Graphical Abstract
References
Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 202 - 214
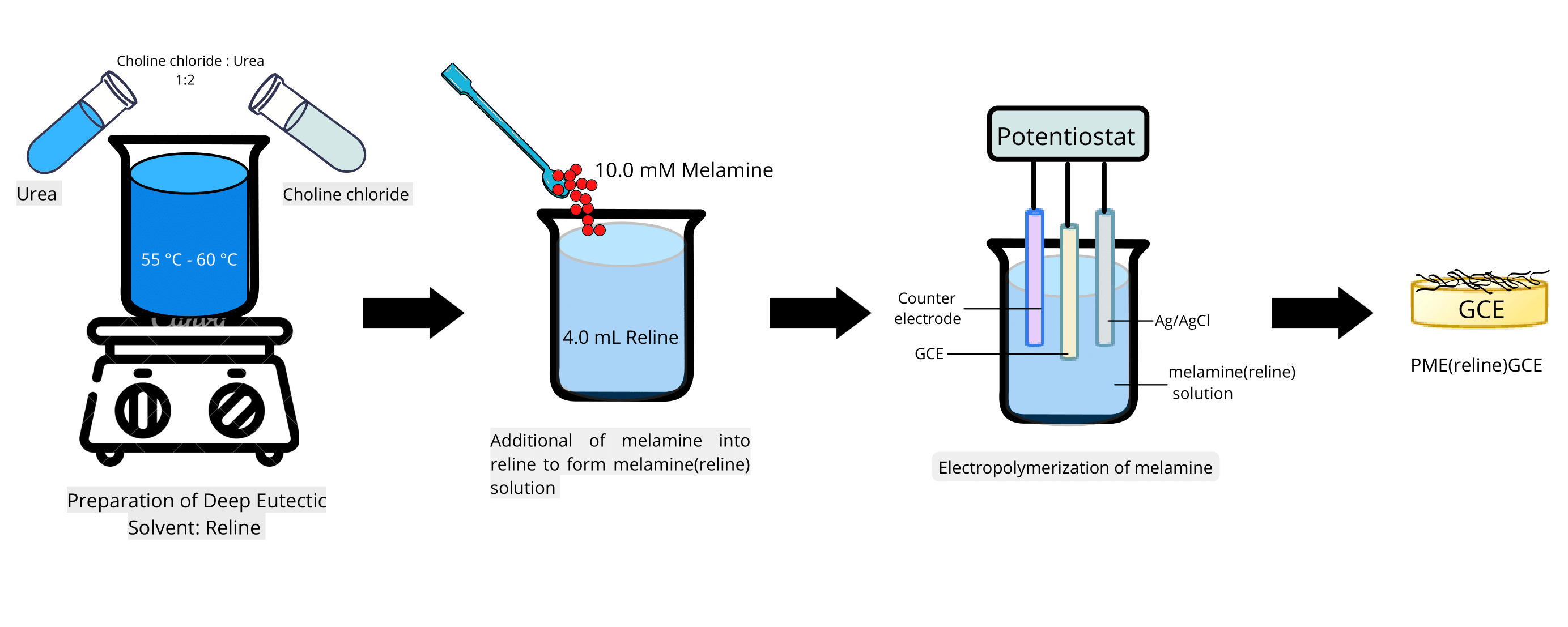
OPTIMIZATION PARAMETERS FOR
ELECTROPOLYMERIZATION OF MELAMINE IN DEEP EUTECTIC SOLVENT
(Pengoptimuman Parameter
Elektropempolimeran Melamin Dalam Pelarut Eutektik Dalam)
Yeet Hoong Chang1, Pei Meng Woi1,2*,
Yatimah Alias1,2
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science
2University Malaya Centre for Ionic Liquids (UMCiL)
University
of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: pmwoi@um.edu.my
Received: 15 September 2021;
Accepted: 10 December 2021; Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
Polymelamine is a new class of polymer that
possess electrocatalytic behavior in dopamine (DA) detection. Our previous
studies have successfully replaced the
conventional acidic electrolyte to deep eutectic solvent (DES) has open the opportunity for a greener
solvent in used. Herein we report the optimization process of melamine
electropolymerize in DES- reline. Various electrochemical techniques have been
employed to studies the ideal parameters. The optimum potential window, scan rate, and number of scan cycles were recorded as
-0.20 V – 1.60 V, 50 mV s-1 and
five scan cycles, respectively. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was employed in the
electropolymerization of melamine to optimize the redox behavior of
polymelamine film on electrode surface. The growing of polymer film which
indicated by the increased of reduction current can be well-controlled by the
slow scan rate and optimum scan cycles which leads to strong adhesion and
uniform morphology. Amperometry sensing on DA was performed to study and
compare the sensitivity and limit of detection for the polymers synthesized in
varied parameters. A brief discussion on the principal polymerization factors
that would affecting the electrocatalytic behavior of melamine is included.
Keywords: deep
eutectic solvent, electropolymerization, melamine, optimization
Abstrak
Polimelamin
adalah kelas polimer baharu yang mempunyai tingkah laku elektromangkin dalam pengesanan dopamin (DA). Kajian yang
dilaporkan terdahulu menujukkan kerjayaan penggantian elektrolit berasid
konvensional kepada pelarut eutektik (DES). Kejayaan ini membuka
peluang untuk pelarut yang lebih mesra alam digunakan. Dengan ini,
kami melaporkan proses pengoptimum elektropolimerisasi melamin dalam DES-relin.
Pelbagai teknik elektrokimia telah digunakan untuk mengkaji parameter yang
terbaik. Julat keupayaan, kadar
imbasan dan bilangan kitaran imbasan yang terbaik dicatat pada -0.20 V – 1.60
V, 50 mVs-1 dan lima kitaran imbasan. Siklik voltametri (CV) telah
digunakan dalam elektropolimerisasi melamin untuk mengoptimumkan tingkah laku elektropemangkinan lapisan
polimelamin pada permukaan elektrod. Pertumbuhan lapisan polimer yang
ditunjukkan dalam penainkkan arus penurunan boleh dikawal baik dengan kadar
imbasan yang perlahan dan kitaran imbasan optimum untuk mencapai lekatan yang
kuat dan morfologi yang seragam. Penderiaan amperometri pada DA telah
dijalankan untuk mengkaji dan membandingkan kepekaan dan had pengesanan rendah untuk polimer
yang disintesis dalam parameter yang berbeza-beza. Perbincangan ringkas tentang
faktor-faktor elektropolimerisasi yang mempengaruhi tingkah laku elektromangkin melamin telah
disertakan.
Kata
Kunci: pelarut eutektik dalam,
elektropempolimeran, melamin, pengoptimuman
Graphical Abstract

References
1. Gupta, P. and Goyal, R. N. (2014). Polymelamine
modified edge plane pyrolytic graphite sensor for the electrochemical assay of
serotonin. Talanta, 120: 17-22.
2. Kesavan, S., Kumar, D. R., Lee, Y. R. and Shim, J. J.
(2017). Determination of tetracycline in the presence of major interference in
human urine samples using polymelamine/electrochemically reduced graphene oxide
modified electrode. Sensors and Actuators
B: Chem, 241: 455-465.
3. Khosropour, H., Rezaei, B., Alinajafi, H. A. and
Ensafi, A. A. (2021). Electrochemical sensor based on glassy carbon electrode
modified by polymelamine formaldehyde/graphene oxide nanocomposite for
ultrasensitive detection of oxycodone. Microchimica
Acta, 188(1): 1.
4. Farida, A. N., Fitriany, E., Baktir, A., Kurniawan, F.
and Harsini, M. (2019). Voltammetric study of ascorbic acid using
polymelamine/gold nanoparticle modified carbon paste electrode. IOP Conference Series: Earth
Environmental Science, 217: 012004.
5. Qin, H., Hu, X., Wang, J., Cheng, H., Chen, L. and Qi,
Z. (2020). Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties
and applications. Green Energy and
Environment, 5(1): 8-21.
6. Zante, G. and Boltoeva, M. (2020). Review on
hydrometallurgical recovery of metals with deep eutectic solvents. Sustainable Chemistry, 1(3): 238-255.
7. Cen, P., Spahiu, K., Tyumentsev, M. S. and Foreman, M.
R. S. J. (2020). Metal extraction from a deep eutectic solvent, an insight into
activities. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22(19): 11012-11024.
8. Paiva, A., Craveiro, R., Aroso, I., Martins, M., Reis,
R. L. and Duarte, A. R. C. (2014). Natural deep eutectic solvents – solvents
for the 21st century. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,
2(5): 1063- 1071.
9. Mendonça, P. V., Lima, M. S., Guliashvili, T., Serra,
A. C. and Coelho, J. F. (2017). Deep eutectic solvents (DES): Excellent green
solvents for rapid SARA ATRP of biorelevant hydrophilic monomers at ambient
temperature. Polymer, 132: 114-121.
10. Sánchez-Leija, R. J., Torres-Lubián, J. R.,
Reséndiz-Rubio, A., Luna-Bárcenas, G. and Mota-Morales, J. D. (2016).
Enzyme-mediated free radical polymerization of acrylamide in deep eutectic
solvents. RSC Advances, 6(16): 13072-13079.
11. Fernandes, P. M. V., Campiña, J. M., Pereira, N. M.,
Pereira, C. M. and Silva, F. (2012). Biodegradable deep-eutectic mixtures as
electrolytes for the electrochemical synthesis of conducting polymers. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 42(12): 997-1003.
12. Mąka, H., Spychaj, T. and Adamus, J. (2015).
Lewis acid type deep eutectic solvents as catalysts for epoxy resin
crosslinking. RSC Advances, 5(101): 82813-82821.
13. Chang, Y. H., Woi, P. M. and Alias, Y. B. (2021).
Electrochemical characterization of melamine electropolymerized in deep
eutectic solvents for selective detection of dopamine. Electrocatalysis, 12(3):
238-250.
14. Chen, S., Liu, S., Wen, A., Zhang, J., Nie, H., Chen,
J., Zeng, R., Long, Y., Jin, Y. and Mai, R. (2018). New insight into
electropolymerization of melamine. I: Chloride promoted growth of polymelamine
in different pH medium. Electrochimica
Acta, 271:
312-318.
15. Migliorati, V., Sessa, F. and D’Angelo, P. (2019).
Deep eutectic solvents: A structural point of view on the role of the cation. Chemical Physics Letters, 2:
100001.
16. Li, R., Lin, C. W., Shao, Y., Chang, C., Yao, F. K.,
Kowal, M., Wang, H., Yeung, M., Huang, S. C. and Kaner, R. (2016).
Characterization of aniline tetramer by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry upon
oxidative and reductive cycling. Polymers,
8(11): 401.
17. Gabrielli, C., Huet, F. and Keddam, M. (1993).
Fluctuations in electrochemical systems. I. General theory on diffusion limited
electrochemical reactions. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 99: 7232.