Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 546 - 553
SYNTHESIS OF ZnO ON 3D GRAPHENE/NICKEL FOAM FOR
PHOTOELECTROCHEMICAL WATER SPLITTING
(Sintesis ZnO pada 3D Grafin/Busa Nikel untuk Pembelahan
Molekul Air Secara Fotoelektrokimia)
Nur Rabiatul Adawiyah Mohd Shah,
Rozan Mohamad Yunus*, Nurul Nabila Rosman, Wai Yin Wong, Khuzaimah Arifin, Lorna Jeffery
Minggu
Fuel Cell Institute,
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 UKM Bangi, Selangor,
Malaysia
*Corresponding author:
rozanyunus@ukm.edu.my
Received: 13 December 2021; Accepted: 27 February 2022;
Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is a promising method that
involves a direct route to produce green hydrogen (H2). An efficient
semiconductor photoelectrode that has a suitable band gap between the valence
and conduction band is stable in an aqueous solution and cost-effective.
Efficient charge transfer and outstanding light absorption are required to
achieve enhanced PEC water splitting performance. However, the wide band gap of
current photoelectrode such as zinc oxide (ZnO) limits their ability to
transport electron, causing photogenerated electron–hole pair recombination and
poor PEC performance. This study aims to design an efficient photoelectrode by
incorporating a three-dimensional (3D) graphene with ZnO, where 3D graphene
serves as a co-catalyst/support to enhance the photocatalytic activity of ZnO.
The 3D graphene was first synthesized on nickel foam (Ni-foam) via chemical
vapor deposition method with the flow of argon, H2, and methane gas
flow in a quartz tube, followed by the growth of ZnO via a hydrothermal method
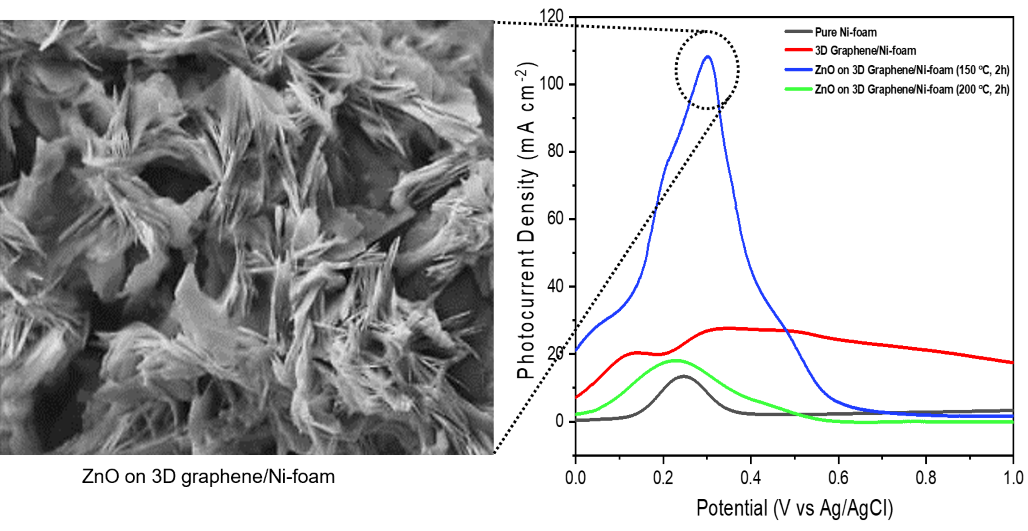
at 150 °C and 200 °C. FESEM, EDX and Raman confirmed the successful growth of ZnO on 3D
graphene/Ni-foam. The flower-like ZnO was observed by FESEM after the
hydrothermal method, and the highest photocurrent density was measured at 150
°C (108.2 mA cm-2). Therefore, flower-like ZnO flower-like on 3D
graphene/Ni-foam can be used as an efficient semiconductor photoelectrode in
PEC water splitting.
Keywords: 3D graphene, zinc oxide, photoelectrode,
photoelectrochemical water splitting
Abstrak
Pembelahan molekul air secara fotoelektrokimia (PEC)
merupakan kaedah yang menggunakan laluan yang mudah untuk menghasilkan hidrogen
(H2). Fotoelektrod semikonduktor yang cekap mempunyai jurang jalur
yang sesuai antara jalur valensi dan konduksi, stabil dalam larutan berair dan
kos yang rendah. Pemindahan cas yang cekap dan penyerapan cahaya yang baik
diperlukan untuk mencapai prestasi pembelahan molekul air PEC yang tinggi.
Walau bagaimanapun, jurang jalur fotoelektrod yang lebar seperti zink oksida
(ZnO) menghadkan kebolehannya untuk pengangkutan elektron, menyebabkan
penggabungan semula lubang–elektron terjana dan prestasi PEC yang rendah.
Kajian ini bertujuan untuk merekacipta fotoelektrod yang cekap dengan
menggabungkan tiga-dimensi (3D) grafin dengan ZnO, di mana 3D grafin bertindak
sebagai pemangkin bersama/sokongan untuk meningkatkan aktiviti fotokatalitik
ZnO. 3D grafin disintesis pada busa nikel (busa-Ni) melalui kaedah pemendapan
wap kimia dengan aliran gas argon, H2 dan metana dalam tiub kuarza,
diikuti dengan pertumbuhan ZnO melalui kaedah hidrotherma pada 150 °C and 200 °C. FESEM,
EDX dan Raman mengesahkan pertumbuhan ZnO pada 3D grafin/busa-Ni. Pertumbuhan
ZnO seperti bunga dapat dilihat dengan alat FESEM selepas melalui kaedah
hidrotherma dan ketumpatan foto arus yang tinggi diukur pada suhu 150 °C (108.2
mA cm-2). Oleh itu, ZnO berbentuk seperti bunga pada 3D
grafin/busa-Ni boleh digunakan untuk fotoelektrod semikondutor yang cekap dalam
pembelahan air secara PEC.
Kata
kunci: 3D grafin, zink oksida,
fotoelektrod, pembelahan molekul air secara fotoelektrokimia
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Li, Y. and Tsang, S. C. E. (2020).
Recent progress and strategies for enhancing photocatalytic water splitting. Mater.
Today Sustain., 9: 100032.
2.
Li, X., Zhao, L., Yu, J., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Liu, H. and
Zhou, W. (2020). Water splitting: From electrode to green energy system. Nano-Micro
Letters, Springer Singapore 12.
3.
Dias, P. and Mendes, A. (2018). Hydrogen production from
photoelectrochemical water splitting. In encyclopedia of sustainability science
and technology (Meyers, R. A., ed.). Springer New York, New York: pp 1-52.
4.
Cao, S., Piao, L. and Chen, X. (2020). Emerging
photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Trends Chemistry, Elsevier Inc.
2: pp. 57-70.
5.
Hisatomi, T. and Domen, K. (2019). Reaction systems for solar
hydrogen production via water splitting with particulate semiconductor
photocatalysts. Nature Catalyst, 2: 387-399.
6.
Young, J. L., Steiner, M. A., Döscher, H., France, R. M.,
Turner, J. A. and Deutsch, T. G. (2017). Direct solar-to-hydrogen conversion
via inverted metamorphic multi-junction semiconductor architectures. Nature
Energy, 2: 1-8.
7.
Kuang, P., Sayed, M., Fan, J., Cheng, B. and Yu, J. (2020).
3D graphene-based H2-production photocatalyst and electrocatalyst. Advance
Energy Materials, 10: 1-53.
8.
Mohd Shah, N. R. A., Mohamad Yunus, R., Rosman, N. N., Wong,
W. Y., Arifin, K. and Jeffery Minggu, L. (2021). Current progress on 3D
graphene-based photocatalysts: From synthesis to photocatalytic hydrogen
production. International Journal Hydrogen Energy, 46: 9324-9340.
9.
Gowtham, M., Chandrasekar, S., Mohanraj, C. and Senthil
Kumar, N. (2020). Morphology dependent photocatalytic activity of ZnO
nanostructures-A short review. NanoNEXT, 1: 30-38.
10.
Baruah, S. and Dutta, J. (2009). Hydrothermal growth of ZnO
nanostructures. Science Technology Advance Materials, 10: 013001.
11.
Vaseem, M., Umar, A. and Hahn, Y. (2010). ZnO nanoparticles:
Growth, properties, and applications. Metal Oxide Nanostructures Their
Applications, 5: 1-36.
12.
Singh, P., Shandilya, P., Raizada, P., Sudhaik, A.,
Rahmani-Sani, A. and Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. (2020). Review on various
strategies for enhancing photocatalytic activity of graphene based
nanocomposites for water purification. Arabian Journal Chemistry, 13:
3498-3520.
13.
Gao, C., Zhong, K., Fang, X., Fang, D., Zhao, H., Wang, D.,
Li, B., Zhai, Y., Chu, X. and Li, J. (2021). Brief review of photocatalysis and
photoresponse properties of ZnO–graphene nanocomposites. Energies, 14:
6403.
14.
Mohd Shah, N. R. A., Rosman, N. N., Wong, W. Y., Arifin, K.,
Jeffery Minggu, L. and Mohamad Yunus, R. (2021). Effect of annealing time on
chemical vapor deposition growth of 3D graphene for photoelectrochemical water
splitting. Material Today Proceeding, 57(3): 1215-1219.
15.
Ong, C. B., Ng, L. Y. and Mohammad, A. W. (2018). A review of
ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and
applications. Renewable Sustainable Energy Review, 81: 536–551.
16.
Mohamed, M. A., M. Zain, M. F., Jeffery Minggu, L., Kassim,
M. B., Jaafar, J., Saidina Amin, N. A., Mastuli, M. S., Wu, H., Wong, R. J. and
Ng, Y. H. (2019). Bio-inspired hierarchical hetero-architectures of in-situ
C-doped g-C3N4 grafted on C, N co-doped ZnO micro-flowers with booming solar
photocatalytic activity. Journal Industry Engineering Chemistry, 77:
393-407.
17.
Wang, W. X., Zhang, S. C., Xing, Y. L., Wang, S. B. and Ren,
Y. B. (2016). The closed-environment CVD method for preparing three-dimensional
defect controllable graphene foam with a conductive interconnected network for
lithium-ion battery applications. RSC Advance, 6: 75414-75419.
18.
Ghorbani, M., Abdizadeh, H., Taheri, M. and Golobostanfard,
M. R. (2018). Enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting in hierarchical
porous ZnO/Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite synthesized by sol-gel method. Int.
J. Hydrogen Energy, 43, 7754–7763.
19.
Gadisa, B. T., Baye, A. F., Appiah-Ntiamoah, R. and Kim, H.
(2021). ZnO@Ni foam photoelectrode modified with heteroatom doped graphitic
carbon for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting under solar light. International
Journal Hydrogen Energy, 46: 2075-2085.
20.
Men, X., Chen, H., Chang, K., Fang, X., Wu, C., Qin, W. and
Yin, S. (2016). Three-dimensional free-standing ZnO/graphene composite foam for
photocurrent generation and photocatalytic activity. Applied Catalyst B
Environment, 187: 367-374.