Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 191 - 201
A SHORT REVIEW ON THE INFLUENCE OF THE
PREPARATION METHOD ON THE PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF Mg/Al HYDROTALCITE FOR
GLUCOSE ISOMERIZATION
(Ulasan
Ringkas Mengenai Pengaruh Kaedah Penyediaan Terhadap Sifat-Sifat Fizikokimia
Mg/Al Hidrotalsit untuk Pengisomerisasi Glukosa)
Munirah
Zulkifli1,2, Noor Hidayah Pungot1,2*, Nazrizawati Ahmad
Tajuddin1, Mohd Fadhlizil Fasihi Mohd Aluwi3, Nor
Saliyana Jumali4, Zurina Shaameri1,2
1School of Chemistry
and Environment, Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti Teknologi MARA, 40450 Shah
Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
2Organic Synthesis
Laboratory, Institute of Science,
Universiti Teknologi MARA Puncak Alam
Campus, 42300 Bandar Puncak Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
3Faculty of Industrial
Sciences and Technology,
Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Lebuhraya
Tun Razak, 26300 Gambang, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia
4 Department Chemistry,
Kulliyyah of Science,
International Islam University Malaysia,
25200 Bandar Indera Mahkota, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: noorhidayah977@uitm.edu.my
Received: 15 September 2021; Accepted: 3 February 2022;
Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
Hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(OH)16CO34H2O)
is a naturally occurring anionic clay with a layered crystal structure.
Hydrotalcites is classified as heterogeneous catalysts that exhibit an
excellent separation post-reaction. Furthermore, commercial hydrotalcites are
environmentally friendly. Organically synthesised hydrotalcites have attracted
numerous researchers. The compounds are crucial solid base materials for
several organic reactions, such as the Aldol condensation, Knoevenagel,
Claisen-Schmidt, and Michael addition reactions. The present review covers the
synthesis of magnesium aluminide (MgAl) hydrotalcites with varying magnesium to
aluminium (Mg/Al) molar ratios employed to prepare the catalyst. Additionally,
the characterisation of MgAl hydrotalcites with X-ray diffraction (XRD),
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are
highlighted. The instruments were utilised to identify the physicochemical
properties of the catalyst, including crystallinity, surface area, and
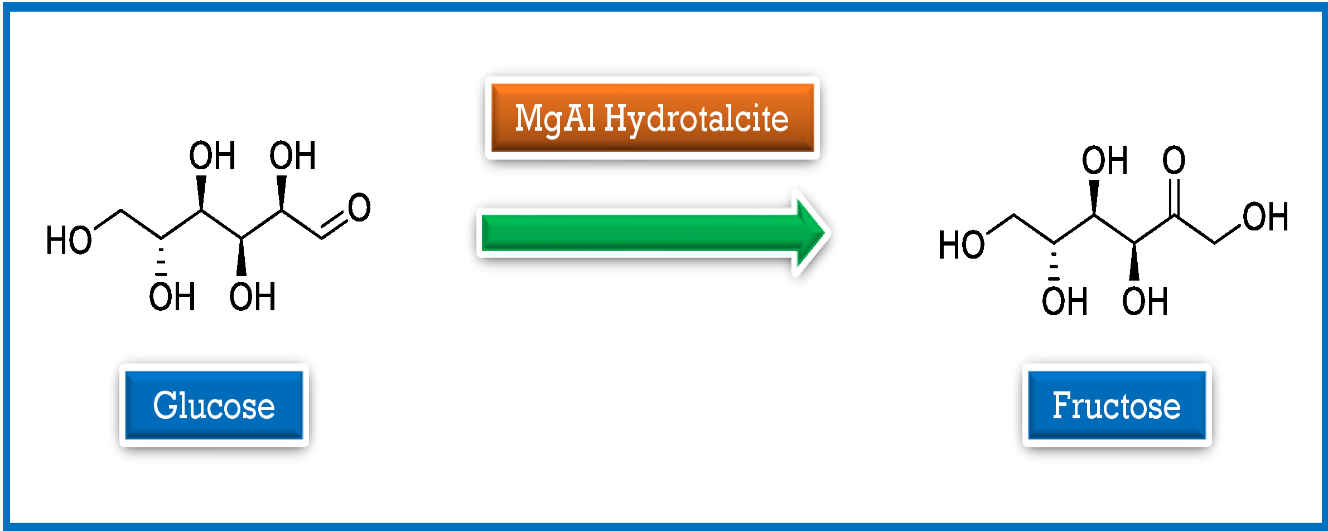
morphology. The catalytic activity of MgAl hydrotalcite was explored in the
isomerisation of glucose into fructose as a model reaction for the catalytic
performance.
Keywords: MgAl
hydrotalcite, Mg/Al molar ratio, physicochemical properties, catalytic activity
Abstrak
Hidrotalsit
(Mg6Al2(OH)16CO34H2O) ialah
tanah liat anionik yang wujud secara semula jadi dengan struktur kristal
berlapis. Hidrotalsit dikelaskan sebagai pemangkin heterogen yang mempamerkan
pemisahan selepas tindak balas yang sangat baik. Tambahan pula, hidrotalsit
komersial adalah mesra alam. Hidrotalsit yang disintesis secara organik telah
menarik ramai penyelidik. Sebatian tersebut merupakan bahan asas pepejal yang
penting untuk beberapa tindak balas organik, seperti tindak balas kondensasi
Aldol, Knoevenagel, Claisen-Schmidt, dan penambahan Michael. Ulasan semula ini
meliputi sintesis magnesium aluminida (MgAl) hidrotalsit dengan pelbagai nisbah
molar magnesium kepada aluminium (Mg/Al) digunakan untuk menyediakan mangkin.
Selain itu, pencirian hidrotalsit MgAl dengan pembelauan sinar-X (XRD),
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), dan mikroskop elektron pengimbasan (SEM)
diserlahkan. Instrumen ini telah digunakan untuk mengenal pasti sifat
fizikokimia mangkin, termasuk kehabluran, luas permukaan, dan morfologi.
Aktiviti pemangkin hidrotalsit MgAl telah diterokai dalam pengisomeran glukosa
kepada fruktosa sebagai tindak balas model untuk prestasi pemangkin.
Kata kunci: MgAl hidrotalsit, nisbah
molar Mg/Al, sifat-sifat fizikokimia, aktiviti pemangkin
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Dębek, R., Motak, M., Grzybek, T., Galvez, M.
E. and Da Costa, P. (2017). A short review on the catalytic activity of
hydrotalcite-derived materials for dry reforming of methane. Catalysts,
7(1): 32.
2.
Gomes, J. F. P., Puna, J. F. B., Gonçalves, L. M.
and Bordado, J. C. M. (2011). Study on the use of MgAl hydrotalcites as solid
heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production. Energy, 36(12): 6770-6778.
3.
Baskaran, T., Christopher, J. and Sakthivel, A.
(2015). Progress on layered hydrotalcite (HT) materials as potential support
and catalytic materials. RSC Advances, 5: 98853-98875.
4.
Tsujimura, A., Uchida, M. and Okuwaki, A. (2007).
Synthesis and sulfate ion-exchange properties of a hydrotalcite-like compound
intercalated by chloride ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143(1–2): 582-586.
5.
Sikander, U., Sufian, S. and Salam, M. A. (2017). A review of
hydrotalcite based catalysts for hydrogen production systems. International
Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42: 19851-19868.
6.
Delidovich, I. and Palkovits, R. (2015).
Structure-performance correlations of Mg-Al hydrotalcite catalysts for the
isomerization of glucose into fructose. Journal of Catalysis, 327: 1-9.
7.
Lee, G., Kang, J. Y., Yan, N., Suh, Y. W. and Jung, J. C. (2016). Simple
preparation method for Mg–Al hydrotalcites as base catalysts. Journal
of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 423: 347-355.
8.
Nur Fazira Edlina, I., Nazrizawati, A. T., Erma
Hafiza, I. A. Z. and Noraini, H. (2020). MgAl mixed oxide derived alkali-free
hydrotalcite for transesterification of waste cooking oil to biodiesel. ASM
Science Journal, 13: 1-7.
9.
Nope, E., Sathicq, G., Martinez, J., Rojas, H.,
Luque, R. and Romanelli, G. (2018). Hydrotalcites in Organic Synthesis:
Multicomponent Reactions. Current Organic Synthesis, 15(8): 1073-1090.
10.
Kikhtyanin, O., Kadlec, D., Velvarská, R. and
Kubička, D. (2018). Using Mg-Al mixed oxide and reconstructed hydrotalcite
as basic catalysts for aldol condensation of furfural and cyclohexanone. ChemCatChem, 10(6): 1464-1475.
11.
Jadhav, A. L. and Yadav, G. D. (2019). Clean
synthesis of benzylidenemalononitrile by Knoevenagel condensation of
benzaldehyde and malononitrile: Effect of combustion fuel on activity and
selectivity of Ti-hydrotalcite and Zn-hydrotalcite catalysts. Journal
of Chemical Sciences, 131(8):
79.
12.
Arias, K. S., Climent, M. J., Corma, A. and
Iborra, S. (2016). Chemicals from biomass: Synthesis of biologically active furanochalcones
by claisen–schmidt condensation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
(HMF) with acetophenones. Topics in Catalysis, 59(13–14): 1257-1265.
13.
Mokhtar, M., Saleh, T. S. and Basahel, S. N.
(2012). Mg-Al hydrotalcites as efficient catalysts for aza-Michael addition
reaction: A green protocol. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 353-354: 122-131.
14.
Park, S., Kwon, D., Kang, J. Y. and Jung, J. C. (2019). Influence of the
preparation method on the catalytic activity of Mg-Al hydrotalcites as solid
base catalysts. Green Energy and Environment, 4(3): 287-292.
15.
Labuschagné, F. J. W. J., Wiid, A., Venter, H. P.,
Gevers, B. R. and Leuteritz, A. (2018). Green synthesis of hydrotalcite from
untreated magnesium oxide and aluminum hydroxide. Green Chemistry
Letters and Reviews, 11: 18-28.
16.
Kang, J. Y., Lee, G., Suh, Y. W. and Jung, J. C. (2017). Effect of Mg/Al
atomic ratio of Mg–Al hydrotalcites on their catalytic properties for the
isomerization of glucose to fructose. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 17(11):
8242-8247.
17.
Yu, S., Kim, E., Park, S., Song, I. K. and Jung,
J. C. (2012). Isomerization of glucose into fructose over Mg-Al hydrotalcite
catalysts. Catalysis Communications, 29: 63-67.
18.
Upare, P. P., Chamas, A., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. C.,
Kwak, S. K., Hwang, Y. K., and Hwang, D. W. (2020). Highly efficient
hydrotalcite/1-butanol catalytic system for the production of the high-yield
fructose crystal from glucose. ACS Catalysis, 10(2): 1388-1396.
19.
Huang, H., Meng, X. G., Yu, W. W., Chen, L. Y. and
Wu, Y. Y. (2021). High selective isomerization of glucose to fructose catalyzed
by amidoximed polyacrylonitrile. ACS Omega, 6(30): 19860-19866.
20.
Yabushita, M., Shibayama, N., Nakajima, K. and
Fukuoka, A. (2019). Selective glucose-to-fructose isomerization in ethanol
catalyzed by hydrotalcites. ACS Catalysis, 9(3): 2101-2109.