Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 708 - 717
FORMULATION OF HIGH-QUALITY UV-CURABLE COATING CONTAINING RENEWABLE
REACTIVE DILUENTS FOR WOOD PROTECTION
(Formulasi
Salutan Awetan-UV Berkualiti Tinggi yang Mengandungi Diluen Reaktif yang Boleh Diperbaharui untuk Perlindungan
Kayu)
Noraini Abd Ghani1,2,3, Emilia Abdulmalek1,2, Rajni Hatti-Kaul4, Azren Aida Asmawi1,2, Mohd Basyaruddin Abdul Rahman1,2*
1Integrated Chemical BioPhysics Research, Faculty of Science
2Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science
Universiti Putra
Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
3Department of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, Faculty of
Science and Information Technology,
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, 32610, Perak, Malaysia
4Department of Biotechnology, Center for Chemistry and
Chemical Engineering,
Lund University, P.O. Box 124, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden
*Corresponding
author: basya@upm.edu.my
Received: 29 November 2021; Accepted: 23 April 2022;
Published: 25 August 2022
Abstract
Fine quality coating materials for a variety of
surfaces using environmentally friendly substrates are continuously in demand.
A large proportion of acrylate derivatives, which are toxic and hazardous, were
found in most of the coating formulations. Many efforts have been done to
replace acrylate derivatives with other materials derived from renewable
resources. In this work, several formulations of wood coating containing
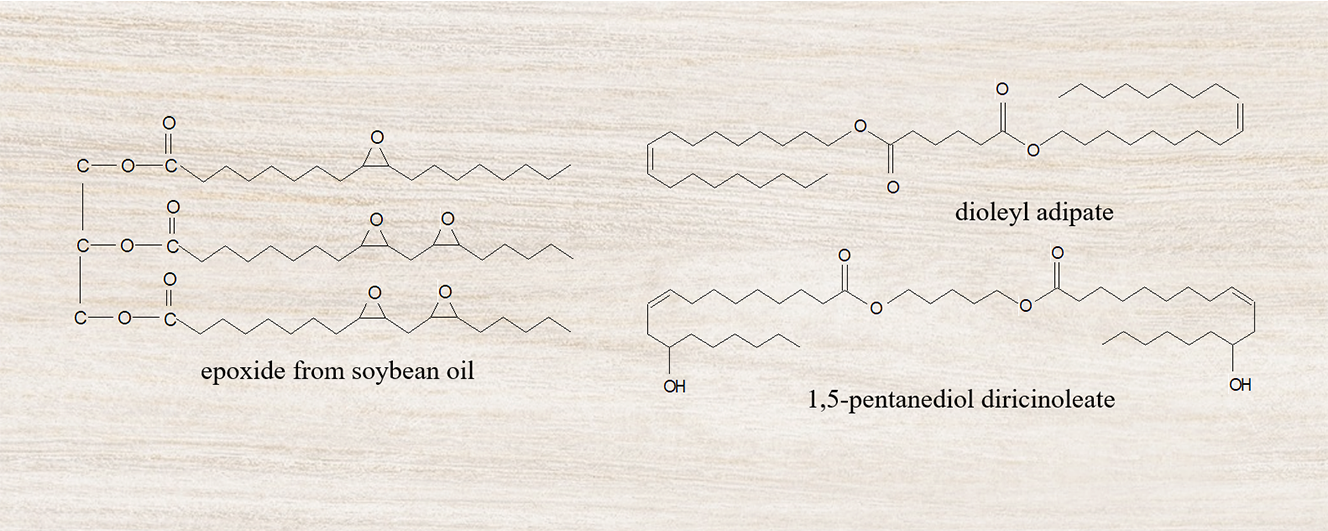
different composition of epoxy acrylate and enzymatically synthesized epoxide
from soybean oil or wax esters mixture of dioleyl adipate and 1,5-pentanediol
diricinoleate were prepared. The formulations were subjected to performance
evaluations including gel content, pendulum hardness, and surface test. Formulation 1 containing 85% epoxy acrylate and 15%
epoxidation from soybean oil exhibited the highest gel content (79.5%),
pendulum hardness (61.02%) and surface resistance to different types of liquid.
Increase in surface resistance was observed using a formulation containing 85%
epoxy acrylate and a mixture of 1,5-pentanediol diricinoleate and dioleyl
adipate (1:1, w/w; 15%). Therefore, these reduced acrylate formulations
showed good potential in the development of high-quality UV-curable wood
coating.
Keywords:
coating, acrylate, epoxide, ester, ricinoleate
Abstrak
Bahan salutan yang
berkualiti untuk pelbagai permukaan menggunakan substrat mesra alam sentiasa
mendapat permintaan. Sebilangan besar derivatif akrilat, yang beracun dan
berbahaya, ditemui dalam kebanyakan rumusan salutan. Pelbagai usaha telah
dilakukan untuk menggantikan derivatif akrilat dengan bahan lain yang diperoleh
daripada sumber yang boleh diperbaharui. Dalam kajian ini, beberapa formulasi
salutan kayu yang mengandungi komposisi epoksi akrilat dan epoksida yang disintesis
secara enzimatik daripada minyak kacang soya atau campuran ester lilin dioleil
adipate dan 1,5-pentanediol dirisinoleate yang
berbeza telah disediakan. Formulasi ini tertakluk kepada penilaian prestasi
termasuk kandungan gel, kekerasan pendulum, dan ujian permukaan. Formulasi 1
yang mengandungi 85% epoksi akrilik dan 15% epoksida dari minyak kacang soya
menunjukan kandungan gel (79.5%), kekerasan pendulum (61.02%) dan rintangan
permukaan terhadap pelbagai jenis cecair yang tertinggi. Selain itu, peningkatan
terhadap rintangan permukaan diperhatikan menggunakan formulasi yang
mengandungi 85% epoksi akrilik dan campuran dioleil adipate dan 1,5-pentanediol
dirisinoleate (1:1, w/w; 15%). Oleh itu, formulasi akrilat yang dikurangkan ini
menunjukan potensi yang baik dalam pembangunan salutan kayu awetan-UV yang
berkualiti tinggi.
Kata kunci: salutan, akrilat, epoksida, ester,
risinoleate
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Andrady, A. L., Pandey, K. K. and
Heikkilä, A. M. (2019). Interactive effects of solar UV radiation and climate
change on material damage. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences,
18(3): 804-825.
2.
Paquet, C., Schmitt, T., Klemberg-Sapieha, J. E., Morin, J.-F. and Landry,
V., (2020). Self-healing UV curable acrylate coatings for wood finishing
system, part 1: Impact of the formulation on self-healing efficiency. Coatings,
10(8): 770.
3.
Teacǎ, C. A., Roşu, D., Bodîrlǎu, R. and Roşu,
L. (2013). Structural changes in wood under artificial UV light irradiation
determined by FTIR spectroscopy and color measurements-a brief review, BioResources,
8(1): 1478-1507.
4.
Ulker, O. C., Ulker, O. and Hiziroglu, S. (2021). Volatile organic
compounds (VOCs) emitted from coated furniture units. Coatings,11(7):
806.
5.
Suriano,
R., Ciapponi, R., Griffini, G., Levi, M. and Turri, S. (2017). Fluorinated zirconia-based sol-gel hybrid coatings on polycarbonate with
high durability and improved scratch resistance. Surface Coatings Technology,
311: 80-89.
6.
Teaca, C. A., Tanasa, F. and Zanoaga, M. (2018). Multi-component polymer
systems comprising wood as bio-based component and thermoplastic polymer
matrices – an overview, BioResources, 13(2): 4728-4769.
7.
Hang, Z., Yu, H., Lu, Y.,
Huai, X. and Luo, L. (2020). Effect of graphene
carbon nitride on ultraviolet-curing coatings. Materials, 13(1): 153.
8.
Pezzana, L., Malmström,
E., Johansson, M. and Sangermano, M. (2021). UV-curable bio-based polymers derived from industrial pulp and paper processes.
Polymers, 13(9): 1530.
9.
Rosu, D., Bodîrləu, R., Teacə, C. A., Rosu, L. and Varganici, C.
D. (2016). Epoxy and succinic anhydride functionalized soybean oil for wood
protection against UV light action. Journal Cleaner Production, 112: 1175-1183.
10.
LoPachin, R. M. and Gavin, T. (2014). Molecular mechanisms of
aldehyde toxicity: a chemical perspective, Chemical Research Toxicology,
27(7): 1081-1091.
11.
Gan, Y. and Jiang, X. (2014).
Chapter 1: Photo-cured materials from vegetable oils, in green materials from
plant oils. Royal Society of Chemistry, pp. 1–27.
12.
Xia, C., Wang, L.,
Dong, Y., Zhang, S., Shi, S. Q., Cai, L. and Li, J. (2015). Soy protein
isolate-based films cross-linked by epoxidized soybean oil. RSC Advances,
5(101): 82765-82771.
13.
Wu, Q., Hu, Y., Tang,
J., Zhang, J., Wang, C., Shang, Q., Feng, G., Liu, C., Zhou, Y. and Lei, W.
(2018). High-performance soybean-oil-based epoxy acrylate resins: “Green”
synthesis and application in UV-curable coatings. ACS Sustainable Chemical
Engineering, 6(7): 8340-8349.
14.
Demengeot, E.-A.-C., Baliutaviciene, I., Ostrauskaite, J., Augulis, L.,
Grazuleviciene, V., Rageliene, L., and Grazulevicius, J. V. (2010).
Crosslinking of epoxidized natural oils with diepoxy reactive diluents. Journal
Applied Polymer Sciences, 115(4): 2028-2038.
15.
Abdul Rahman, M. B., Zaidan, U. H., Basri, M., Hussein, M.
Z., Rahman, R. N. Z. R. A. and Salleh, A. B. (2008). Enzymatic synthesis of
methyl adipate ester using lipase from Candida rugosa immobilised on Mg, Zn and
Ni of layered double hydroxides (LDHs), Journal Molecular Catalyst B Enzyme,
50(1): 33-39.
16.
Chaibakhsh, N., Abdul Rahman, M. B., Abd-Aziz, S., Basri, M., Salleh, A.
B. and Rahman, R. N. Z. R. A. (2009). Optimized lipase-catalyzed synthesis of
adipate ester in a solvent-free system, Journal Industrial Microbiology
Biotechnology, 36(9): 1149-1155.
17.
Abdul Rahman, M. B., Abdul Ghani, N., Salleh, N. G. N., Basri, M., Abdul
Rahman, R. N. Z. and Salleh, A. B. (2010). Development of coating materials
from liquid wax esters for wood top-based coating, Journal Coatings
Technology Research, 8(2): 229-236.
18.
Ma, X., Qiao, Z., Huang,
Z. and Jing, X. (2013). The dependence of
pendulum hardness on the thickness of acrylic coating. Journal Coatings Technology Research, 10(3): 433-439.
19.
Anderson, J., Brown,
M., Kan, C., Nanjundiah, K. and Kalihari, V. (2013). Quantitative method for
evaluating fingernail induced mar damage of coatings. Journal Coatings Technology Research, 10(4): 579-588.
20.
Ferrer, M., Cruces, M. A., Plou, F. J., Pastor, E., Fuentes, G., Bernabé,
M., Parra, J. L. and Ballesteros, A. (2000). Chemical versus enzymatic
catalysis for the regioselective synthesis of sucrose esters of fatty acids, Studies
Surface Science Catalyst, 130: 509-514.
21.
Kondamudi, N., and McDougal, O. M. (2019). Microwave-assisted synthesis
and characterization of stearic acid sucrose ester: a bio-based surfactant. Journal
Surfactants Detergents, 22(4): 721-729.
22.
Ghoshray, S.,
Bhattacharya, D. K. (1992). Enzymatic preparation of ricinoleic acid esters of
long-chain monohydric alcohols and properties of the esters. Journal
American Oil Chemical Society, 69(1): 85-88.
23.
Said, H. M., Nik Salleh, N. G., Alias, M. S. and El-Naggar, A. W. M.
(2013). Synthesis and characterization of hard materials based on radiation
cured bio-polymer and nanoparticles, Journal Radiation Research Applied
Sciences, 6(2): 71-78.