Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 571 - 580
POTENTIAL OF TEXTILE WASTE AS NITROGEN DOPED
POROUS CARBON FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION
(Potensi
Sisa Tekstil Sebagai Karbon Poros Terdop Nitrogen Berliang untuk Tindak Balas
Penurunan Oksigen)
Suhaila Mohd
Sauid1, 3, Siti Kartom Kamarudin1,2*, Loh Kee Shyuan1
1Fuel Cell
Institute
2Department
of Chemical and Process Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Built
Environment
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600
UKM Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
3School of
Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering
Universiti Teknologi MARA, 40450 Shah
Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: ctie@ukm.edu.my
Received: 13 December 2021; Accepted: 27 February 2022;
Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
Transforming waste into
usable materials can protect and conserve the environment, thereby reducing the
dependence on landfills, limiting the use of natural resources, and decreasing
the carbon footprint. Every year, millions of tons of textile waste are sent to
landfills primarily from discarded clothing. Therefore, this waste is
worthwhile to convert into functional carbon product. Herein, textile waste
from used clothing was converted into nitrogen-doped porous carbons (TNPC) by
simple chemical activation followed by carbonisation. Urea and calcium chloride
(CaCl2) served as nitrogen precursor and pore forming agent,
respectively. The surface area and porosity of the prepared TNPCs were affected
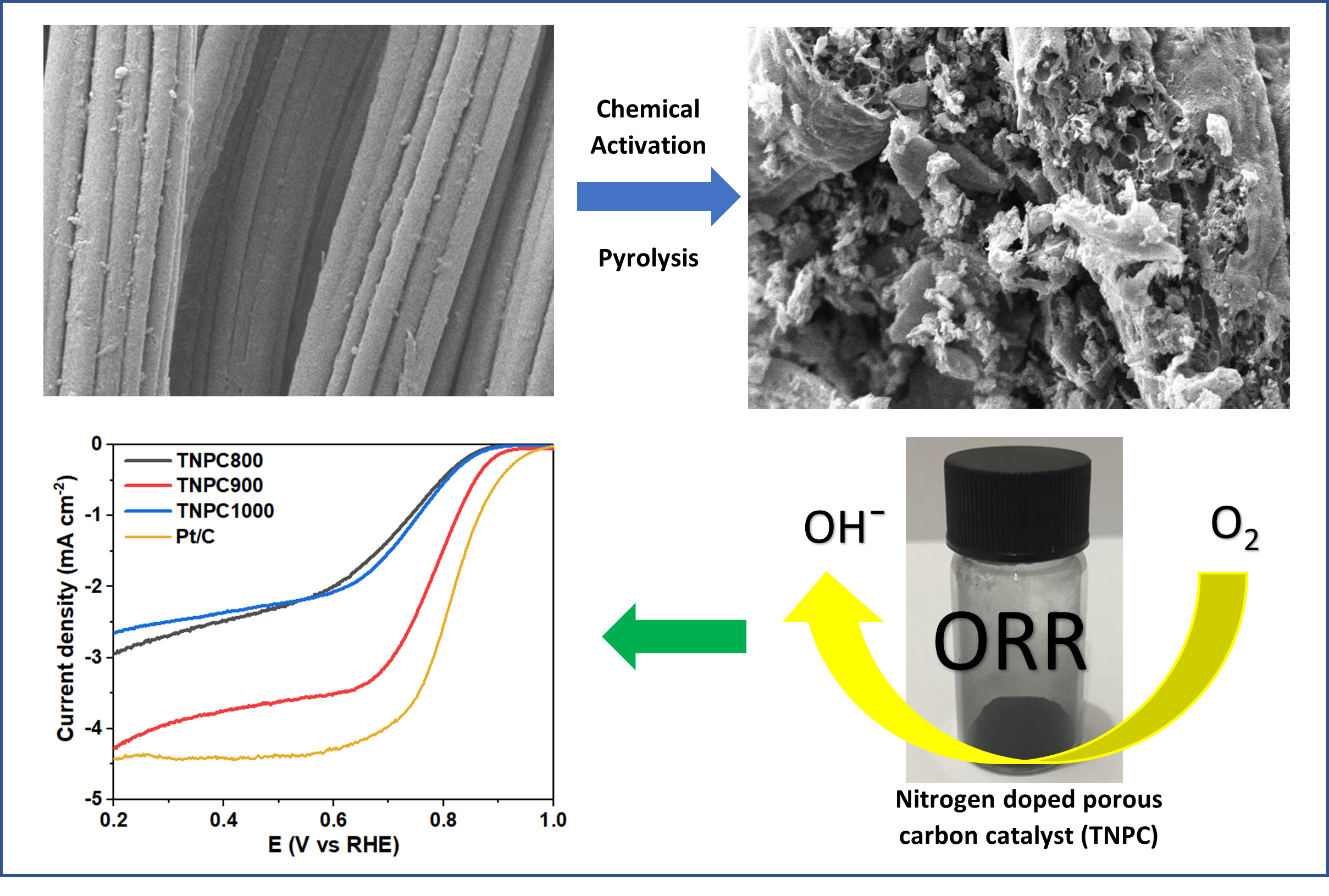
by the activation temperature. The optimal sample (TNPC900) activated at
900 °C exhibited a large surface area (496 m2 g–1)
with appropriate porosity and a reasonable amount of nitrogen doped.
Remarkably, the resultant TNPC900 catalyst tested as the electrode material for
oxygen reduction reaction in 0.1 M KOH exhibited an outstanding positive onset
potential of 0.94 V vs. RHE. TNCP900 catalyst also demonstrated superior stability
and tolerance to methanol than Pt/C. Overall, this study showed that the
conversion of textile waste through a simple synthesis technique into
electrocatalyst could offer a sustainable alternative to Pt for potential
applications in fuel cell and energy-storage technology.
Keywords: textile waste, nitrogen-doped porous carbon, oxygen reduction reaction,
metal-free catalyst
Abstrak
Mengubah sisa menjadi
bahan yang boleh digunakan dapat melindungi dan memulihara alam sekitar
sekaligus dapat mengurangkan kebergantungan pada tapak pelupusan sampah,
mengehadkan penggunaan sumber semula jadi, dan mengurangkan jejak karbon.
Setiap tahun, jutaan ton sisa tekstil dihantar ke tapak pelupusan sampah
terutama dari pakaian terpakai. Oleh itu,
menukar sisa ini menjadi produk karbon berfungsi adalah usaha yang
berbaloi. Di sini, sisa tekstil daripada pakaian terpakai telah
ditukar kepada karbon berliang terdop nitrogen (TNPC) dengan pengaktifan kimia
mudah diikuti dengan langkah karbonisasi. Urea dan kalsium klorida (CaCl2) bertindak masing-masing sebagai bahan sumber nitrogen dan ejen pembentukan
liang. Keluasan permukaan dan keliangan
TNPC yang disediakan telah dipengaruhi oleh suhu pengaktifan. Sampel
optimum (TNPC900) diaktifkan pada 900 °
C mempamerkan keluasan permukaan yang besar
(496 m2 g-1) dengan
keliangan dan jumlah nitrogen terdop yang sesuai. Mangkin TNPC900 yang
diuji sebagai bahan elektrod untuk tindak balas penurunan oksigen (ORR) di
dalam larutan 0.1 M KOH menunjukkan potensi permulaan positif yang luar biasa
iaitu 0.94 V vs RHE. Selain itu, mangkin TNCP900 menunjukkan kestabilan dan
toleransi yang unggul terhadap metanol
daripada mangkin Pt/C. Oleh itu, kajian ini menunjukkan bahawa penukaran
sisa tekstil menggunakan teknik sintesis
yang mudah menjadi elektmangkin
dapat menawarkan alternatif Pt yang
mampan untuk aplikasi di dalam sel bahan api dan teknologi penyimpanan
tenaga.
Kata kunci: sisa tekstil, karbon poros terdop nitrogen, tindak balas
penurunan oksigen, mangkin bebas metal
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Steele, B. C. H. and Heinzel, A. (2001). Materials for
fuel-cell technologies. Nature, 414(6861): 345-352.
2.
Wang,
Y., Li, J. and Wei, Z. (2018). Transition-metal-oxide-based catalysts for the
oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6(18): 8194-8209.
3.
Karim,
N. A. and Kamarudin, S. K. (2013). An overview on non-platinum cathode
catalysts for direct methanol fuel cell. Applied Energy, 103(9): 212-220.
4.
Wu, Z., Song,
M., Wang, J. and Liu, X. (2018). Recent progress in nitrogen-doped metal-free
electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Catalysts, 8(5): 196.
5.
Guo, D.,
Shibuya, R., Akiba, C., Saji, S., Kondo, T. and Nakamura, J. (2016). Active
sites of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction
clarified using model catalysts. Science, 351(6271): 361-365.
6.
Li, J.,
Wang, S., Ren, Y., Ren, Z., Qiu, Y. and Yu, J. (2014). Nitrogen-doped activated
carbon with micrometer-scale channels derived from luffa sponge fibers as electrocatalysts
for oxygen reduction reaction with high stability in acidic media. Electrochimica
Acta, 149: 56-64.
7.
Quílez-Bermejo,
J., Morallón, E. and Cazorla-Amorós, D. (2020). Metal-free heteroatom-doped
carbon-based catalysts for ORR. A critical assessment about the role of
heteroatoms. Carbon, 165: 434-454.
8.
Gao, Z.,
Zhang, Y., Song, N. and Li, X. (2017). Biomass-derived renewable carbon
materials for electrochemical energy storage. Materials Research Letters,
5(2): 69-88.
9.
Borghei,
M., Lehtonen, J., Liu, L. and Rojas, O. J. (2018). Advanced biomass-derived
electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Advanced Materials,
30(24): 1703691.
10.
Kaur,
P., Verma, G. and Sekhon, S. S. (2019). Biomass derived hierarchical porous
carbon materials as oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts in fuel cells. Progress
in Materials Science, 102: 1-71.
11.
Zhou, H.,
Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, C. and Mu, S. (2016). A self-template and
KOH activation co-coupling strategy to synthesize ultrahigh surface area
nitrogen-doped porous graphene for oxygen reduction. RSC Advances, 6(77):
73292-73300.
12.
Zheng,
B., Wang, J., Pan, Z., Wang, X., Liu, S., Ding, S. and Lang, L. (2020). An efficient
metal-free catalyst derived from waste lotus seedpod for oxygen reduction
reaction. Journal of Porous Materials, 27(3): 637-646.
13.
Polajnar
Horvat, K. and Šrimpf Vendramin, K. (2021). Issues surrounding behavior towards
discarded textiles and garments in Ljubljana. Sustainability (Switzerland),
13(11): 1-11.
14.
USEPA (2019).
Textiles: Material-specific data. Available from https://www.epa.gov/facts-and-figures-about-materials-waste-and-recycling/textiles-material-specific-data#TextilesOverview.
[Accessed online: 16-Dec-2019].
15.
Ramamoorthy,
S. K., Skrifvars, M., Alagar, R. and Akhtar, N. (2018). End-of-life textiles as
reinforcements in biocomposites. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,
26(2): 487-498.
16.
Sauid,
S. M., Kamarudin, S. K., Karim, N. A. and Shyuan, L. K. (2021). Superior
stability and methanol tolerance of a metal-free nitrogen-doped hierarchical
porous carbon electrocatalyst derived from textile waste. Journal of
Materials Research and Technology, 11: 1834-1846.
17.
Ge, X.,
Sumboja, A., Wuu, D., An, T., Li, B., Goh, F. W. T., … and Liu, Z. (2015).
Oxygen reduction in alkaline media: from mechanisms to recent advances of
catalysts. ACS Catalysis, 5(8): 4643-4667.
18.
Ratso,
S., Kruusenberg, I., Käärik, M., Kook, M., Saar, R., Kanninen, P., … and Tammeveski,
K. (2017). Transition metal-nitrogen co-doped carbide-derived carbon catalysts
for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline direct methanol fuel cell. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental, 219: 276-286.
19.
Zhou,
R., Zheng, Y., Jaroniec, M. and Qiao, S. Z. (2016). Determination of the
electron transfer number for the oxygen reduction reaction: From theory to
experiment. ACS Catalysis, 6(7): 4720-4728.
20.
Tang,
J., Wang, Y., Zhao, W., Zeng, R. J., Liu, T. and Zhou, S. (2019). Biomass-derived
hierarchical honeycomb-like porous carbon tube catalyst for the metal-free
oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 847:
113230.
21.
Shi, J.,
Lin, N., Lin, H. B., Yang, J. and Zhang, W. L. (2020). A N-doped rice
husk-based porous carbon as an electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction
reaction. Xinxing Tan Cailiao/New Carbon Materials, 35(4): 401-409.
22.
Thommes,
M., Smarsly, B., Groenewolt, M., Ravikovitch, P. I. and Neimark, A. V. (2006).
Adsorption hysteresis of nitrogen and argon in pore networks and characterization
of novel micro- and mesoporous silicas. Langmuir, 22(2): 756-764.
23.
Jiang,
M., Yu, X., Yang, H. and Chen, S. (2020). Optimization strategies of preparation
of biomass-derived carbon electrocatalyst for boosting oxygen reduction
reaction: A minireview. Catalysts, 10(12): 1-17.
24.
Mao, X.,
Cao, Z., Yin, Y., Wang, Z., Dong, H. and Yang, S. (2018). Direct synthesis of
nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped hierarchical porous carbon networks with
biological materials as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction
reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43(22): 10341-10350.
25.
Zhao,
Q., Ma, Q., Pan, F., Wang, Z., Yang, B., Zhang, J. and Zhang, J. (2016). Facile
synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets as metal-free catalyst with
excellent oxygen reduction performance in alkaline and acidic media. Journal
of Solid State Electrochemistry, 20(5): 1469-1479.
26.
Zhang,
W., Qi, J., Bai, P., Wang, H. and Xu, L. (2019). High-level nitrogen-doped,
micro/mesoporous carbon as an efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for the
oxygen reduction reaction: Optimizing the reaction surface area by a
solvent-free mechanochemical method. New Journal of Chemistry, 43(27): 10878-10886.
27.
Lazar,
P., Mach, R. and Otyepka, M. (2019). Spectroscopic fingerprints of graphitic, pyrrolic,
pyridinic, and chemisorbed nitrogen in N-doped graphene. Journal of Physical
Chemistry C, 123(16): 10695-10702.
28.
Zainul
Abidin, A. F., Loh, K. S., Wong, W. Y. and Mohamad, A. B. (2019).
Nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction: Improved
structural and catalytic activity by enhancing nitrogen species and cobalt
insertion. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(54): 28789-28802.
29.
Sharifi,
T., Hu, G., Jia, X. and Wågberg, T. (2012). Formation of active sites for
oxygen reduction reactions by transformation of nitrogen functionalities in
nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano, 6(10): 8904-8912.
30.
Liu, R.,
Zhang, H., Liu, S., Zhang, X., Wu, T., Ge, X., … and Wang, G. (2016).
Shrimp-shell derived carbon nanodots as carbon and nitrogen sources to
fabricate three-dimensional N-doped porous carbon electrocatalysts for the
oxygen reduction reaction. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18(5): 4095-4101.
31.
Zheng, F.
Y., Li, R., Ge, S., Xu, W. R. and Zhang, Y. (2020). Nitrogen and phosphorus
co-doped carbon networks derived from shrimp shells as an efficient oxygen
reduction catalyst for microbial fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources,
446: 227356.
32.
Lai, L.,
Potts, J. R., Zhan, D., Wang, L., Poh, C. K., Tang, C. and Ruoff, R. S. (2012).
Exploration of the active center structure of nitrogen-doped graphene-based
catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Energy and Environmental Science,
5(7): 7936-7942.
33.
Xu, S.
S., Qiu, S. W., Yuan, Z. Y., Ren, T. Z. and Bandosz, T. J. (2019). Nitrogen-containing
activated carbon of improved electrochemical performance derived from cotton
stalks using indirect chemical activation. Journal of Colloid and Interface
Science, 540: 285-294.
34.
Akula,
S. and Sahu, A. K. (2019). Heteroatoms co-doping (N, F) to the porous carbon
derived from spent coffee grounds as an effective catalyst for oxygen reduction
reaction in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Journal of The Electrochemical
Society, 166(2): F93-F101.
35.
Li, D.,
Fan, Y., Yuan, H., Deng, L., Yang, J., Chen, Y. and Luo, B. (2020). Renewable and
metal-free carbon derived from aquatic scindapsus affording meso–microporosity,
large interface, and enriched pyridinic-N for efficient oxygen reduction
reaction catalysis. Energy & Fuels, 34(10): 13089-13095.
36.
Fan, Z.,
Li, J., Zhou, Y., Fu, Q., Yang, W., Zhu, X. and Liao, Q. (2017). A green,
cheap, high-performance carbonaceous catalyst derived from Chlorella
pyrenoidosa for oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. International
Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(45): 27657-27665.
37.
Cao, C.,
Wei, L., Zhai, Q., Wang, G. and Shen, J. (2017). Biomass-derived nitrogen and
boron dual-doped hollow carbon tube as cost-effective and stable synergistic
catalyst for oxygen electroreduction. Electrochimica Acta, 249: 328-336.