Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 532 - 545
BIOSORPTION CAPACITY OF HEAVY METAL LEAD (Pb(II)) USING DRY SEAWEED Eucheuma denticulatum
(Kapasiti Biojerapan
Logam Berat Plumbum (Pb(II)) Mengunakan Rumpai Laut Kering Eucheuma
denticulatum)
Hamad Maalim Sharif 1, Yahya Makame 2, Mohammed
Ali Sheikh 3, Hasrizal Shaari 1,4*, Rokiah Suriadi1
1Institute of
Oceanography and Environment,
Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
2Chemistry Department,
School of Natural and Applied Sciences,
University of Dar es Salaam, P.O. Box 35065, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
3School of Natural and
Social Sciences,
The State University of Zanzibar, P. O. Box 146, Zanzibar, Tanzania
4Faculty of Science and
Marine Environment,
Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: riz@umt.edu.my
Received: 29 October 2021;
Accepted: 27 February 2022 ; Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
The seaweed industry plays a significant
socio-economic role in tropical
coastal communities. This study
presents the biosorption behaviour of Pb(II) aqueous
solution onto seaweed E. denticulatum.
The impact of pH contact time, the initial concentration
of the metals, and the adsorption-desorption activities were studied. The
findings demonstrated that the Pb(II) uptake rate rose with
increased concentration and contact time. The Pb(II) uptake reached saturation
at 1000 mg/L after 120 min at room temperature. Pb(II) biosorption onto Eucheuma denticulatum fitted well to the Langmuir
isotherm, with a
maximum adsorption capacity (qmax)
of 416.67 mg/g. The results suggest that this type of seaweed, E. denticulatum, is an
effective biosorbent for removing Pb (II) and may control toxic metal pollution
in tropical aquatic ecosystems.
Keywords: biosorption, Eucheuma
denticulatum, heavy metals, Langmuir and Freundlich models
Abstrak
Industri
rumpai laut memainkan peranan sosio-ekonomi yang sangat penting bagi masyarakat
pesisir pantai tropika. Kajian ini menunjukkan tingkah laku biojerapan larutan
akues Pb(II) ke atas Eucheuma denticulatum.
Pengaruh hubungan masa pH, kepekatan awal logam, dan kajian
penjerapan-penyerapan telah dilakukan. Hasil kajian menunjukkan bahawa kadar
pengambilan Pb(II) meningkat dengan peningkatan kepekatan dan masa hubungan.
Pengambilan Pb(II) mencapai titik tepu pada 1000 mg/L setelah 120 minit pada
suhu bilik. Biojerapan Pb(II) ke atas E.
denticulatum dipasang dengan baik pada isoterm Langmuir dengan kapasiti
penjerapan maksimum (qmax) 416.67 mg/g. Hasilnya menunjukkan
bahawa rumpai laut E. denticulatum
adalah biopenjerap yang berkesan untuk menghilangkan Pb(II) dan mungkin boleh
digunakan untuk mengawal pencemaran logam toksik di ekosistem perairan tropika.
Kata
kunci: biojerapan, Eucheuma
denticulatum, logam berat, model Langmuir dan Freundlich
Graphical Abstract
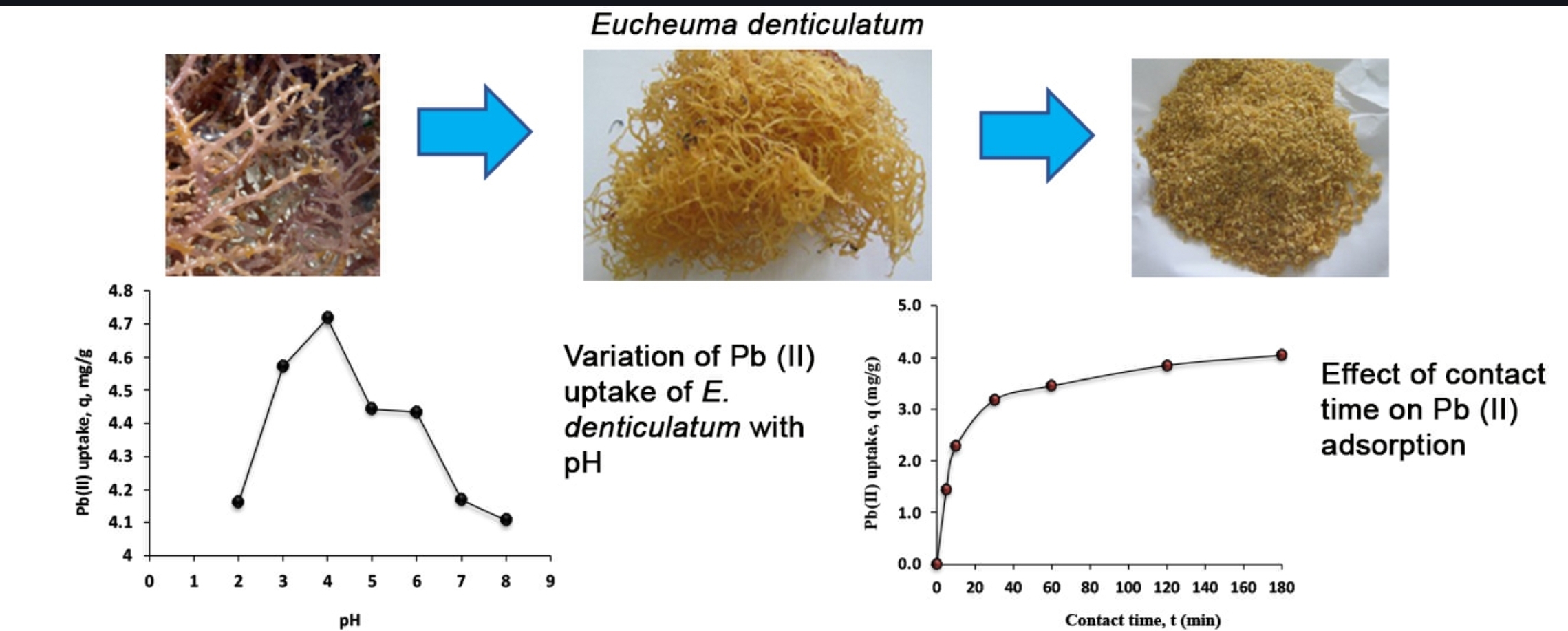
References
1.
Asnani, P. U. and Zurbrugg, C.
(2007). Improving municipal solid waste management in India: A sourcebook for
policymakers and practitioners. World Bank Publications.
2.
Tian, H. Z., Lu, L., Cheng, K., Hao,
J. M., Zhao, D., Wang, Y., Jia, W. X. and Qiu, P. P. (2012). Anthropogenic
atmospheric nickel emissions and its distribution characteristics in China. Science
of the Total Environment, 417–418: 148-157.
3.
Yoon, J., Cao, X., Zhou, Q. and Ma,
L. Q. (2006). Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a
contaminated Florida site. Science of the Total Environment, 368(2–3):
456-464.
4.
Dixit, R., Wasiullah, Malaviya, D.,
Pandiyan, K., Singh, U. B., Sahu, A., Shukla, R., Singh, B. P., Rai, J. P.,
Sharma, P. K., Lade, H. and Paul, D. (2015). Bioremediation of heavy metals
from soil and aquatic environment: An overview of principles and criteria of
fundamental processes. Sustainability (Switzerland), 7(2): 2189-2212.
5.
Das, N. (2005). Heavy metals
biosorption by mushrooms. Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources,
4(6): 454-459.
6.
Volesky, B. (2007). Biosorption and
me. Water Research, 41(18): 4017-4029.
7.
Zeraatkar, A. K., Ahmadzadeh, H.,
Talebi, A. F., Moheimani, N. R. and McHenry, M. P. (2016). Potential use of
algae for heavy metal bioremediation, a critical review. Journal of
Environmental Management, 181: 817–831.
8.
Mousavi, S. A., Almasi, A., Navazeshkh,
F. and Falahi, F. (2019). Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by algae
biomass: Optimization and modeling. Desalination and Water Treatment, 148:
229-237.
9.
Dwivedi, S., Mishra, A. and Saini, D.
(2012). Removal of heavy metals in liquid media through fungi isolated from
waste water. International Journal of Science and Research, 1:
2319-7064.
10.
Vijayaraghavan, K. and Yun, Y. S.
(2008). Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnology Advances,
26(3): 266-291.
11.
Elangovan, R., Philip, L. and Chandraraj,
K. (2008). Biosorption of chromium species by aquatic weeds: Kinetics and
mechanism studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152(1): 100-112.
12.
Rahman, H. U., Shakirullah, M.,
Ahmad, I., Shah, S. and Shah, A. A. (2005). Removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous
medium by sawdust of wood. In Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan,
27(3): 233-238.
13.
Tabaraki, R., Nateghi, A. and
Ahmady-Asbchin, S. (2014). Biosorption of lead (II) ions on Sargassum
ilicifolium: Application of response surface methodology. International
Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 93: 145-152.
14.
Taşar, Ş., Kaya, F. and
Özer, A. (2014). Biosorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solution by peanut
shells: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Journal of
Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2(2): 1018-1026.
15.
Blázquez, G., Calero, M., Hernáinz,
F., Tenorio, G. and Martín-Lara, M. A. (2010). Equilibrium biosorption of
lead(II) from aqueous solutions by solid waste from olive-oil production. Chemical
Engineering Journal, 160(2): 615-622.
16.
Gerola, G. P., Boas, N. V., Caetano,
J., Tarley, C. R. T., Gonçalves, A. C. and Dragunski, D. C. (2013). Utilization
of passion fruit skin by-product as lead(II) ion biosorbent. Water, Air, and
Soil Pollution, 224(2): 1-11.
17.
Senthilkumar, R., Vijayaraghavan, K.,
Thilakavathi, M., Iyer, P. V. R. and Velan, M. (2007). Application of seaweeds
for the removal of lead from aqueous solution. Biochemical Engineering
Journal, 33(3): 211-216.
18.
Abdel -Aty, A. M., Ammar, N. S.,
Abdel Ghafar, H. H. and Ali, R. K. (2013). Biosorption of cadmium and lead from
aqueous solution by freshwater alga Anabaena sphaerica biomass. Journal
of Advanced Research, 4(4): 367-374.
19.
Putri, L. S.(2016). Biosorption of
lead using macroalgae Eucheuma spinosum, Padina minor, and Sargassum
crassifolium in an aqueous solution. Asian Journal of Applied Sciences,
4: 520-525.
20.
Abdel Ghafar, H. H., Abdel-Aty, A.
M., Ammar, N. S. and Embaby, M. A. (2014). Lead biosorption from aqueous
solution by raw and chemically modified green freshwater algae Scenedesmus
obliquus. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52(40–42): 7906-7914. https://doi.org/10.1080/ 19443994.2013.856345
21.
Shrestha, R., Ban, S., Devkota, S.,
Sharma, S., Joshi, R., Tiwari, A. P., Kim, H. Y. and Joshi, M. K. (2021).
Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A
review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4): 105688.
22.
Pan, Y., Wernberg, T., de Bettignies,
T., Holmer, M., Li, K., Wu, J., Lin, F., Yu, Y., Xu, J., Zhou, C., Huang, Z.
and Xiao, X. (2018). Screening of seaweeds in the East China Sea as potential
bio-monitors of heavy metals. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,
25(17): 16640-16651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1612-3
23.
Valderrama, D., Cai, J., Hishamunda,
N., Ridler, N., Neish, I. C., Hurtado, A. Q., Msuya, F. E., Krishnan, M.,
Narayanakumar, R., Kronen, M., Robledo, D., Gasca-Leyva, E. and Fraga, J.
(2015). The economics of Kappaphycus seaweed cultivation in developing countries:
A comparative analysis of farming systems. Aquaculture Economics and
Management, 19(2): 251-277.
24.
Rönnbäck, P., Bryceson, I. and
Kautsky, N. (2002). Coastal aquaculture development in eastern Africa and the
western Indian Ocean: Prospects and problems for food security and local
economies. Ambio, 31(7–8): 537-542.
25.
TWAS. (2004). TWAS newsletter.
pp. 1–84.
26.
Vijayaraghavan, K., Raj Jegan, J.,
Palanivelu, K. and Velan, M. (2004). Copper removal from aqueous solution by
marine green alga Ulva reticulata. Electronic Journal of
Biotechnology, 7(1): 47-54.
27.
Chove, B. E., Ballegu, W. R. and
Chove, L. M. (2006). Copper and lead levels in two popular leafy vegetables
grown around Morogoro Municipality, Tanzania. Tanzania Health Research
Bulletin, 8(1): 37-40.
28.
Mwegoha, W. J. S. and Kihampa, C.
(2010). Heavy metal contamination in agricultural soils and water in Dar es
Salaam city, Tanzania. African Journal of Environmental Science and
Technology, 4(11): 763-769.
29.
Shemdoe, R. S. (2010). Heavy metal
concentrations in soils and leachates of Mtoni dumpsite bordering the Indian
Ocean in Dar es salaam, Tanzania. Scientific Research and Essays, 5(16):
2143-2147.
30.
Awasthi, M. K., Guo, D., Awasthi, S.
K., Wang, Q., Chen, H., Liu, T., Duan, Y., Soundari, P. G. and Zhang, Z.
(2020). Recent advances in phytoremediation of toxic metals from contaminated
sites: A road map to a safer environment. Bioremediation of Industrial Waste
for Environmental Safety, 2: 77-112.
31.
Diniz, V. and Volesky, B. (2005).
Biosorption of La, Eu, and Yb using Sargassum biomass. Water Research,
39(1): 239-247.
32.
Nirmal Kumar, J. I., Oommen, C. and
Kumar, R. N. (2009). Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by green
marine macroalgae from Okha Port, Gulf of Kutch, India. American Eurasian
Journal Agriculture and Environmental Sciences, 6(3): 317-323.
33.
Luis, G., Rubio, C., Gutiérrez, Á.
J., González-Weller, D., Revert, C. and Hardisson, A. (2014). Evaluation of
metals in several varieties of sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas L.):
Comparative study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(1):
433-440.
34.
Rubio,
C., Lucas, J. R. D., Gutiérrez, A. J., Glez-Weller, D., Pérez Marrero, B., Caballero,
J. M., Revert, C. and Hardisson, A. (2012). Evaluation of metal concentrations
in mentha herbal teas (Mentha piperita, Mentha pulegium and Mentha
species) by inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Journal of
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 71: 11-17.
35.
Vieira, D. M., Da Costa, A. C. A.,
Henriques, C. A., Cardoso, V. L. and De França, F. P. (2007). Biosorption of
lead by the brown seaweed Sargassum filipendula - Batch and continuous
pilot studies. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 10(3): 368-375. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol10-issue3-fulltext-3
36.
Da̧browski, A. (2001).
Adsorption - From theory to practice. Advances in Colloid and Interface
Science, 93(1–3): 135-224.
37.
Yang, C. hai. (1998). Statistical
mechanical study on the Freundlich isotherm equation. Journal of Colloid and
Interface Science, 208(2): 379-387.
38.
Hall, K. R., Eagleton, L. C.,
Acrivos, A. and Vermeulen, T. (1966). Pore- and solid diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed
adsorption under constant pattern conditions. Industrial and Engineering
Chemistry Fundamentals, 5(2): 212-223. https://doi.org/10.1021/i160018a011
39.
Febrianto, J., Kosasih, A. N.,
Sunarso, J., Ju, Y. H., Indraswati, N. and Ismadji, S. (2009). Equilibrium and
kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of
recent studies. Journal Of Hazardous Materials, 162(2-3): 616-645.
40.
Ho, Y. S. and Ofomaja, A. E. (2006).
Pseudo-second-order model for lead ion sorption from aqueous solutions onto
palm kernel fiber. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 129(1–3): 137-142.
41. Sheikh, M.
A., Noah, N. M., Tsuha, K. and Oomori, T. (2007). Occurrence of tributyltin
compounds and characteristics of heavy metals. International Journal of
Environmental Science and Technology, 4(1): 49-59.
42.
Yoonaiwong, W., Kaewsarn, P. and
Reanprayoon, P. (2011). Biosorption of lead and cadmium ions by non-living
aquatic macrophyte, Utricularia aurea. Sustainable Environment
Research, 21(6): 369-374.
43.
Oyedepo, T. A. (2011). Biosorption of
lead (II) and copper (II) metal ions on Calotropis procera (Ait.). Science
Journal of Purel & Applied Chemistry, 2011: 1-7.
44.
Vilar, V. J. P., Botelho, C. M. S.
and Boaventura, R. A. R. (2008). Copper removal by algae Gelidium, agar
extraction algal waste and granulated algal waste: Kinetics and equilibrium. Bioresource
Technology, 99(4): 750-762.
45.
Ali Redha, A. (2020). Removal of
heavy metals from aqueous media by biosorption. Arab Journal of Basic and
Applied Sciences, 27(1): 183-193.
46.
Murphy, V., Hughes, H. and
McLoughlin, P. (2007). Cu(II) binding by dried biomass of red, green, and brown
macroalgae. Water Research, 41(4): 731-740.
47.
Vilar, V. J. P., Botelho, C. M. S.
and Boaventura, R. A. R. (2008b). Lead uptake by algae Gelidium and composite
material particles in a packed bed column. Chemical Engineering Journal,
144(3): 420-430.
48.
Farooq, U., Kozinski, J. A., Khan, M.
A. and Athar, M. (2010). Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat-based
biosorbents - A review of the recent literature. Bioresource Technology,
101(14): 5043-5053.
49.
Escudero, C., Fiol, N., Villaescusa,
I. and Bollinger, J. C. (2009). Arsenic removal by a waste metal hydroxide
entrapped into calcium alginate beads. Journal of Hazardous Materials,
164(2–3), 533–541.
50.
Yipmantin, A., Maldonado, H. J., Ly,
M., Taulemesse, J. M. and Guibal, E. (2011). Pb(II) and Cd(II) biosorption on Chondracanthus
chamissoi (a red alga). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185(2–3):
922-929.
51.
Lee, S. H., & Park, C. H. (2012).
Biosorption of heavy metal ions by brown seaweeds from the southern coast of
Korea. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 17(4): 853-861.
52.
Nessim, R. B., Bassiouny, A. R.,
Zaki, H. R., Moawad, M. N. and Kandeel, K. M. (2011). Biosorption of lead and
cadmium using marine algae. Chemistry and Ecology, 27(6): 579-594.
53.
Akpomie,
K. G., Ezeofor, C. C., Olikagu, C. S., Odewole, O. A. and Ezeorah, C. J.
(2018). Abstraction and regeneration potential of temperature-enhanced rice
husk montmorillonite combo for oil spill. Environmental Science and
Pollution Research, 25(34): 34711-34719.
54.
Aroua, M. K., Leong, S. P. P., Teo,
L. Y., Yin, C. Y. and Daud, W. M. A. W. (2008). Real-time determination of the
kinetics of lead(II) adsorption onto palm shell-based activated carbon using an
ion-selective electrode. Bioresource Technology, 99(13): 5786-5792.
55.
Wu, Y., Zhang, S., Guo, X. and Huang,
H. (2008). Adsorption of chromium(III) on lignin. Bioresource Technology,
99(16): 7709-7715.
56.
Bishnoi, N. R. and Pant, A. (2004).
Biosorption of copper from an aqueous solution using algal biomass. Journal
of Scientific and Industrial Research, 63: 813-816.
57.
Wang, G., Zhang, S., Yao, P., Chen,
Y., Xu, X., Li, T. and Gong, G. (2018). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous
solutions by Phytolacca americana L. biomass as a low-cost
biosorbent. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 11(1): 99-110.
58.
Ghasemi, M., Naushad, M., Ghasemi, N.
and Khosravi-fard, Y. (2014). Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using
new adsorbents prepared from agricultural waste: Adsorption isotherm and
kinetic studies. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(4):
2193-2199.
59.
Ibrahim, W. M. (2011). Biosorption of
heavy metal ions from an aqueous solution by red macroalgae. Journal of
Hazardous Materials, 192(3): 1827-1835.
60.
Ozudogru, Y. (2017). Biosorption of
Cu (II) and Pb (ii) ions by using marine brown algae Padina pavonica. Fresenius
Environmental Bulletin, 22: 3725-3729.
61.
Arshadi, M., Amiri, M. J. and
Mousavi, S. (2014). Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic investigations of
Ni(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), and Co(II) adsorption on barley straw ash. Water
Resources and Industry, 6: 1-17.
62.
Naiya, T. K., Bhattacharya, A. K.,
Mandal, S. and Das, S. K. (2009). The sorption of lead(II) ions on rice husk
ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(2–3): 1254-1264.
63.
Meitei, M. D. and Prasad, M. N. V.
(2014). Adsorption of Cu(II), Mn(II), and Zn(II) by Spirodela polyrhiza
(L.) Schleiden: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ecological
Engineering, 71: 308-317.
64.
Al-Homaidan, A. A., Al-Houri, H. J.,
Al-Hazzani, A. A., Elgaaly, G. and Moubayed, N. M. S. (2014). Biosorption of
copper ions from aqueous solutions by Spirulina platensis biomass. Arabian
Journal of Chemistry, 7(1): 57-62.
65.
Onwuka, J. C., Ajibola, V. O., Kagbu,
J. A. and Manji, A. J. (2011). Biosorption of Cr(VI) and Co(II) ions from
synthetic wastewater using dead biomass of freshwater green algae Cosmarium
panamense. Archives of Applied Science Research, 3(6): 191-207.
66.
Ashraf, M. A., Mahmood, K., Wajid,
A., Maah, M. J. and Yusoff, I. (2011). Study of low-cost biosorbent for
biosorption of heavy metals. In Proceedings of the International
Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology, 9: pp. 60-68.
67.
Ayawei, N., Ekubo, A. T., Wankasi, D.
and Dikio, E. D. (2015). Adsorption of congo red by Ni/Al-CO3:
Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Oriental Journal of
Chemistry, 31(3): 1307-1318.
68.
Lasheen, M. R., Ammar, N. S. and
Ibrahim, H. S. (2012). Adsorption/desorption of Cd(II), Cu(II), and Pb(II)
using chemically modified orange peel: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Solid-State
Sciences, 14(2): 202-210.
69.
Yalçın, S. (2014). The mechanism
of heavy metal biosorption on green marine macroalga Enteromorpha linza.
CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 42(3): 251-259.
70.
Weber, T. W. and Chakravorti, R. K.
(1974). Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed‐bed adsorbers. AIChE
Journal, 20(2): 228-238.