Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 845 - 854
ASSESSMENT OF
METALS IN SEDIMENT OF A MONSOON-DOMINATED REGION IN THE NORTHERN MALACCA STRAIT
(Penilaian Logam dalam Sedimen di Wilayah yang Didominasi
Monsun di Utara Selat Melaka)
Mohamad Arif Che Abd Rahim1,
Shengfa Liu2,3, Xuefa Shi2,3, Che Abd Rahim Mohamed1*
1Faculty of Science and Technology,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 UKM Bangi, Selangor,
Malaysia
2Key Laboratory of Marine Geology and
Metallogeny,
First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources,
Qingdao, China
3Laboratory for Marine Geology,
Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and
Technology, Qingdao, China
*Corresponding author: carmohd@ukm.edu.my
Received: 23 March 2022; Accepted: 18 May 2022; Published: 25
August 2022
Abstract
Fluctuation levels of geochemical elements, sediment
texture and nutrients were analysed from five surface sediments taken from the
northern Malacca Straits. These samples were obtained during the RV Discovery
Scientific cruises in September 2017 and April 2018, to assess pollution
sources during monsoonal events. The results show a high output of clay and
silt, revealing that the monsoonal season and cross-shelf inputs affect
textural sediment. On the other hand, fluctuations in geochemical
concentrations are due to industrialisation and urbanisation along the Malacca
Straits, contributed by the local drainage basin. The presence of the monsoon
also affects the diffusivity and absorption between the water-sediment
interfaces, leading to constant fluctuation along the straits. Principal
Component Analysis (PCA) of the association between the geochemical elements,
sediment texture and nutrients reveal hydrological factors, mobility and
accumulation through the sediment interface.
Keywords: weathering,
pollution, monsoon, sediment, Malacca Strait
Abstrak
Tahap kepekatan unsur geokimia,
tekstur sedimen dan nutrien telah dianalisis daripada lima sedimen permukaan
yang diambil dari kawasan utara Selat Melaka. Sampel ini diperoleh semasa
pelayaran RV Discovery Scientific pada September 2017 dan April 2018 untuk
menilai sumber pencemaran semasa peristiwa monsun. Keputusan menunjukkan
keluaran lempung dan kelodak yang lebih tinggi, menunjukkan bahawa musim monsun
dan input rentas pelantar mempengaruhi sedimen tekstur. Sebaliknya, fluktuasi
kepekatan geokimia adalah disebabkan oleh kawasan perindustrian dan pembandaran
di sepanjang Selat Melaka, disumbangkan oleh lembangan saliran tempatan.
Kehadiran monsun juga menjejaskan resapan dan penyerapan antara antara muka
air-mendapan, yang membawa kepada fluktuasi yang berterusan di sepanjang selat.
Analisis Komponen Utama (PCA) perkaitan antara unsur geokimia tekstur sedimen
dan nutrien mendedahkan faktor hidrologi, mobiliti dan pengumpulan melalui
antara muka sedimen.
Kata kunci: luluhawa,
pencemaran, monsun, sedimen, Selat Melaka
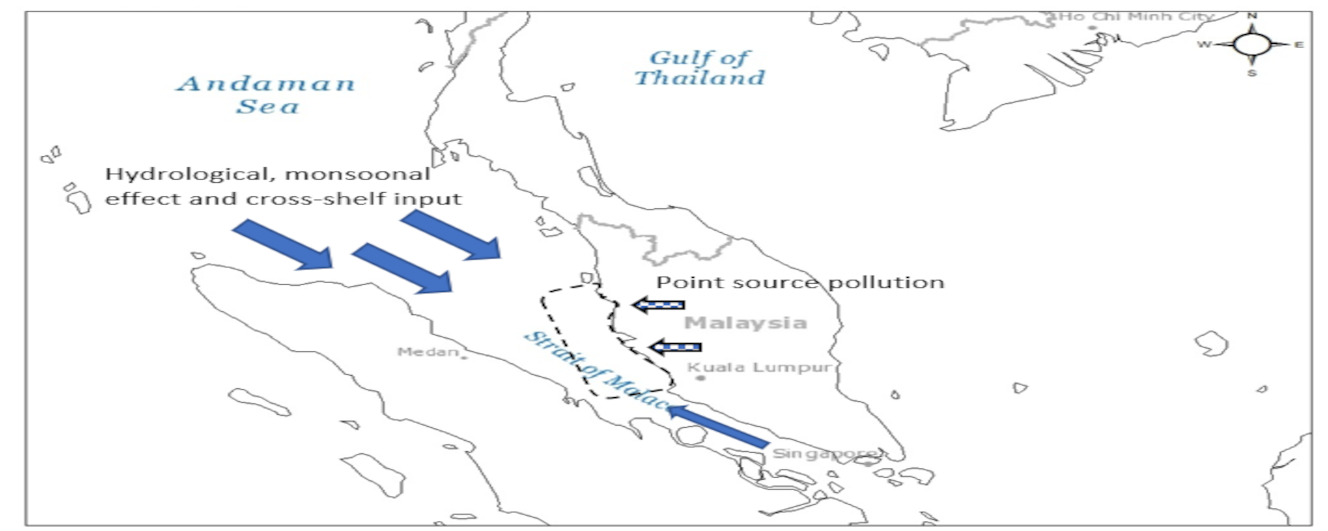
Graphical Abstract
References
1. Thia-Eng, A., Gorre, I. R. L., Ross, S. A., Bernad, S. R.,
Gervacio, B. and Ebarvia, C. (2000). The Malacca straits. Marine Pollution
Bulletin, 41: 160-178.
2. Liu, Z., Wang, H., Hantoro, W.S.,
Sathiamurthy, E., Colin, C., Zhao, Y. and Li, J. (2012). Climatic and tectonic
controls on chemical weathering in tropical Southeast Asia (Malay Peninsula,
Borneo, and Sumatra). Chemical Geology, 291: 1-12.
3. Haditiar, Y., Putri, M.R., Ismail, N.,
Muchlisin, Z.A., Ikhwan, M. and Rizal, S. (2020). Numerical study of tides in
the Malacca Strait with a 3-D model. Heliyon, 6(9): e04828.
4. Tan, C.K., Ishizaka, J., Matsumura, S.,
Yusoff, F.M., and Mohamed, M.I.H. (2006). Seasonal variability of SeaWiFS
chlorophyll a in the Malacca Straits in relation to Asian monsoon. Continental
Shelf Research, 26(2): 168-178.
5. Fujita, M., Kimura, F. and Yoshizaki, M.
(2010). Morning precipitation peak over the strait of Malacca under a calm
condition. Monthly Weather Review, 138(4): 1474-1486.
6. Amin, M. Z. M., Shaaban, A. J., Ercan, A.,
Ishida, K., Kavvas, M. L., Chen, Z. Q. and Jang, S. (2017). Future climate
change impact assessment of watershed scale hydrologic processes in Peninsular
Malaysia by a regional climate model coupled with a physically-based hydrology
modelo. Science of the Total Environment, 575: 12-22.
7. Yusoff, A. H., and Mohamed, C. A. R. (2016).
Mini review uranium-thorium decay series in the marine environment of the
Southern South China Sea. Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 5(03):
1-9.
8. Schwartz, M. O., Rajah, S. S., Askury, A.
K., Putthapiban, P. and Djaswadi, S. (1995). The Southeast Asian tin belt. Earth
Science Reviews, 38(2–4): 95-293.
9. Shoieb, M. A., Sum, C. W., Ismail, M. S.,
and Tsegab, H. (2019). Geological characteristic of the Kroh formation in the upper
Perak shales, western Peninsula Malaysia. International Journal of Advanced
and Applied Sciences, 6(2): 102-106.
10. Zakariah, M. N. A., Roslan, N., Sulaiman, N.,
Lee, S. C. H., Hamzah, U., Noh, K. A. M. and Lestari, W. (2021). Gravity
analysis for subsurface characterization and depth estimation of Muda River
basin, Kedah, Peninsular Malaysia. Applied Sciences, 11(14): 6363.
11. Abdul Hamid, F. A. Z., Abu Bakar, A. F., Ng,
T. F., Ghani, A. A. and Mohamad Zulkifley, M. T. (2019). Distribution and contamination
assessment of potentially harmful elements (As, Pb, Ni, Cd) in top soil of
Penang Island, Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(21): 1-13.
12. Khandaker, M. U., Asaduzzaman, K., Sulaiman,
A. F. Bin, Bradley, D. A. and Isinkaye, M.O. (2018). Elevated concentrations of
naturally occurring radionuclides in heavy mineral-rich beach sands of Langkawi
Island, Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 127 (12): 654-663.
13. Aboobacker, V. M. (2017). Wave energy resource
assessment for eastern Bay of Bengal and Malacca Strait. Renewable Energy,
114 (3): 72-84.
14. Redzwan, G., Halim, H. A., Alias, S. A. and
Rahman, M. M. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal contamination at west and east
coastal area of Peninsular Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Science, 33
(1): 23-31.
15. Saili, N. A. B. and Mohamed, C. A. R. (2021).
Natural radioactivity of 210Pb in mussels at the semi-enclosed water
of the johor strait, malaysia through statistical approach. Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences, 25(1): 166-183.
16. Rahim, M. A. C. A., Aproi, A. A., Shi, X.,
Liu, S., Ali, M. M., Yaacob, W. Z. W. and Mohamed, C. A. R. (2019).
Distribution of chromium and gallium in the total suspended solid and surface
sediments of sungai kelantan, kelantan, Malaysia. Sains Malaysiana,
48(11): 2343-2353.
17. Miller, W. P. and Miller, D. M. (1987). A
micro‐pipette method for soil mechanical analysis. Communications in
Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 18(1): 1-15.
18. Miller, W. P. (1993). A micro-pipette method
for water dispersible clay. Communications in Soil Science and Plant
Analysis, 24 (19–20): 2531-2544.
19. Kaur, A. and Fanourakis, G. C. (2018). Effect
of sodium carbonate concentration in calgon on hydrometer analysis results. Periodica
Polytechnica Civil Engineering, 62(4): 866-872.
20. Gray, J. E. and Riehle, J. R. (1998). Geologic
Studies in Alaska by the US Geological Survey 1998: 200.
21. Santisteban, J. I., Mediavilla, R.,
López-Pamo, E., Dabrio, C.J., Blanca Ruiz Zapata, M., José Gil García, M.,
Castańo, S. and Martínez-Alfaro, P. E. (2004). Loss on ignition: a qualitative
or quantitative method for organic matter and carbonate mineral content in
sediments? Journal of Paleolimnology, 32(3): 287-299.
22. Othman, S. Z., Adlan, M. N., and Selamat, M.
R. (2015). A study on the potential of riverbank filtration for the removal of
color, iron, turbidity and E. Coli in Sungai Perak, Kota Lama Kiri,
Kuala Kangsar, Perak, Malaysia. Jurnal Teknologi, 74(11): 83-91.
23. Ramaswamy, V., Rao, P. S., Rao, K. H., Thwin,
S., Rao, N. S. and Raiker, V. (2004). Tidal influence on suspended sediment
distribution and dispersal in the northern Andaman Sea and Gulf of Martaban. Marine
Geology, 208(1): 33-42.
24. Rizal, S., Damm, P., Wahid, M. A., Sündermann,
J., Ilhamsyah, Y., Iskandar, T. and Muhammad (2012). General circulation in the
Malacca Strait and Andaman Sea: A numerical model study. American Journal of
Environmental Sciences, 8(5): 479-488.
25. Mohamed, K. N., Godon, E., Adnan, N. A.,
Rahim, Q. A., Liew, C., Abidin, A. I. Z. and Zainuddin, M. F. (2019). Study of
dissolved nutrient condition at pulau perhentian, Terengganu. Pertanika
Journal of Science and Technology, 27(2): 601-617.
26. Shaari, H., Mohamad Azmi, S. N. H., Sultan,
K., Bidai, J. and Mohamad, Y. (2015). Spatial distribution of selected heavy
metals in surface sediments of the EEZ of the East Coast of Peninsular
Malaysia. International Journal of Oceanography, 2015(5): 1-10.
27. Rezai, H., Yusoff, F. M., Kawamura, A.,
Arshad, A. and Othman, B. H. R. (2003). Zooplankton biomass in the Straits of
Malacca. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 32(3): 222-225.
28. Kok, P. H., Mohd
Akhir, M. F., Tangang, F. and Husain, M. L. (2017). Spatiotemporal trends in
the southwest monsoon wind-driven upwelling in the southwestern part of the
South China Sea. PLOS ONE, 12(2): e0171979.
29. Schroeder, A.,
Wiesner, M. G. and Liu, Z. (2015). Fluxes of clay minerals in the South China
Sea. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 430: 30-42.
30. Väli, G., Zhurbas, V., Laanemets, J. and
Elken, J. (2011). Simulation of nutrient transport from different depths during
an upwelling event in the Gulf of Finland. Oceanologia, 53(1-TI):
431-448.
31. Haditiar, Y., Putri, M. R., Ismail, N.,
Muchlisin, Z. A. and Rizal, S. (2019). Numerical simulation of currents and
volume transport in the Malacca Strait and part of South China Sea. Engineering
Journal, 23(6): 129-143.
32. Batista, A. H., Melo, V. F., Gilkes, R. and
Roberts, M. (2018). Identification of heavy metals in crystals of sand and silt
fractions of soils by scanning electron microscopy (SEM EDS/WD-EPMA). Revista
Brasileira de Ciencia do Solo, 42: 1-16.
33. Singh, S.K. and Subramanian, V. (1984).
Hydrous fe and mn oxides — scavengers of heavy metals in the aquatic
environment. Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, 14(1): 33-90.
34. Taylor, K. G. and Macquaker, J. H. S. (2014).
Diagenetic alterations in a silt- and clay-rich mudstone succession: an example
from the Upper Cretaceous Mancos Shale of Utah, USA. Clay Minerals,
49(2): 213-227.
35. Raj, J. K. (2021). Soil moisture retention
characteristics of saprock from the weathering profile over a biotite-muscovite
granite in Peninsular Malaysia. Warta Geologi, 47(3): 217-225.
36. Yap, C. K. and Pang, B. H. (2011). Assessment
of Cu, Pb, and Zn contamination in sediment of north western Peninsular
Malaysia by using sediment quality values and different geochemical indices. Environmental
Monitoring and Assessment, 183(1–4): 23-39.
37. Pitt, R., Lantrip, J. and O’Connor, T. P.
(2004). Infiltration through disturbed urban soils. Joint Conference on
Water Resource Engineering and Water Resources Planning and Management 2000:
Building Partnerships: p. 104.
38. Bobrowsky, P. T. and Marker, B. (2018). Encyclopedia
of Engineering Geology, Springer International Publishing AG, Cham,
Switzerland.
39. Zorluer, I., Icaga, Y., Yurtcu, S. and Tosun,
H. (2010). Application of a fuzzy rule-based method for the determination of
clay dispersibility. Geoderma, 160(2): 189-196.
40. Ismail, A., Toriman, M. E., Juahir, H., Zain,
S. M., Habir, N. L. A., Retnam, A., Kamaruddin, M. K. A., Umar, R., and Azid,
A. (2016). Spatial assessment and source identification of heavy metals
pollution in surface water using several chemometric techniques. Marine
Pollution Bulletin, 106(1–2): 292-300.
41. Idriss, A. A. (2012). Concentration of
selected heavy metals in water of the Juru River, Penang, Malaysia. African
Journal of Biotechnology, 11(33): 8234-8240.