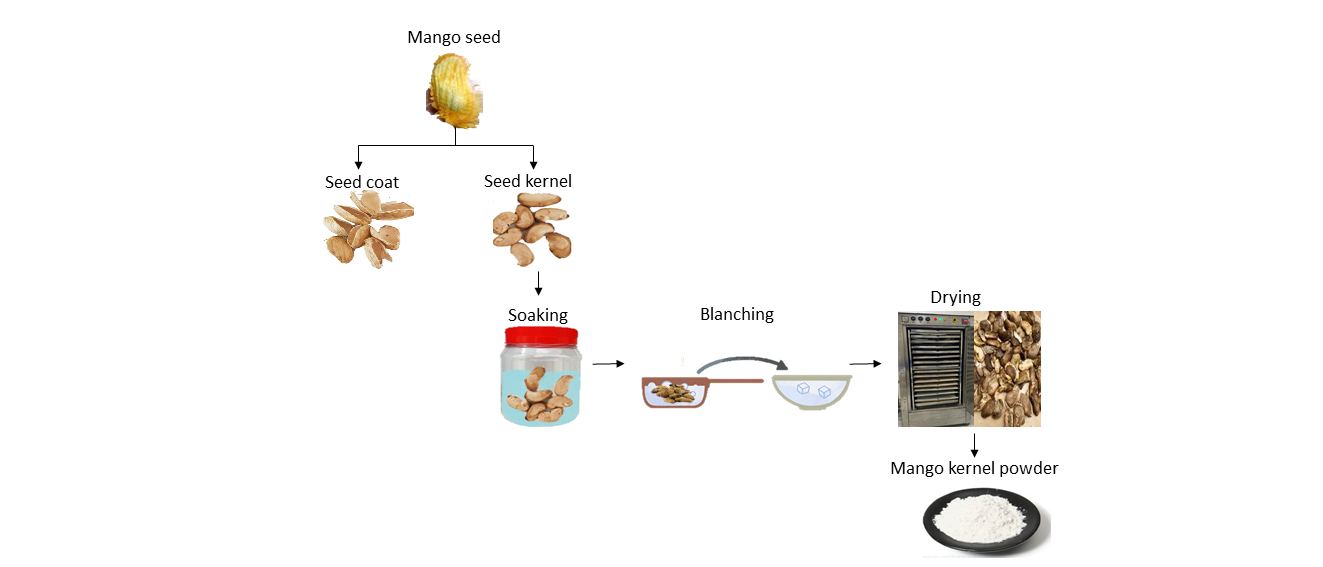
in baking products. The findings proposed that the soaking, blanching, and
drying processes have an impact on the nutritional value, functional
properties, and bioactive compounds of mango kernel flour. Further
investigation into optimising processing parameters is required to obtain
high-quality mango kernel flour.
Keywords: mango kernel
flour, soaking, blanching, nutritional composition, anti-nutrient
Abstrak
Mangga (Mangifera indica Linn) merupakan salah satu buah tropika yang
terkenal di pasaran. Bagi mengurangkan sisa biji manga, biji mangga biasanya
diproses menjadi tepung biji mangga kerana komposisi nutrisi dan sebatian
bioaktifnya. Bagaimanapun, kaedah pemprosesan semasa penghasilan tepung biji
manga telah mengurangkan nilai nutrisi dan mempengaruhi kualiti tepung biji
mangga. Selain itu, anti-nutrien yang terdapat di dalam biji mangga juga
mempengaruhi kualiti tepung. Oleh itu, ulasan ini memberikan gambaran
keseluruhan kesan parameter pemprosesan ke atas kualiti tepung biji mangga
(dari segi komposisi nutrisi, sifat fungsi dan sebatian bioaktif) dan penggunaan
tepung biji mangga dalam produk bakeri. Hasil kajian menunjukkan bahawa proses
rendaman, penceluran dan pengeringan adalah faktor yang mempengaruhi nilai
nutrisi, sifat berfungsi dan sebatian bioaktif dalam tepung biji mangga.
Siasatan lanjut keatas pengoptimuman parameter pemprosesan diperlukan bagi
mendapatkan tepung biji mangga yang berkualiti tinggi.
Kata kunci: tepung biji mangga,
rendaman, blanching, komposisi nutrisi, anti-nutrien
Graphical Abstract
References
1. Awolu,
O. O., Sudha, M. L. and Monohar, B. (2018). Influence of defatted mango kernel
seed flour addition on the rheological characteristics and cookie making
quality of wheat flour. Food Science
Nutrition, 6(8): 2363-2373.
2. Ediriweera,
M. K., Tennekoon, K. H. and Samarakoon, S. R. (2017). A review on
ethnopharmacological applications, pharmacological activities, and bioactive
compounds of Mangifera indica
(mango). Evidence-based Complementry
Alternative Medicines, 2017: 6949835.
3. Mwaurah,
P. W., Kumar, S., Kumar, N., Panghal, A., Attkan, A. K., Singh, V. K. and Garg,
M. K. (2020). Physicochemical characteristics, bioactive compounds and
industrial applications of mango kernel and its products: A review. Comprehensive Review Food Science Food
Safety, 19(5): 2421-2446.
4. Izli, N., İzli, G. and Taskin, O. (2017). Influence
of different drying techniques on drying parameters of mango. Food Science Technology, 37(4): 604-612.
5. Masibo,
M. and He, Q. (2009). Mango bioactive compounds and related nutraceutical
properties-a review. Food Review International, 25(4): 346-370.
6. Torres-León,
C., Rojas, R., Contreras-Esquivel, J. C., Serna-Cock, L., Belmares-Cerda, R. E.
and Aguilar, C. N. (2016). Mango
seed: functional and nutritional properties. Trends Food Sci Technology, 55(2016): 109-117.
7. Jahurul,
M. H., Zaidul, I. S., Ghafoor, K., Al-Juhaimi, F. Y., Nyam, K. L., Norulaini,
N. A. and Mohd Omar, A. K. (2015). Mango (Mangifera
indica l.) by-products and their valuable components: a review. Food Chemistry, 183: 173-180.
8. Uzombah,
T. A., Awonorin, S. O., Shittu, T. A. and Adewumi, B. A. (2019). Effect of
processing parameters on the proximate and antinutritive properties of mango
kernel flour processed for food applications. Journal Food Processing Preservation, 43(10): e14131.
9. Diarra,
S. S. (2019). Potential of mango (Mangifera
indica L.) seed kernel as a feed ingredient for poultry: a review. Worlds Poultry Science Journal, 70(2): 279-288.
10. Shabeer,
M., Sultan, M. T., Abrar, M., Suffyan Saddique, M., Imran, M., Saad Hashmi, M.
and Sibt-e-Abbas, M. (2016). Utilization of defatted mango kernel in
wheat-based cereals products: Nutritional and functional properties. International
Journal Fruit Sciences, 16(4): 444-460.
11. Yatnatti, S., Vijayalakshmi, D. and Chandru, R.
(2014). Processing and nutritive value of mango
seed kernel flour. Current Research
Nutrition Food Science Journal, 2(3):
170-175.
12. Ram, R. A., Rahim, M. A. and Alam,
M. S. (2020). Diagnosis and management of nutrient constraints in mango. Fruit Crops, 2020: 629-650.
13. Afiqah,
A. N., Nulit, R., Hawa, Z. E. J. and Kusnan, M. (2014). Improving the yield of
‘Chok Anan’ (MA 224) mango with potassium nitrate foliar sprays. International
Journal Fruit Sciences, 14(4): 416-423.
14. Okpala, L. C. and Gibson-Umeh, G. I. (2013). Physicochemical
properties of mango seed flour. Nigeria
Food Journal, 31(1): 23-27.
15. Beyene,
G. and Araya, A. (2015). Review of mango (Mangifera
indica) seed-kernel waste as a diet for poultry. Journal Biology Agriculture Healthcare, 5(11): 156-159.
16. Lauricella,
M., Emanuele, S., Calvaruso, G., Giuliano, M. and D’Anneo, A. (2017).
Multifaceted health benefits of Mangifera
indica l.(mango): the inestimable value of orchards recently planted in
Sicilian rural areas. Nutrients, 9(5): 525.
17. Matheyambath, A. C., Subramanian, J.
and Paliyath, G. (2016). Mangoes. In Encyclopedia
of Food and Health: pp. 641-645.
18. Elsheshetawy,
H. E., Mossad, A., Elhelew, W. K. and Farina, V. (2016). Comparative study on
the quality characteristics of some Egyptian mango cultivars used for food
processing. Annals Agriculture Sciences, 61(1): 49-56.
19. Mas’ud,
F., Rifai, A. and Sayuti, M. (2020). Mango seed kernel flour (Mangifera indica): nutrient composition
and potential as food. Malaysian Journal
Nutrition, 26(1): 101.
20. Patel,
G. N. and Kheni, J. (2018). Mango seed kernel, a highly nutritious food, should
we continue to trash or use? Journal Pharmacognosy
Phytochemistrt, 7(4): 04-07.
21. Bejo,
S. K. and Kamaruddin, S. (2014). Determination of Chokanan Mango sweetness ('Mangifera indica') using
non-destructive image processing technique. Australian
Journal Crop Sciences, 8(4): 475.
22. Das,
P. C., Khan, M. J., Rahman, M. S., Majumder, S. and Islam, M. N. (2019).
Comparison of the physico-chemical and functional properties of mango kernel
flour with wheat flour and development of mango kernel flour based composite
cakes. NFS Journal, 17: 1-7.
23. Perez, I. C., Mu, T. H., Zhang, M. and Ji, L. L.
(2017). Effect of heat treatment to sweet potato
flour on dough properties and characteristics of sweet potato-wheat bread. Food Science Technology International, 23(8):
708-715.
24. Gumte,
S., Taur, A., Sawate, A. and Kshirsagar, R. (2018). Effect of fortification of
mango (Mangifera indica) kernel flour
on nutritional, phytochemical and textural properties of biscuits. Journal Pharmacognosy Phytochemistry, 7(3):
1630-1637.
25. Amin,
K., Akhtar, S. and Ismail, T. (2018). Nutritional and organoleptic evaluation
of functional bread prepared from raw and processed defatted mango kernel
flour. Journal Food Processing
Preservation, 42(4): e13570.
26. Lakshmi,
M., Preetha, R. and Usha, R. (2016). Mango (Mangifera
indica) stone kernel flour-a novel food ingredient. Malaysian Journal Nutrition, 22(3):
461-467.
27. Gumte,
S., Taur, A., Sawate, A. and Thorat, P. (2018). Effect of processing on
proximate and phytochemical content of mango (Mangifera indica) kernel. International
Journal Chemical Studies, 6(2):
3728-3733.
28. Ojha, P., Raut, S., Subedi, U. and Upadhaya, N.
(2019). Study of nutritional, phytochemicals and
functional properties of mango kernel powder. Journal Food Science Technology Nepal, 11: 32-38.
29. Florence, O. S., Abdoulaye, T., Tidiane, K., Rodrigue, K.
N., Monon, K. and Rene, S. Y. (2020). Chemical
composition, functional and antioxidant properties of mango seed kernel (Kent
variety) flour grown in Korhogo (Ivory Coast). International Journal Science Engineering
Research, 11(11) : 357-369.
30. Ekorong,
F. J. A. A., Zomegni, G., Desobgo, S. C. Z. and Ndjouenkeu, R. (2015).
Optimization of drying parameters for mango seed kernels using central
composite design. Bioresource Bioprocessing,
2(1): 1-9.
31.
Sogi, D. S., Siddiq, M.,
Greiby, I. and Dolan, K. D. (2013). Total phenolics, antioxidant activity, and
functional properties of 'Tommy Atkins'
mango peel