Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 855 - 866
APPLICATIONS OF NINHYDRIN: SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF
HYDRAZINE AND HYDROXYLAMINE
(Aplikasi Ninhidrin: Penentuan Spektrofotometri bagi
Hidrazin dan Hidroksil Amina)
Khaled Elgendy*, Mohamed Alaa Eldeen Elmosallamy, Mohamed Hassan, Hend Gamal
Department of Chemistry, Faculty
of Science,
Zagazig University, Egypt
*Corresponding author: elgendykh64@gmail.com
Received: 15 September 2021;
Accepted: 18 May 2022; Published: 25 August 2022
Abstract
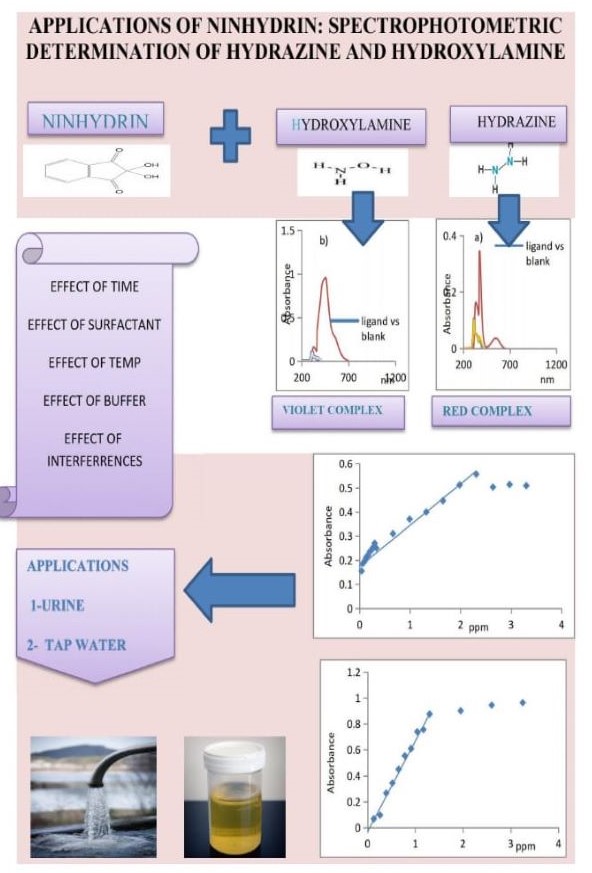
A rapid, accurate, and sensitive
spectrophotometric method for the determination of micro amounts of
hydroxylamine and hydrazine is described. The proposed method is based on the
interaction of ninhydrin with the amino group of hydroxylamine and hydrazine.
Hydroxylamine reacted with ninhydrin as a chromogenic
reagent in
phosphate buffer at pH 9.14, forming a violet complex with a maximum absorbance
at 375 nm after heating for 10 min at 70 °C. Hydrazine reacted with ninhydrin upon
heating for 10 min at 85 °C in the presence of phosphate buffer (pH 9), giving a red-brown complex
with a maximum absorbance at 425 nm. The optimum conditions affecting the
method, such as pH and buffer, sequence of addition, time, temperature, organic
solvent, and surfactant, were studied. The complexes of ninhydrin with hydroxylamine
and hydrazine were formed in a molar ratio of 1:2. The hydroxylamine–ninhydrin and hydrazine–ninhydrin complexes obeyed Beer's law in a
concentration range of 0.033-3.3 and 0.130-3.25 µg mL−1,
respectively. Molar absorptivity and Sandell's sensitivity were
0.21508 × 102 L mol−1 cm−1 and
1.53 µg cm−2,
respectively, for hydroxylamine and 0.8583 × 102 L mol−1 cm−1
and 1.51 µg cm−2, respectively, for hydrazine. The limit of detection and quantification was calculated. The interference effect of various foreign ions
and substances was also studied. The proposed method was applied for the
determination of micro amounts of hydroxylamine in urine and tap water and
hydrazine in tap water.
Keywords: spectrophotometric method, ninhydrin, hydroxylamine, hydrazine, urine
Abstrak
Kaedah spektrofotometri yang
cepat, tepat dan sensitif untuk penentuan jumlah mikro hidroksilamin dan
hidrazin diterangkan. Kaedah yang dicadangkan adalah berdasarkan interaksi
ninhidrin dengan kumpulan amino yang terdapat dalam hidroksilamin dan hidrazin.
Hidroksilamin bertindak balas dengan ninhidrin sebagai reagen kromogenik dalam
medium beralkali pada pH = 9.14 menggunakan penimbal fosfat membentuk kompleks
ungu dengan penyerapan maksimum pada 375 nm selepas dipanaskan selama 10 minit
pada 70 °C. Hidrazin bertindak balas dengan
ninhidrin apabila dipanaskan selama 10 minit pada 85 °C dengan kehadiran
penimbal fosfat (pH = 9) memberikan kompleks merah-coklat dengan penyerapan
maksimum pada 425 nm. Keadaan optimum yang mempengaruhi kaedah dikaji seperti
pH dan penimbal, jujukan penambahan, masa, suhu, pelarut organik, dan surfaktan.
Dua kompleks yang terbentuk bagi ninhidrin dengan hidroksilamin dan hidrazin
terbentuk dengan nisbah molar (1:2). Kompleks hidroksilamin–ninhidrin dan hidrazin–ninhidrin mematuhi hukum Beer
dalam julat kepekatan 0.033-3.3 dan 0.130-3.25 µg mL−1, masing-masing. Penyerapan molar dan
kepekaan Sandell masing-masing ialah 0.21508 × 102 L mol−1
cm−1 dan 1.53 µg cm−2, untuk hidroksilamin
dan 0.8583 × 102 L mol−1 cm−1 dan
1.51 µg cm−2 masing-masing, untuk hidrazin.
Had pengesanan dan kuantifikasi telah dikira. Kesan gangguan pelbagai ion dan
bahan asing turut dikaji. Kaedah yang dicadangkan digunakan untuk penentuan
jumlah mikro hidroksilamin dalam air kencing dan air paip dan hidrazin dalam
air paip
Kata kunci: kaedah spektrofotometri, ninhidrin,
hidroksilamin, hidrazin, urin
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Rahman,
N. and Kashif, M. (2003). Application of ninhydrin to spectrophotometric
determination of famotidine in drug formulations. Il Farmaco, 58(10):
1045-1050.
2.
Mahmood,
K., Wattoo, F. H., Wattoo, M. H. S., Imran, M., Asad, M. J., Tirmizi, S. A. and
Wadood, A. (2012). Spectrophotometric estimation of cobalt with ninhydrin. Saudi
Journal of Biological Sciences, 19(2): 247-250.
3.
Friedman,
M. (2004). Applications of the ninhydrin reaction for analysis of amino acids,
peptides, and proteins to agricultural and biomedical sciences. Journal of
Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 52(3): 3854-3806.
4.
Surleva,
A., Zaharia, M., Ion, L., Gradinaru, R. V., Drochioiu, G. and Mangalagiu, I.
(2013). Ninhydrin-based spectrophotometric assays of trace cyanide. Acta
Chemica Iasi, 21: 57-70.
5.
Alsamarrai,
K. F., Al-Abbasi, M. A. and Alsamarrai, E. T. (2019). Spectrophotometric
determination of neomycin sulphate in tablets form via reaction with ninhydrin
reagent. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Science,
10(2): 1392-1396.
6.
Siddiquia,
F. A., Araynea, M. S., Sultanab, N., Qureshia, F., Mirzaa, A. Z., Zuberia, M.
H., Bahadura, S. S., Afridia, N. S., Shamshadb, H. and Rehman, N. (2010).
Spectrophotometric determination of gabapentin in pharmaceutical formulations
using ninhydrin and
7.
Rahman,
N. and Azmi, S. N. H. (2001). Spectrophotometric method for the determination
of amlodipine besylate with ninhydrin in drug formulations. Il Farmaco,
56: 731-735.
8.
Bhaskara,
B. L. and Nagaraja, P. (2006). Direct sensitive spectrophotometric
determination of glyphosate by using ninhydrin as a chromogenic reagent in
formulations and environmental water samples. Helvetica Chimica Acta,
89: 2686-2693.
9.
Baker,
H. M. and Alzboon, K. F. (2015). Spectrophotometric determination of ammonia
using ninhydrin assay and kinetic studies. European Journal of Chemistry,
6(2): 135-140.
10.
Arp,
D. J., Stein, L. Y. (2003). Metabolism of inorganic N compounds by
ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular
Biology, 38(6): 471-495.
11.
Jetten,
M. S. M. (2001). New pathways for ammonia conversion in soil and aquatic
systems. Plant and Soil, 230: 9-19.
12.
Guzowski
Jr, J. P., Golanoski, C. and Montgomery, E. R. (2003). A gas chromatographic method for the indirect determination of
hydroxylamine in pharmaceutical preparations, conversion into nitrous oxide.
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 33(5): 963-974.
13.
Smith,
R. P., and Layne, W. R. (1969). A comparison of the lethal effects of nitrite and hydroxylamine in the mouse. Journal
of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 165: 30-35.
14.
Deepa,
B., Balasubramanian, N. and Nagaraja, K. S. (2004). Spectrophotometric
determination of hydroxylamine and its derivatives in pharmaceuticals. Chemical
and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 52(12): 1473-1475.
15.
Hu,
B., Tian, X. L., Shi, W. N., Zhao, J. Q., Wu, P. and Mei, S. T. (2018).
Spectrophotometric determination of hydroxylamine in biological wastewater
treatment processes. International Journal of Environmental Science and
Technology, 15: 323-332.
16.
Afkhami,
A., Madrakian, T. and Maleki, A. (2006). Indirect kinetic spectrophotometric
determination of hydroxylamine based on its reaction with iodate. Analytical
Sciences, 22: 329-331.
17.
Afkhami,
A., Madrakian, T. and Maleki, A. (2005). Spectrophotometric determination of
hydroxylamine and nitrite in mixture in water and biological samples after
micelle-mediated extraction. Analytical Biochemistry, 347: 162-164.
18.
Guzowski,
J. P., Golanoski, C. and Montgomery, E. R. (2003). A gas chromatographic method
for the indirect determination of hydroxylamine in pharmaceutical preparations,
conversion into nitrous oxide. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical
Analysis, 33(5): 963-974.
19.
Ardakani,
M. M., Beitollahi, H., Taleat, Z. and Naeimi, H. (2010). Voltammetric
determination of hydroxylamine at the surface of a quinizarine/TiO2
nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode. Analytical Methods, 2:
1764-1769.
20.
Reddy,
A. V. B., Venugopal, N. and Madhavi, G. (2014). A selective and sensitive
LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of two potential genotoxic
impurities in celecoxib. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology,
5(18): 1-8.
21.
Kaveeshwar,
R. and Gupta, V. K. (1992). A new spectrophotometric method for the
determination of hydrazine in environmental samples. Fresenius Journal of
Analytical Chemistry, 344: 114-117.
22.
Majeed,
S. Y. and Bashir, W. A. (2019). Spectrophotometric determination of hydrazine
sulphate using Fe (ii)-2,2'-bipyridyl-application to various water samples. The
Eurasia Proceedings of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics, 7:
23-32.
23.
Mitic,
V. D., Nikolic, S. D. and Jovanovic, V. P. S. (2010). Kinetic
spectrophotometric determination of hydrazine. Central European Journal of
Chemistry, 8(3): 559-565.
24.
Kosyakov,
D. S., Amosov, A. S., Ul’yanovskii, N. V., Ladesov, A. V., Khabarov, Yu. G. and
Shpigun, O. A. (2017). Spectrophotometric determination of hydrazine,
methylhydrazine, and 1, 1–dimethylhydrazine with preliminary derivatization by
5–nitro-2–furaldehyde. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2: 171-177.
25.
Yu,
L., Zhang, X. and Yu, L. (2012). Flow injection spectrophotometric
determination of hydrazine in environmental water samples. Advanced
Materials Research, 396–398: 130-133.
26.
Britton,
H. T. S. (1952). Hydrogen ions, 4th edition, Chapman and Hall, 28: pp. 359-364.
27.
Bower
and Bates (1955). pH values of the Clark and Lubs buffer solutions at 25 °C. Journal
of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, 55: 197-202.
28.
Lurie,
J. U. (1978); Handbook of Analytical Chemistry, 2nd edition, Mir
Publishers, Moscow.
29.
Yoe,
J. H. and Jones, A. L. (1944); Colorimetric determination of Fe with disodium
1, 2-dihydroxybenzene-3, 5-disulfonate, Industrial Engineering Chemistry,
16: 111-118.
30.
Job,
P. (1928). Formation and stability of inorganic complexes in solution, Analytical
Chemistry, 9: 113-119.
31.
Watt,
G. W. and Chirsp, J. D. (1952). Spectrophotometric method for determination of
hydrazine, Analytical Chemistry, 24(12): 2006-2008.
32.
Frear,
D. S. and Burrell, R. C. (1955). Spectrophotometric method for determining
hydroxylamine reductase in higher plants. Analytical Chemistry, 27(10):
1664-1665.