Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 215 - 228
PREPARATION AND
ADSORPTION STUDIES OF MOLECULARLY IMPRINTED POLYMER FOR SELECTIVE RECOGNITION
OF TRYPTOPHAN
(Penyediaan dan Kajian Penjerapan Polimer Molekul Tercetak
untuk Pengecaman Selektif Triptofan)
Nur Habibah Safiyah Jusoh1, Faizatul Shimal
Mehamod2*, Noor Fadilah Yusof3, Abd Mutalib Md Jani4, Faiz Bukhari Mohd Suah5, Marinah Mohd Ariffin1,
Nur Asyiqin Zulkefli1
1Faculty of
Science and Marine Environment
2Advanced Nano
Materials (ANoMA) Research Group, Faculty of Science and Marine Environment
Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030 Kuala Nerus,
Terengganu, Malaysia
3School of
Chemical and Energy Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor Bahru,
Malaysia.
4Faculty of
Applied Sciences,
Universiti Teknologi MARA, Perak Branch, Tapah Campus, 35400
Perak, Malaysia
5School of Chemical
Sciences,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden, Pulau Pinang,
Malaysia
*Corresponding author: fshimal@umt.edu.my
Received: 13 September 2021;
Accepted: 18 December 2021;
Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
One of the effective technologies in molecular
recognition is based on the molecular imprinting process. In this work, the
polymers were prepared by bulk polymerization, using methacrylic acid and
ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as the functional monomer and crosslinking agent,
respectively. The polymers were characterized by Fourier transform infrared
spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and surface area and porosity
analyses. Several parameters influencing the adsorption efficiency of
Tryptophan (Tryp) such as adsorbent dosage, contact time, pH of sample solution
as well as selectivity and reproducibility study, have been evaluated. The
Tryptophan-imprinted polymer (Tryp-IP) showed significantly higher removal
efficiency and selective binding capacity towards Tryp compared to
non-imprinted polymer (NIP). The adsorption isotherm demonstrated that the
Tryp-IP followed Langmuir isotherm model, indicating the Tryp-IP owning the
homogenous surface type of adsorbent. In contrast, the NIP fit with the
Redlich-Peterson model, indicating that mechanism adsorption is a mixed type.
The kinetic study revealed that pseudo-second order was the appropriate kinetic
model for Tryp-IP and the adsorption kinetic of NIP appeared to fit with
pseudo-first order.
Keywords: molecularly imprinted polymer, tryptophan,
adsorption study
Abstrak
Salah
satu teknologi yang efektif dalam pengecaman molekul adalah berdasarkan proses
pencetakan molekul. Dalam kajian ini, polimer telah disediakan melalui
pempolimeran pukal, masing-masing menggunakan asid metakrilik dan etilena
glikol dimetakrilat sebagai monomer berfungsi dan agen tautsilang. Polimer
dicirikan oleh spektroskopi inframerah transformasi Fourier, pengimbasan
mikroskop elektron dan analisis luas permukaan dan keliangan. Beberapa
parameter yang mempengaruhi kecekapan penjerapan Triptofan (Tryp) seperti dos
penjerap, masa sentuhan, pH larutan sampel serta kajian selektiviti dan
kebolehulangan telah dinilai. Polimer tercetak-Triptofan (Tryp-IP) menunjukkan
kecekapan penyingkiran dan kapasiti pengikatan yang lebih tinggi terhadap Tryp
berbanding polimer tidak dicetak (NIP). Isoterma penjerapan menunjukkan bahawa
Tryp-IP mematuhi model isoterma Langmuir, ini menunjukkan Tryp-IP memiliki
jenis penjerap permukaan homogen. Sebaliknya, NIP mematuhi model
Redlich-Peterson, menunjukkan mekanisme penjerapan adalah jenis campuran.
Kajian kinetik mendedahkan bahawa tertib pseudo-kedua adalah model kinetik yang
sesuai untuk Tryp-IP dan kinetik penjerapan NIP kelihatan lebih sesuai dengan tertib
pseudo-pertama.
Kata
kunci: polimer tercetak molekul, triptofan, kajian penjerapan
Graphical Abstract
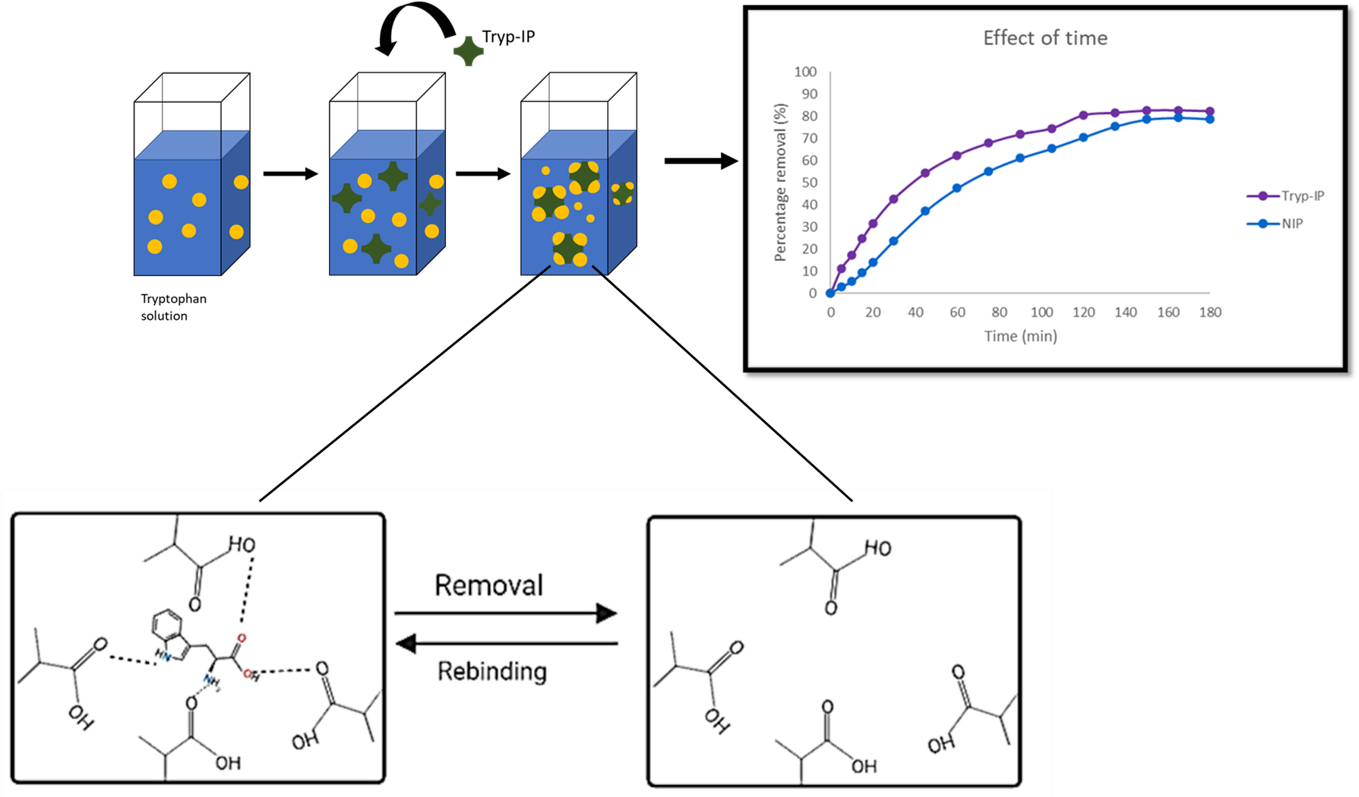
References
1.
Friedman, M. (2018). Analysis, nutrition, and health
benefits of tryptophan. International Journal of Tryptophan Research,
11: 1178646918802282.
2.
Richard,
D. M., Dawes, M. A., Mathias, C. W., Acheson, A., Hill-Kapturczak, N. and
Dougherty, D. M. (2009). L-tryptophan: basic metabolic functions, behavioral
research and therapeutic indications. International Journal of Tryptophan
Research, 23(2): 45-60.
3.
Lindseth,
G., Helland, B. and Caspers, J. (2015). The effects of dietary tryptophan on
affective disorders. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 29(2): 102-107.
4.
Jenkins,
T. A., Nguyen, J. C. D., Polglaze, K. E. and Bertrand, P. P. (2016). Influence
of tryptophan and serotonin on mood and cognition with a possible role of the
gut-brain axis. Nutrients, 8(1): 56.
5.
Sundaresan,
R., Mariyappan, V., Chen, S.-M., Keerthi, M. and Ramachandran, R. (2021).
Electrochemical sensor for detection of tryptophan in the milk sample based on
MnWO4 nanoplates encapsulated RGO nanocomposite. Colloids and
Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 625: 126889.
6.
Capuron,
L., Ravaud, A., Neveu, P. J., Miller, A. H., Maes, M. and Dantzer, R. (2002).
Association between decreased serum tryptophan concentrations and depressive symptoms in cancer patients undergoing cytokine
therapy. Molecular Psychiatry, 7(5): 468-473.
7.
de Jong,
R. A., Nijman, H. W., Boezen, H. M., Volmer, M., Klaske, A., Krijnen, J., van
der Zee, A. G. J., Hollema, H. and Kema, I. P. (2011). Serum tryptophan and
kynurenine concentrations as parameters for indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase
activity in patients with endometrial, ovarian, and vulvar cancer. International
Journal of Gynecologic Cancer, 21(7): 1320-1327.
8.
Onesti,
C. E., Boemer, F., Josse, C., Leduc, S., Bours, V. and Jerusalem, G. (2019).
Tryptophan catabolism increases in breast cancer patients compared to healthy
controls without affecting the cancer outcome or response to chemotherapy. Journal
of Translational Medicine, 17(1): 1-11.
9.
Tian,
Y., Deng, P., Wu, Y., Ding, Z., Li, G., Liu, J. and He, Q. (2019). A simple and
efficient molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the selective
determination of tryptophan. Biomolecules, 9(7): 294.
10.
Jiao,
P., Wei, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, X., Zhang, H. and Yuan, X. (2021). Adsorption
separation of l-tryptophan based on the hyper-cross-linked resin XDA-200. ACS
Omega, 6(3): 2255-2263.
11.
Lee, D.,
Hussain, S., Yeo, J. and Pang, Y. (2021). Adsorption of dipeptide
L-alanyl-L-tryptophan on gold colloidal nanoparticles studied by
surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular
and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 247: 119064.
12.
Belhamdi,
B., Merzougui, Z., Laksaci, H. and Trari, M. (2019). The removal and adsorption
mechanisms of free amino acid l-tryptophan from aqueous solution by
biomass-based activated carbon by H3PO4 activation:
regeneration study. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C,
114: 102791.
13.
Mehamod,
F. S., KuBulat, K., Yusof, N. F. and Othman, N. A. (2015). The development of
molecular imprinting technology for caffeine extraction. International
Journal of Technology, 6(4): 546-554.
14.
Samarth,
N. B., Kamble, V., Mahanwar, P. A., Rane, A. V. and Abitha, V. K. (2015). A
historical perspective and the development of molecular imprinting polymer-A
review. Chemistry International, 4: 202-210.
15.
Mujahid,
A. and Dickert, F. L. (2016). Molecularly Imprinted polymers: principle,
design, and enzyme-like catalysis. Molecularly Imprinted Catalysts:
Principles, Syntheses, and Applications, pp. 79-101.
16.
Zhang,
H., Ye, L. and Mosbach, K. (2006). Non‐covalent molecular imprinting with
emphasis on its application in separation and drug development. Journal of
Molecular Recognition: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 19(4), 248-259.
17.
Yusof,
N. F., Mehamod, F. S., Kadir, M. A. and Suah, F. B. M. (2018). Characteristics
of adsorption isotherm and kinetic study for newly prepared Co2+-imprinted
polymer linkage with dipicolinic acid. IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 440(1): 012005.
18.
Yusof,
N. F., Mehamod, F. S. and Suah, F. B. M. (2018). The effect of RAFT
polymerization on the physical properties of thiamphenicol-imprinted polymer. E3S
Web of Conferences, 67(12): 03050.
19.
Abdul
Hamid, N. S., Naseeruteen, F., Wan Ngah, W. S., Yusof, N. F., Mehamod, F. S.
and Mohd Suah, F. B. (2020). Synthesis of chitin-ionic liquid beads as
potential adsorbents for methylene blue. Malaysian Journal of Chemistry,
22(2): 98-110.
20.
Yusof,
N. F., Mehamod, F. S. and Suah, F. B. M. (2019). Fabrication and binding
characterization of ion imprinted polymers for highly selective Co2+ ions in an
aqueous medium. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(2):
103007.
21.
Ayawei,
N., Ebelegi, A. N. and Wankasi, D. (2017). Modelling and interpretation of
adsorption isotherms. Journal of Chemistry, 2017: 3039817.
22.
Alveroglu,
E., Balouch, A., Khan, S., Mahar, A. M., Jagirani, M. S. and Pato, A. H.
(2021). Evaluation of the performance of a selective magnetite molecularly
imprinted polymer for extraction of quercetin from onion samples. Microchemical
Journal, 162: 105849.
23.
Fareghi,
A. R., Moghadam, P. N., Khalafy, J., Bahram, M. and Moghtader, M. (2017).
Preparation of a new molecularly imprinted polymer based on
self‐crosslinkable cellulose acrylate in aqueous solution: A drug
delivery system for furosemide. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,
134(48): 45581.
24.
Prabakaran,
K., Jandas, P. J., Luo, J., Fu, C. and Wei, Q. (2021). Molecularly imprinted
poly (methacrylic acid) based QCM biosensor for selective determination of
L-tryptophan. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering
Aspects, 611: 125859.
25.
Azodi-Deilami,
S., Abdouss, M. and Seyedi, S. R. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of
molecularly imprinted polymer for controlled release of tramadol. Central
European Journal of Chemistry, 8(3): 687-695.
26.
Wang,
L., Zhi, K., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, L., Yasin, A. and Lin, Q. (2019).
Molecularly imprinted polymers for gossypol via sol?gel, bulk, and surface
layer imprinting?a comparative study. Polymers, 11(4): 602.
27.
Xia, Q.,
Yun, Y., Li, Q., Huang, Z. and Liang, Z. (2017). Preparation and
characterization of monodisperse molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres by
precipitation polymerization for kaempferol. Designed Monomers and Polymers,
20(1): 201-209.
28.
Madikizela,
L. M., Zunngu, S. S., Mlunguza, N. Y., Tavengwa, N. T., Mdluli, P. S. and
Chimuka, L. (2018). Application of molecularly imprinted polymer designed for
the selective extraction of ketoprofen from wastewater. Water SA, 44(3):
406-418.
29.
Hasanah,
A. N., Susanti, I., Marcellino, M., Maranata, G. J., Saputri, F. A. and
Pratiwi, R. (2021). Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction
for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol. Open
Chemistry, 19(1): 604-613.