Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 600 - 612
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF
LSCF/YSZ-SDC AND LSCF/YSZ-SDCC DUAL COMPOSITE CATHODES FOR INTERMEDIATE-TEMPERATURE SOLID OXIDE FUEL CELL
(Formulasi
dan Ciri Dwi-Komposit Katod LSCF/YSZ-SDC dan LSCF/YSZ-SDC Karbonat untuk Sel Bahan
Api Oksida Pepejal Bersuhu Pertengahan)
Nurul Farhana Abdul
Rahman, Umira Asyikin Yusop, Yohannes Nyambong Lowrance,
Faculty
of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering,
Universiti
Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, 86400 Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: hamimah@uthm.edu.my
Received:
28 November 2021; Accepted: 27 February 2022; Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
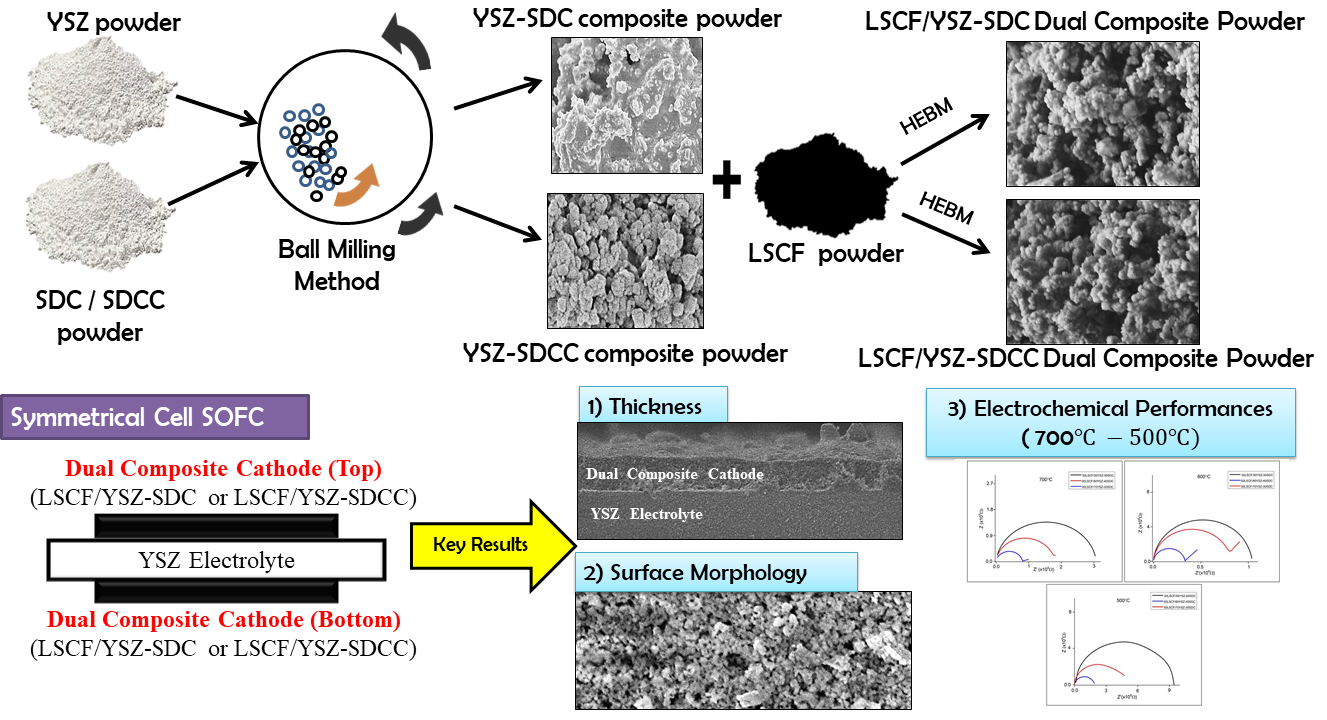
A cathode component solid oxide fuel
cell (SOFC) is important in the manufacturing of the cells. This study
evaluated two dual composite cathodes, namely, (La0.6Sr0.4)0.97Co0.2Fe0.8O3
(LSCF)/Y0.8Zr0.92O1.96 (YSZ)-Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9
(SDC) and LSCF/YSZ-SDC carbonate (SDCC). The dual composite cathodes with
different compositions were developed through high-energy ball milling (HEBM)
for the production of dual composite powder and screen-printing method for the
fabrication of symmetrical cells. The properties of the dual composite cathodes
were studied. Phase identification was carried out via X-ray diffractometry
(XRD), and the electrochemical performance of the symmetrical cells was
measured by impedance test. The physical morphologies of LSCF/YSZ-SDC and
LSCF/YSZ-SDCC were slightly different. The XRD patterns of the LSCF/YSZ-SDC
cathode powder showed no secondary peak, whereas the LSCF/YSZ-SDCC cathode
powder had SrCO3 as an impurity. Microstructure and powder
homogeneity are considered essential in addition to the good formulation of the
dual composite’s cathodes. The particle sizes of LSCF/YSZ-SDC and LSCF/YSZ-SDCC
as analyzed by ImageJ software were in the range of 130–160 nm. The printed
cathode was investigated under heat treatment from 700 °C to 500 °C. The
electrochemical performance of LSCF/YSZ-SDCC was slightly better compared with
that of LSCF/YSZ-SDC because of the addition of the carbonate; however, the
polarization resistance obtained did not meet the standard range. The electrochemical
performance obtained from this study was not favorable because of severe
problems, such as the technique applied during cell fabrication and the
presence of impurity after the HEBM process.
Keywords:
dual composite cathodes, intermediate temperature,
screen printing, solid oxide fuel cell
Abstrak
Komponen katod untuk sel bahan api
oksida pepejal (SOFC) adalah penting dalam pembuatan sel. Dalam kajian ini,
penilaian katod komposit dwi (LSCF)/(YSZ)-(SDC) and (LSCF)/(YSZ)-Karbonat
(SDCC) dibentangkan. Komposisi yang berbeza bagi katod komposit dwi telah
dibangunkan melalui teknik pengisaran bebola tenaga tinggi untuk penghasilan
serbuk komposit dwi dan kaedah percetakan skrin telah digunakan untuk fabrikasi
sel simetri. Pencirian sifat katod komposit dwi telah dikaji. Pengenalpastian
fasa melalui kaedah pembelauan sinaran-X telah dijalankan dan prestasi
electrokimia sel simetri diukur dengan menggunakan ujian impedans. Perbandingan
antara morfologi fizikal LSCF/YSZ-SDC and LSCF/YSZ-SDCC menunjukkan sedikit
perbezaan dengan penambahan karbonat. Corak sinar-X untuk komposit dwi campuran
LSCF/YSZ-SDC katod serbuk tidak memaparkan puncak sekunder. Bagaimanapun,
Komposit dwi campuran LSCF/YSZ-SDCC katod serbuk memaparkan kehadiran sebagai
bendasing. Kehomogenan struktur mikro dan serbuk dianggap pentiing sebagai
tambahan kepada perumusan katod dwi komposit yang baik. Purata saiz zarah
purata bagi LSCF/YSZ-SDC and LSCF/YSZ-SDCC dwi komposit selepas dianalisis oleh
perisian Image J didedahkan berada dalam julat antara 130-160. Filem bercetak
katod telah disiasat di bawah suhu rawatan haba dari 700
Kata kunci: katod komposit dwi, suhu pertengahan,
percetakan skrin, sel bahan api oksida pepejal
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Udomsilp, D., Thaler, F.,
Menzler, N. H., Bischof, C., de Haart, L. G. J., Opitz, A. K. and Bram,
M.(2019). Dual-phase cathodes for metal-supported solid oxide fuel cells:
Processing performance, durability. Journal of the Electrochemical
Society, 166(8): F506.
2.
Rahman, N. F. A., Rahman,
H. A and Azmi, M. A. (2021). Perovskite-type oxide-based dual composite cathode
for solid oxide fuel cells: A short review. Solid State Phenomena, 317:
417-425.
3.
Ko, H. J., Myung, J. H., Hyun, S. H. and Chung, J. S. (2012). Synthesis
of LSM–YSZ–GDC dual composite SOFC cathodes for high-performance
power-generation systems. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 42(4):
209-215.
4.
Ko, H. J., Myung, J. H.,
Lee, J. H., Hyun, S. H. and Chung, J. S. (2012). Synthesis and evaluation of (
5.
Railsback, J., Choi, S.
H. and Barnett, S. A. (2019). Effectiveness of dense Gd-doped ceria barrier
layers for (La,Sr)(Co,Fe)
6.
Fergus, J., Hui, R., Li,
X., Wilkinson, D. P and Zhang, J. (2016). Solid oxide fuel cells:
Materials properties and performance. CRC press.
7.
Rahman, H. A., Ng, K. H.,
Ahmad, S., Taib, H., Mahzan, S., Salleh, S. M. and Muchtar, A. (2019, March).
Influence of microstructure on the electrochemical behaviour of LSCF-SDCC.
In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,
494(1): 012062.
8.
Mohammad, S. F., Ahmad,
S., Rahman, H. A. and Muchtar, A. (2019). Effect of SSC Loading on the
microstructural stability SSC-SDCC composite cathode as new potential
SOFC. International Journal of Integrated Engineering, 11(7):
162-168.
9.
Somalu, M. R., Muchtar,
A., Daud, W. R. W. and Brandon, N. P. (2017). Screen-printing inks for the
fabrication of solid oxide fuel cell films: a review. Renewable and
Sustainable Energy Reviews, 75: 426-439.
10.
Huang, J., Gao, Z. and
Mao, Z. (2010). Effects of salt composition on the electrical properties of
samaria-doped ceria/carbonate composite electrolytes for low-temperature
SOFCs. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(9):
4270-4275.
11.
Abd Rahman, H., Agun, L.,
Hoa, N. K., Ahmad, S. and Nordin, N. A. (2020). Effects of binary
(lithium/natrium
12.
Mohammad, S. F., Ahmad, S., Rahman, H. A. and Muchtar, A. (2019). Effect
of SSC loading on the microstructural stability SSC-SDCC composite cathode as
new potential SOFC. International Journal of Integrated Engineering, 11(7):
162-168.
13.
Ghasdi, M. and Alamdari,
H. (2010). CO sensitive nanocrystalline
14. Baharuddin, N. A., Abd Rahman, H., Muchtar, A.,
Sulong, A. B. and Abdullah, H. (2013). Development of lanthanum strontium
cobalt ferrite composite cathodes for intermediate-to low-temperature solid
oxide fuel cells. Journal of Zhejiang University Science A, 14(1):
11-24.
15.
Gao, D., Zhao, J., Zhou, W., Ran, R. and Shao, Z. (2011). Influence of
high-energy ball milling of the starting powder on the sintering; microstructure
and oxygen permeability of
16. Parwaiz, S., Khan,
M. M. and Pradhan, D. (2019).
17.
Lu, X., Heenan, T. M., Bailey, J. J., Li, T., Li, K., Brett, D. J. and
Shearing, P. R. (2017). Correlation between triple phase boundary and the
microstructure of solid oxide fuel cell anodes: The role of composition,
porosity and Ni densification. Journal of Power Sources, 365:
210-219.
18.
Somalu, M. R., Muchtar, A., Daud, W. R. W. and Brandon, N. P. (2017).
Screen-printing inks for the fabrication of solid oxide fuel cell films: a
review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 75: 426-439.
19.
Zhang, J. and Jung, Y. G.
(2018). Advanced ceramic and metallic coating and thin film materials for
energy and environmental applications Berlin: Springer: pp. 20.
20.
Baharuddin, N. A., Abdul Rahman, N. F., Abd. Rahman, H., Somalu, M. R.,
Azmi, M. A. and Raharjo, J. (2020). Fabrication of high‐quality electrode
films for solid oxide fuel cell by screen printing: a review on important
processing parameters. International Journal of Energy Research, 44(11):
8296-8313.
21.
Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Su, D., Yang, Z. and Chen, F.
(2014). Low temperature solid oxide fuel cells with hierarchically porous
cathode nano-network. Nano Energy, 8: 25-33.
22.
Talebi, T., Haji, M. and Raissi, B. (2010). Effect of sintering temperature
on the microstructure, roughness and electrochemical impedance of
electrophoretically deposited YSZ electrolyte for SOFCs. International
Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(17): 9420-9426.
23.
Ali, S. M., Muchtar, A., Sulong, A. B., Muhamad, N. and Majlan, E. H.
(2013). Influence of sintering temperature on the power density of
samarium-doped-ceria carbonate electrolyte composites for low-temperature solid
oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 39(5): 5813-5820.