Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 3
(2022): 562 - 570
EFFECT OF pH IN THE SYNTHESIS OF GOLD-COPPER
NANOPARTICLES SUPPORTED ON ANODIC ALUMINIUM OXIDE AS CATALYST FOR THE REDUCTION
OF p-NITROPHENOL
(Kesan pH dalam Sintesis Emas-Kuprum (Au-Cu) Partikel Nano
Disokong pada Anodik Aluminium Oksida Sebagai Mangkin bagi Penurunan p-Nitrofenol)
Norizwan Nordin1, Hanani Yazid1,2,
Nor Azira Irma Muhammad2 and Abdul Mutalib Md Jani3*
1Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA, 40450 Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
2Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA, Perlis Branch, Arau Campus, 02600 Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
3Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA, Perak Branch, Tapah Campus, 35400 Tapah Road, Perak, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: abdmutalib@uitm.edu.my
Received: 9 December 2021; Accepted: 6 March 2022; Published: 27 June 2022
Abstract
Gold–copper (Au–Cu)
bimetallic catalysts were prepared through chemical reduction with Cu and Au
precursors at the pH of 3, 5, 7 and 9 and hexadecylamine as the capping agent
to produce Au–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles (Au–Cu NPs). The colloidal Au–Cu NPs
were then grafted onto an anodic aluminium oxide (AAO) support through spin coating.
The AAO support was fabricated via a two-step anodization method at 80 V by
using oxalic acid as the electrolyte. The Au–Cu/AAO catalysts were
characterized through field emission scanning electron microscopy–energy
dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and inductive
coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy. The catalytic activities of the
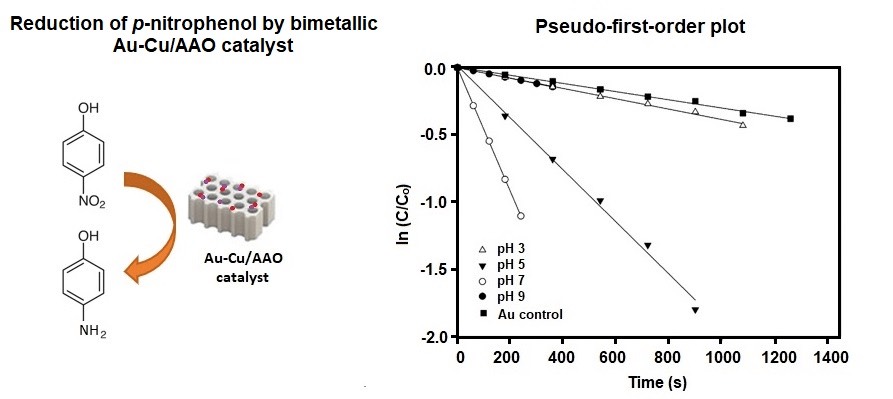
Au–Cu bimetallic catalysts in the reduction of p-nitrophenol (p-NP) were evaluated. Results showed
that the rate constant (k) varied in accordance with the pH of the Au
precursor. The highest k value of 4.6 × 10−3 s−1
was obtained with the Au–Cu catalyst prepared at pH 7. The better performance
of the investigated bimetallic catalyst than that of the monometallic Au and Cu
catalysts demonstrated the promotional role of the second metal in the
reduction of p-NP.
Keywords: Au–Cu NPs, pH, anodic
aluminium oxide
Abstrak
Pemangkin dwilogam Au-Cu dengan prekursor Au pH 3, 5, 7 dan 9
disediakan dengan menggunakan prekursor Cu secara kaedah penurunan kimia dengan
heksadesilamin (HDA) sebagai agen penutup untuk penghasilan nanopartikel Au-Cu (NP
Au-Cu). Dwilogam NP Au-Cu telah
dicantumkan pada sokongan anodik aluminium oxida (AAO) melalui kaedah salutan
putaran. Sokongan AAO telah difabrikasi pada 80 V menggunakan asid oksalik
sebagai elektrolit melalui kaedah anodisasi dua langkah. Pemangkin Au-Cu/AAO
dicirikan oleh mikroskopi elektron pengimbasan pelepasan medan-spektroskopi sinar-X
penyerakan tenaga (FESEM-EDX), spektroskopi inframerah transformasi fourier (FTIR)
dan spektroskopi pelepasan plasma-optik berganding induktif (ICP-OES). Penurunan
p-nitrofenol digunakan untuk menilai aktiviti pemangkin bimetal Au-Cu.
Keputusan menunjukkan bahawa pemalar kadar, (k) adalah berbeza bergantung
kepada pH prekursor. Nilai k tertinggi iaitu 4.6 x 10-3
s-1 telah diperolehi
daripada pemangkin Au-Cu yang disediakan pada pH 7. Daripada kajian ini,
pemangkin dwilogam menunjukkan prestasi yang lebih baik berbanding pemangkin Au
dan Cu logam mono, menunjukkan peranan promosi logam kedua ke arah penurunan p-nitrophenol.
Kata kunci: NP Au-Cu, pH, anodik aluminium oksida
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Ahmad Zulkifli, F. W.,
Yazid, H. and Jani, A. M. M. (2021). Immobilization of carbon nanotubes decorated
gold nanoparticles on anodized aluminium oxide (Au-CNTs-AAO) membrane for
enhanced catalytic performance. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 264:
124445.
2.
Behera, M., Tiwari, N.,
Basu, A., Rekha Mishra, S., Banerjee, S., Chakrabortty, S. and Tripathy, S. K.
(2021). Maghemite/ZnO nanocomposites: A highly efficient, reusable and
non-noble metal catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Advanced Powder
Technology, 32(8): 2905-2915.
3.
He, R., Wang, Y.-C.,
Wang, X., Wang, Z., Liu, G., Zhou, W., Wen, L., Li, Q., Wang, X., Chen, X.,
Zeng, J. and Hou, J. G. (2014). Facile synthesis of pentacle gold–copper alloy
nanocrystals and their plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nature Communications,
5: 1-10.
4.
Heiligtag, F. J. and Niederberger,
M. (2013). The fascinating world of nanoparticle research. Materials Today,
16: 262-271.
5.
Odenbrand, C. U. I.,
Blanco, J., Avila, P. and Knapp, C. (1999). Lean NOx reduction in real diesel
exhaust with copper and platinum titania based monolithic catalysts. Applied
Catalysis B: Environmental, 23: 37-44.
6.
Yazid, H., Adnan, R.,
Farrukh, M. A. and Hamid, S. A. (2011). Synthesis of Au/Al2O3 nanocatalyst
and its application in the reduction of p-Nitrophenol. Journal of the
Chinese Chemical Society, 58(5): 593-601.
7.
Rout, L., Kumar, A.,
Dhaka, R. S., Reddy, G. N., Giri, S. and Dash, P. (2017). Bimetallic Au-Cu
alloy nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide support: Synthesis, catalytic
activity and investigation of synergistic effect by DFT analysis. Applied
Catalysis A: General, 538: 107-122.
8.
Sobczak, I. and Wolski,
Ł. (2015). Au–Cu on Nb2O5 and Nb/MCF supports –
Surface properties and catalytic activity in glycerol and methanol oxidation. Catalysis
Today, 254: 72-82.
9.
Sharma, G., Kumar, A.,
Sharma, S., Naushad, M., Prakash Dwivedi, R., Al Othman, Z. A. and Mola, G. T.
(2017). Novel development of nanoparticles to bimetallic nanoparticles and their
composites: A review. Journal of King Saud University-Science. 31(2): 257-269.
10. Zeng,
S., Yong, K. T., Roy, I., Dinh, X. Q., Yu, X. and Luan, F. (2011). A review on
functionalized gold nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Plasmonics,
6(3): 491-506.
11. Rocha
Rocha, M. Cortez Valadez, A. R. Hernandez Martinez, R. Gamez Cor-rales, R. A.
Alvarez, R. Brito Hurtado, M. and Flores Acosta, (2019). Green synthesis of
Ag-Cu nanoalloys using opuntia ficus-indica, Journal of Electronic Material,
46: 802-807.
12.
Kumar, V., Singh, D. K.,
Mohan, S., Bano, D., Gundampati, R. K. and Hasan, S. H. (2017). Green synthesis
of silver nanoparticle for the selective and sensitive colorimetric detection
of mercury (II) ion. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology,
168: 67-77.
13. Chen,
H. J., Shao, L., Li, Q. and Wang, J. F. (2013). Gold nanorods and their
plasmonic properties, Chemical Society Reviews, 42: 2679-2724.
14. Brust,
M. and Kiely, C. J. (2002). Some recent advances in nanostructure preparation
from gold and silver particles: a short topical review, Colloids Surf. A,
Physicochemical and Engineering Aspect 202
175-186.
15.
Seo, M. H., Choi, S. M.,
Seo, J. K., Noh, S. H., Kim, W. B., & Han, B. (2013). The
graphene-supported palladium and palladium–yttrium nanoparticles for the oxygen
reduction and ethanol oxidation reactions: Experimental measurement and
computational validation. Applied Catalysis B, Environmental, 129: 163-171.
16.
Habiballah, A. S., Jani,
A. M. M., Mahmud, A. H., Osman, N. and Radiman, S. (2016). Facile synthesis of
Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ (BSCF) perovskite nanowires by templating from
nanoporous anodic aluminium oxide membranes. Materials Chemistry and Physics,
177: 371-378.
17.
Chung, C. K., Tsai, C.
H., Hsu, C. R., Kuo, E. H., Chen, Y. and Chung, I. C. (2017). Impurity and
temperature enhanced growth behaviour of anodic aluminium oxide from AA5052
Al-Mg alloy using hybrid pulse anodization at room temperature. Corrosion
Science, 125: 40-47.
18.
Nordin, N., Noor, N. M.,
Wahab, N. A. A., Yazid, H. and Jani, A. M. (2020). Preparation of bimetallic
catalyst: gold-copper (Au-Cu) nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of
p-nitrophenol. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,
957(1): 012036.