Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 507 - 519
THE REMOVAL OF BISPHENOL-A FROM SYNTHETIC
WASTEWATER USING THIN-FILM COMPOSITE MEMBRANE
(Penyingkiran Bisfenol A
daripada Sisa Air Sintetik Mengunakan Membran Lapisan Komposit Nipis)
Taofiq Damilare Aiyelabegan , Siti Nur Alwani Shafie, Shafiq Mohd
Hizam, Nik Abdul Hadi Nordin*
Department of Chemical Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, 32610 Seri Iskandar, Perak,
Malaysia
*Corresponding author: nahadi.sapiaa@utp.edu.my
Received: 22 August 2021;
Accepted: 24 March 2022; Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
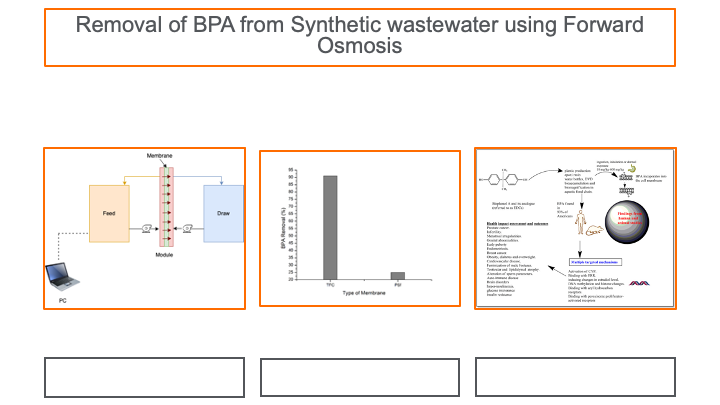
In this study, the removal
performance of bisphenol A (BPA) from synthetic wastewater using the forward
osmosis method was compared between polyamide thin film composite membrane (PA
-TFC) and polysulfone (PSf) membrane substrate. The thin-film composite
membrane was prepared by using flat polysulfone (PSf) sheets as membrane
substrate through in-situ interfacial polymerization technique. To generate the
thin film surface on the PSf substrate, M-phenylenediamine (MPD) and
1,3,5-benzene trichloride (TMC) were utilized as monomers in aqueous and
organic solutions, respectively. The BPA retention efficiency of the PSf and
TFC membranes was examined and compared accordingly. The membranes were
characterized by using atomic force microscopy (AFM), field emission scanning
electron microscope (FESEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR),
and contact angle analysis. The fabricated thin film on the PSf substrate
membrane has enhanced its hydrophilicity which aids in wastewater treatment by
increasing the membranes water flow rate. A synthetic BPA wastewater solution
of 100 mgL-1 was prepared to evaluate the performance of the membrane. Based on
the finding of this study, the PSf substrate and PA -TFC membrane yielded 25%
and 91% of BPA removal from the feed solution, respectively.
Keywords: bisphenol-a, polyamide, thin-film composite
membrane, forward osmosis
Abstrak
Dalam kajian ini, penyingkiran
bisfenol A (BPA) dari air sisa sintetik disiasat menggunakan membran filem
komposit nipis poliamida (PA -TFC) dan dibandingkan dengan substrat membran
polisulfon (PSf) menggunakan proses osmosis hadapan. Membran TFC diperbuat melalui
teknik pempolimeran dengan menggunakan permukaan PSf sebagai substrat membran.
M-fenildiamina (MPD) dan 1,3,5-benzena triklorida (TMC) digunakan sebagai
monomer dalam larutan berair dan organik untuk menghasilkan permukaan filem
nipis pada substrat PSf. Penyingkiran BPA melalui membran PSf dan TFC disiasat
dan dibandingkan. Setiap membran dicirikan dengan mikroskopi tekanan atom
(AFM), mikroskopi imbasan elektron pancaran medan (FESEM), spektroskopi
inframerah transformasi Fourier (FTIR) dan analisa sudut sentuhan. Lapisan
filem nipis yang dihasilkan pada membran substrat PSf meningkatkan daya
hidrofiliknya, yang membantu dalam rawatan air sisa dengan meningkatkan kadar
pengeluaran air. 100 ppm larutan sisa air BPA sintetik disediakan untuk menguji
prestasi membran. Dari data yang diperoleh dari kajian ini, substrat PSf dan
membran PA -TFC menghasilkan 25% dan 91% penurasan BPA dari sisa tersebut.
Kata
kunci: bisfenol a, poliamida, membran filem komposit nipis, osmosis hadapan
Graphical Abstract
References
1. Li, J., Liu, Q., Liu, Y. and Xie, J. (2017). Development of electro-active forward osmosis
membranes to remove phenolic compounds and reject salts. Environmental
Science: Water Research & Technology, 3(1): 139-146.
2.
Silva, C. P., Otero, M. and Esteves, V. (2012).
Processes for the elimination of estrogenic steroid hormones from water: A
review. Environmental Pollution, 165: 38-58.
3.
Xiao,
M., Zhou, J., Tan, Y., Zhang, A., Xia, Y. and Ji, L. (2006). Treatment of
highly-concentrated phenol wastewater with an extractive membrane reactor using
silicone rubber. Desalination, 195(1-3): 281-293.
4.
Mohammadi,
S., Kargari, A., Sanaeepur, H., Abbassian, K., Najafi, A. and Mofarrah, E.
(2015). Phenol removal from industrial wastewaters: a short review. Desalination
and Water Treatment, 53(8): 2215-2234.
5.
Huang,
Y. Q., Wong, C. K. C., Zheng, J. S., Bouwman, H., Barra, R., Wahlström, B.,
Neretin, L., & Wong, M. H. (2012). Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A review of
sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environment
International, 42: 91-99.
6.
Kumar, A., Gupta, K., Tomer, V., Kaur, A., & Kumar, V.
(2018). Bisphenols as human health
hazard: A systematic review on potent sources, route of exposure, harmful
effects and safe alternatives. Toxicology International, 25(1):
78-92.
7.
Katibi, K. K., Yunos, K. F., Man, H. C., Aris, A. Z., Mohd
Nor, M. Z. and Azis, R. S. (2021). Recent
advances in the rejection of endocrine-disrupting compounds from water using
membrane and membrane bioreactor technologies: A review. Polymers,
13(3): 392.
8.
Tsai, W.
T. (2006). Human health risk on environmental exposure to bisphenol-A: A
review. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part C Environmental
Carcinogenesis and Ecotoxicology Reviews, 24(2), 225-255.
9.
Rubin,
B. S. (2011). Bisphenol A: An endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and
multiple effects. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
127(12): 27-34.
10.
Viñas,
R., Jeng, Y. J. and Watson, C. S. (2012). Non-genomic effects of xenoestrogen
mixtures. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
9(8): 2694-2714.
11.
Zoeller, R. T., & Belcher, S. M. (2007). In vitro molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A action. Reproductive
Toxicology, 24(2): 178-198.
12.
Rochester,
J. R. (2013). Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reproductive
Toxicology, 42: 132-155.
13.
Kundakovic,
M. and Champagne, F. A. (2011). Epigenetic perspective on the developmental
effects of bisphenol A. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 25(6): 1084-1093.
14.
Chen, H. W., Liang, C. H., Wu, Z. M., Chang, E. E., Lin, T.
F., Chiang, P. C. and Wang, G. S. (2013). Occurrence and assessment of treatment efficiency of
nonylphenol, octylphenol and bisphenol-A in drinking water in Taiwan. Science
of the Total Environment, 449: 20-28.
15.
Kleywegt,
S., Pileggi, V., Yang, P., Hao, C., Zhao, X., Rocks, C., Thach, S., Cheung, P.
and Whitehead, B. (2011). Pharmaceuticals, hormones and bisphenol A in
untreated source and finished drinking water in Ontario, Canada - Occurrence
and treatment efficiency. Science of the Total Environment, 409(8):
1481-1488.
16.
Sodré,
F. F., Locatelli, M. A. F. and Jardim, W. F. (2010). Occurrence of emerging
contaminants in Brazilian drinking waters: A sewage-to-tap issue. Water,
Air, and Soil Pollution, 206(14): 57-67.
17.
Muhamad,
M. S., Salim, M. R., Lau, W. J. and Yusop, Z. (2016). A review on bisphenol A
occurrences, health effects and treatment process via membrane technology for
drinking water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(12): 11549-11567.
18.
Yüksel,
S., Kabay, N. and Yüksel, M. (2013). Removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from water by
various nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. Journal of
Hazardous Materials, 263: 307-310.
19.
Mehwish,
N., Kausar, A. and Siddiq, M. (2014). Advances in Polymer-based Nanostructured
Membranes for Water Treatment. Polymer - Plastics Technology and Engineering,
53(12): 1290-1316.
20.
Kim, I. C. And Lee, K. H. (2003). Effect of various additives on pore size of polysulfone
membrane by phase-inversion process. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,
89(9): 2562-2566.
21.
Zhao, F.
B., Tang, C. C., Liu, X. Y., Shi, F. J., Song, X. R., Tian, Y. and Li, Z. S.
(2015). Transportation characteristics of bisphenol A on ultrafiltration
membrane with low molecule weight cut-off. Desalination, 362: 18-25.
22.
Heo, J.,
Flora, J. R. V., Her, N., Park, Y. G., Cho, J., Son, A. and Yoon, Y. (2012).
Removal of bisphenol A and 17β-estradiol in single walled carbon
nanotubes-ultrafiltration (SWNTs-UF) membrane systems. Separation and
Purification Technology, 90: 39-52.
23.
Bing-zhi,
D., Hua-qiang, C., Lin, W., Sheng-ji, X. and Nai-yun, G. (2010). The removal of
bisphenol A by hollow fiber microfiltration membrane. Desalination,
250(2): 693-697.
24.
Yüksel,
S., Kabay, N. and Yüksel, M. (2013). Removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from water by
various nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. Journal of
Hazardous Materials, 263: 307-310.
25.
Lutchmiah,
K., Verliefde, A. R. D., Roest, K., Rietveld, L. C. and Cornelissen, E. R.
(2014). Forward osmosis for application in wastewater treatment: A review. Water
Research, 58: 179-197.
26.
Cartinella,
J. L., Cath, T. Y., Flynn, M. T., Miller, G. C., Hunter, K. W. and Childress,
A. E. (2006). Removal of natural steroid hormones from wastewater using
membrane contactor processes. Environmental Science and Technology,
40(23): 7381-7386.
27.
Lee, S.,
Boo, C., Elimelech, M. and Hong, S. (2010). Comparison of fouling behavior in
forward osmosis (FO) and reverse osmosis (RO). Journal of Membrane Science,
365(1-2): 34-39.
28.
Mi, B.
and Elimelech, M. (2010). Organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes: Fouling
reversibility and cleaning without chemical reagents. Journal of Membrane
Science, 348(1-2): 337-345.
29. Adamczak, M., Kamińska, G. and Bohdziewicz, J. (2019).
Preparation of polymer membranes by in situ interfacial polymerization. International
Journal of Polymer Science, 2019: 6217924.
30.
Khorshidi,
B., Thundat, T., Fleck, B. A. and Sadrzadeh, M. (2016). A novel approach toward
fabrication of high performance thin film composite polyamide membranes. Scientific
Reports, 6(1): 1-10.
31.
Al-Hobaib, A. S., El Ghoul, J., Ghiloufi, I. and El Mir, L.
(2016). Synthesis and
characterization of polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membrane reached by
aluminum doped ZnO nanoparticles. Materials Science in Semiconductor
Processing, 42: 111-114.
32.
Mehwish,
N., Kausar, A. and Siddiq, M. (2014). Advances in polymer-based nanostructured
membranes for water treatment. Polymer - Plastics Technology and Engineering,
53(12): 1290-1316.
33.
Wei, J., Qiu, C., Tang, C. Y., Wang, R.
and Fane, A. G. (2011). Synthesis
and characterization of flat-sheet thin film composite forward osmosis
membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 372(12): 292302.
34.
Syahida
Mat Anan, N., Jaafar, J., Sato, S. and Mohamud, R. (2021). Titanium dioxide
incorporated polyamide thin film composite photocatalytic membrane for
bisphenol a removal. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and
Engineering, 1142(1): 012015.
35.
Miao,
L., Jiang, T., Lin, S., Jin, T., Hu, J., Zhang, M. and Liu, G. (2020).
Asymmetric forward osmosis membranes from p-aramid nanofibers. Materials
& Design, 191: 108591.
36.
El-Arnaouty,
M. B., Abdel Ghaffar, A. M., Eid, M., Aboulfotouh, M. E., Taher, N. H. and
Soliman, E.-S. (2018). Nano-modification of polyamide thin film composite
reverse osmosis membranes by radiation grafting. Journal of Radiation
Research and Applied Sciences, 11(3): 204-216.
37.
Park, H.
M., Takaba, H., & Lee, Y. T. (2020). Preparation and characterization of
TFC NF membrane with improved acid resistance behavior. Journal of Membrane
Science, 616: 118620.
38.
Song,
X., Qi, S., Tang, C. Y. and Gao, C. (2017). Ultra-thin, multi-layered polyamide
membranes: Synthesis and characterization. Journal of Membrane Science,
540: 10-18.
39.
Morgan, P. W. and Kwolek, S. L. (1996). Interfacial polycondensation. II. Fundamentals of polymer
formation at liquid interfaces. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer
Chemistry, 40(137): 299-327.
40.
Rajaeian,
B., Rahimpour, A., Tade, M. O. and Liu, S. (2013). Fabrication and
characterization of polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) nanofiltration
membrane impregnated with TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination,
313: 176-188.