Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 384 - 398
ADSORPTION OF METHYLENE BLUE
FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS BY ACTIVATED CARBON PREPARED FROM BANANA TRUNK USING
ZINC CHLORIDE ACTIVATION
(Penjerapan Metilena Biru
daripada Larutan Akueus oleh Karbon Teraktif yang Disediakan dari Batang Pisang
secara Pengaktifan Zink Klorida)
Zaidi Ab Ghani1*,
Muhammad Taufiq Hafizuddin R. Azemi1, Mohd Hafiz
Yaacob1, Noor Hafizah Uyup1, Lee Sin Ang1, Nor
Azliza Akbar2
1Faculty of Applied Science,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA Cawangan Perlis, 02600 Arau Perlis, Malaysia.
2School of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA Cawangan Pulau Pinang, 13500 Permatang Pauh, Pulau Pinang,
Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: zaidi433@uitm.edu.my
Received:
10 September 2021; Accepted: 18 December 2021; Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
In
this study, the banana trunk-derived activated carbon (BTAC) used was prepared
via zinc chloride (ZnCl2) activation. BTAC is used as an adsorbent
to remove methylene blue (MB) from the aqueous solutions. The BET surface area,
total pore volume and pore diameters of the BTAC were 1329.5 m2/g,
1.16 cm3/g and 3.8 nm, respectively. The effect of adsorbent dosage,
initial concentration, contact time and solution pH were studied in batch
experiments. The experimental data were analyzed by Langmuir, Freundlich,
Temkin, and Dubinin-Radushkevich (D-R) adsorption isotherms model. Data
analysis study via RMSE and
Keywords: adsorption, activated carbon, methylene blue,
isotherm, kinetic
Abstrak
Dalam kajian ini, karbon teraktif
daripada batang pisang (BTAC) yang digunakan telah disediakan melalui
pengaktifan zink klorida (ZnCl2). BTAC telah digunakan sebagai penjerap
untuk menyingkirkan metilena biru (MB) daripada larutan akueus. Keluasan
permukakaan BET, jumlah isipadu dan diameter liang pori bagi BTAC masing-masing
adalah 1329.5 m2/g, 1.16 cm3/g dan 3.8 nm. Kesan dos
penjerap, kepekatan permulaan, masa kontak dan pH larutan dilakukan secara
eksperimen kelompok. Data ekperimen telah dianalisa menggunakan model Langmuir,
Freundlich, Temkin dan Dubinin–Radushkevich. Analisa data kajian melalui RMSE
dan
Kata kunci: penjerapan, karbon teraktif,
metilena biru, isoterma, kinetik
Graphical Abstract
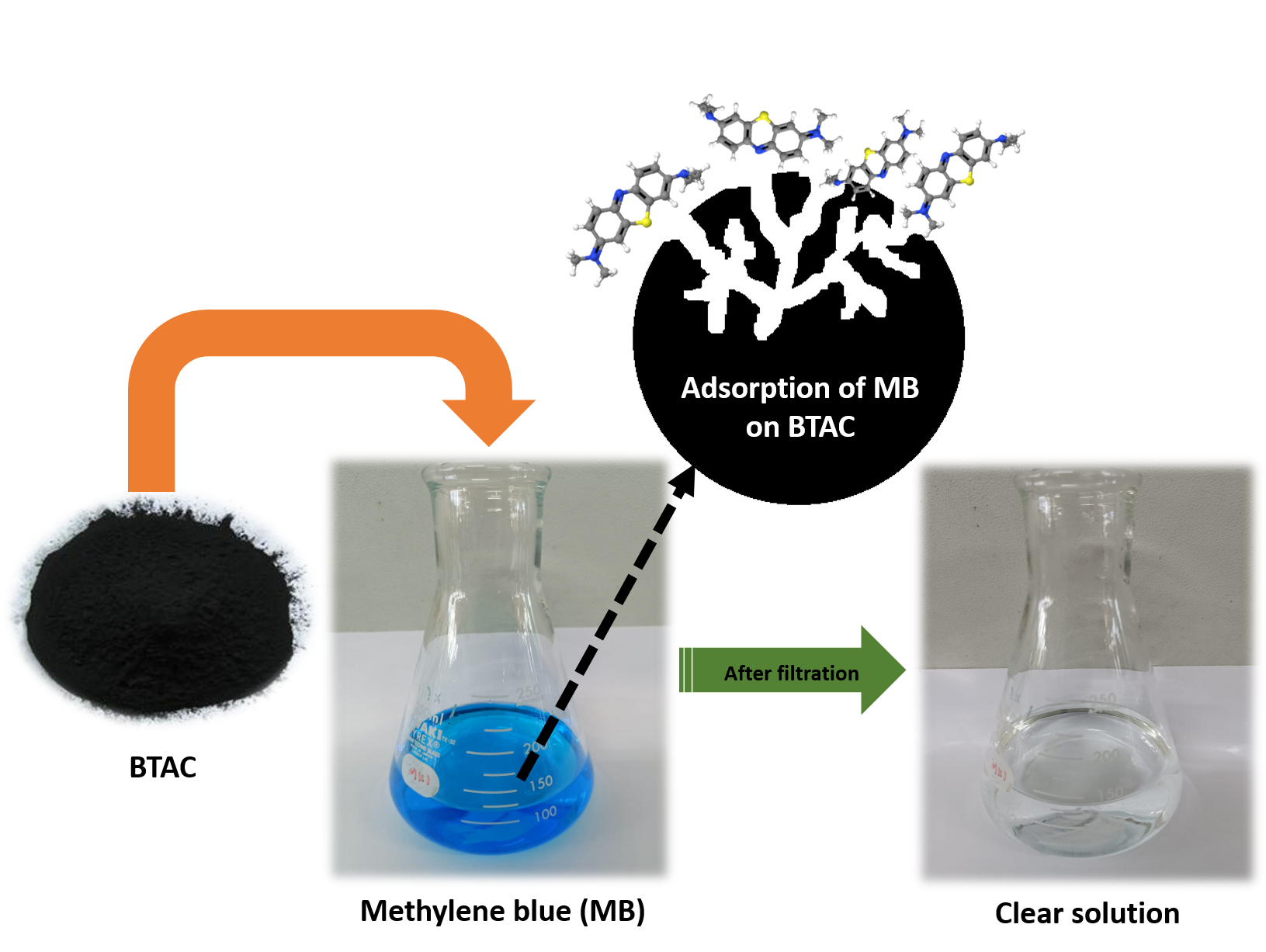
References
1.
Amran, F. and Zaini, M.
A. A. (2021). Sodium hydroxide-activated Casuarina empty fruit: Isotherm,
kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue and congo red adsorption. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 23:
101727.
2.
Misran, E., Bani, O., Situmeang, E. M. and Purba,
A. S. (2022). Banana stem based activated carbon as a low-cost adsorbent for
methylene blue removal: Isotherm, kinetics, and reusability. Alexandria
Engineering Journal, 61(3): 1946-1955.
3.
Wu, J. and Upreti, S. R. (2015). Continuous ozonation of methylene blue
in water. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 8: 142-150.
4.
Hoang, N. T. T., Tran, A. T. K., Hoang, M. H., Nguyen, T. T. H. and Bui,
X. T. (2021). Synergistic effect of TiO2/chitosan/glycerol
photocatalyst on color and COD removal from a dyeing and textile secondary
effluent. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 21: 101255.
5.
Singh, J. and Dhaliwal, A. S. (2022). Electrochemical and photocatalytic
degradation of methylene blue by using rGO/AgNWs nanocomposite synthesized by
electroplating on stainless steel. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of
Solids, 160: 110358.
6.
Sahinkaya, E., Sahin, A., Yurtsever, A. and Kitis, M. (2018).
Concentrate minimization and water recovery enhancement using pellet
precipitator in a reverse osmosis process treating textile wastewater. Journal
of Environmental Management, 222: 420-427.
7.
Dotto, J., Fagundes-Klen, M. R., Veit, M. T., Palacio, S. M. and Bergamasco,
R. (2019). Performance of different coagulants in the coagulation/flocculation
process of textile wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208:
656-665.
8.
Gnanasekaran, G., Sudhakaran, M. S. P., Kulmatova, D., Han, J.,
Arthanareeswaran, G., Jwa, E. and Mok, Y. S. (2021). Efficient removal of
anionic, cationic textile dyes and salt mixture using a novel CS/MIL-100 (Fe)
based nanofiltration membrane. Chemosphere, 284: 131244.
9.
Sinha, A. K., Sasmal, A. K., Pal, A., Pal, D. and Pal, T. (2021). Ammonium
phosphomolybdate [(NH4)3PMo12O40]
an inorganic ion exchanger for environmental application for purification of
dye contaminant wastewater. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology
A: Chemistry, 418: 113427.
10.
Muniyandi, M. and Govindaraj, P. (2021). Potential removal of Methylene
Blue dye from synthetic textile effluent using activated carbon derived from
Palmyra (Palm) shell. Materials Today: Proceedings, 47: 299-311.
11.
De Gisi, S., Lofrano, G., Grassi, M. and Notarnicola, M. (2016). Characteristics
and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: a
review. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 9: 10-40.
12.
Alver, E., Metin, A. Ü. and Brouers, F. (2020). Methylene blue
adsorption on magnetic alginate/rice husk bio-composite. International
Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 154: 104-113.
13.
Rohaizad, A., Shahabuddin, S., Shahid, M. M., Rashid, N. M., Hir, Z. A.
M., Ramly, M. M., ... and Aspanut, Z. (2020). Green synthesis of silver
nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus dried bark extract deposited on
graphene oxide for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye. Journal
of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(4): 103955.
14.
Arabpour, A., Dan, S. and Hashemipour, H. (2021). Preparation and
optimization of novel graphene oxide and adsorption isotherm study of methylene
blue. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 14(3): 103003.
15.
Gemici, B. T., Ozel, H. U. and Ozel, H. B. (2021). Removal of methylene
blue onto forest wastes: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic
analysis. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 22: 101501.
16.
Li, W., Xie, Z., Xue, S., Ye, H., Liu, M., Shi, W. and Liu, Y. (2021).
Studies on the adsorption of dyes, Methylene blue, Safranin T, and Malachite
green onto Polystyrene foam. Separation and Purification Technology, 276:
119435.
17.
Meili, L., Lins, P. V. S., Costa, M. T., Almeida, R. L., Abud, A. K. S.,
Soletti, J. I., ... and Erto, A. (2019). Adsorption of methylene blue on
agroindustrial wastes: experimental investigation and phenomenological
modelling. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 141: 60-71.
18.
Shamsabadi, A. S., Bazarganipour, M. and Tavanai, H. (2021). An
investigation on the pore characteristics of dates stone based microwave
activated carbon nanostructures. Diamond and Related Materials, 120:
108662.
19.
Xue, H., Wang, X., Xu, Q., Dhaouadi, F., Sellaoui, L., Seliem, M. K.,
... and Li, Q. (2022). Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution on
activated carbons and composite prepared from an agricultural waste biomass: A
comparative study by experimental and advanced modeling analysis. Chemical
Engineering Journal, 430: 132801.
20.
Khairiah, K., Frida, E., Sebayang, K., Sinuhaji, P. and Humaidi, S.
(2021). Data on characterization, model, and adsorption rate of banana peel
activated carbon (Musa Acuminata) for adsorbents of various heavy metals (Mn,
Pb, Zn, Fe). Data in Brief, 39: 107611.
21.
Salem, S., Teimouri, Z. and Salem, A. (2020). Fabrication of magnetic
activated carbon by carbothermal functionalization of agriculture waste via
microwave-assisted technique for cationic dye adsorption. Advanced
Powder Technology, 31(10): 4301-4309.
22.
Mariana, M., Mistar, E. M., Alfatah, T. and Supardan, M. D. (2021).
High-porous activated carbon derived from Myristica fragrans shell using
one-step KOH activation for methylene blue adsorption. Bioresource
Technology Reports, 16: 100845.
23.
Lewoyehu, M. (2021).
Comprehensive review on synthesis and application of activated carbon from
agricultural residues for the remediation of venomous pollutants in wastewater.
Journal of Analytical and Applied
Pyrolysis, 159: 105279.
24.
Ab Ghani, Z., Yusoff, M. S., Zaman, N. Q., Zamri, M. F. M. A. and Andas,
J. (2017). Optimization of preparation conditions for activated carbon from
banana pseudo-stem using response surface methodology on removal of color and
COD from landfill leachate. Waste Management, 62: 177-187.
25.
Olu-Owolabi, B. I., Diagboya, P. N. and Ebaddan, W. C. (2012). Mechanism
of Pb2+ removal from aqueous solution using a nonliving moss
biomass. Chemical Engineering Journal, 195: 270-275.
26.
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Tang, J., Tang, J. and Li, X. (2017).
Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived
biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. Journal
of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(1): 601-611.
27.
Saif Ur Rehman, M., Kim, I., Rashid, N., Adeel Umer, M., Sajid, M. and Han,
J. I. (2016). Adsorption of brilliant green dye on biochar prepared from
lignocellulosic bioethanol plant waste. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 44(1):
55-62.
28.
Manna, S., Roy, D., Saha, P., Gopakumar, D. and Thomas, S. (2017). Rapid
methylene blue adsorption using modified lignocellulosic materials. Process
Safety and Environmental Protection, 107, 346-356.
29.
Benhouria, A., Islam, M. A., Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H., Boutahala, M. and Hameed,
B. H. (2015). Calcium alginate–bentonite–activated carbon composite beads as
highly effective adsorbent for methylene blue. Chemical Engineering
Journal, 270: 621-630.
30.
Pathania, D., Sharma, S. and Singh, P. (2017). Removal of methylene blue
by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arabian
Journal of Chemistry, 10: S1445-S1451.
31.
Li, Z., Wang, G., Zhai, K., He, C., Li, Q. and Guo, P. (2018). Methylene
blue adsorption from aqueous solution by loofah sponge-based porous
carbons. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering
Aspects, 538: 28-35.
32.
Maneerung, T., Liew, J., Dai, Y., Kawi, S., Chong, C. and Wang, C. H.
(2016). Activated carbon derived from carbon residue from biomass gasification
and its application for dye adsorption: kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic
studies. Bioresource technology, 200: 350-359.
33.
Jawad, A. H., Abdulhameed, A. S., Bahrudin, N. N., Hum, N. N. M. F., Surip,
S. N., Syed-Hassan, S. S. A., .. and Sabar, S. (2021). Microporous activated
carbon developed from KOH activated biomass waste: surface mechanistic study of
methylene blue dye adsorption. Water Science and Technology, 84(8):
1858-1872.
34.
Hassan, A. F. and Elhadidy, H. (2017). Production of activated carbons
from waste carpets and its application in methylene blue adsorption: Kinetic
and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical
Engineering, 5(1): 955-963.
35.
Miraboutalebi, S. M., Nikouzad, S. K., Peydayesh, M., Allahgholi, N.,
Vafajoo, L. and McKay, G. (2017). Methylene blue adsorption via maize silk
powder: Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic studies and residual error
analysis. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 106:
191-202.
36.
Banerjee, S. and Chattopadhyaya, M. C. (2017). Adsorption
characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous
solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arabian Journal of
Chemistry, 10: S1629-S1638.
37.
Ezechi, E. H., bin Mohamed Kutty, S. R., Malakahmad, A. and Isa, M. H.
(2015). Characterization and optimization of effluent dye removal using a new
low cost adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic study. Process
Safety and Environmental Protection, 98: 16-32.
38.
Abbas, M. and Trari, M. (2015). Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic
study on the removal of Congo Red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto
apricot stone. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 98:
424-436.
39.
Nnadozie, E. C. and Ajibade, P. A. (2020). Adsorption, kinetic and
mechanistic studies of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) ions using APTES functionalized
magnetic biochar. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 309:
110573.
40.
Ahmad, M. A., Puad, N. A. A. and Bello, O. S. (2014). Kinetic, equilibrium
and thermodynamic studies of synthetic dye removal using pomegranate peel
activated carbon prepared by microwave-induced KOH activation. Water
Resources and industry, 6: 18-35.
41.
Zhang, Z., Xu, L., Liu, Y., Feng, R., Zou, T., Zhang, Y., ... and Zhou,
P. (2021). Efficient removal of methylene blue using the mesoporous activated
carbon obtained from mangosteen peel wastes: Kinetic, equilibrium, and
thermodynamic studies. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 315:
110904.
42.
Kumar, A. and Jena, H. M. (2016). Removal of methylene blue and phenol
onto prepared activated carbon from Fox nutshell by chemical activation in
batch and fixed-bed column. Journal of Cleaner Production, 137:
1246-1259.
43.
Subbaiah, M. V. and Kim, D. S. (2016). Adsorption of methyl orange from
aqueous solution by aminated pumpkin seed powder: Kinetics, isotherms, and
thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 128:
109-117.
44.
Khosravi, M. and Azizian, S. (2014). Adsorption of anionic dyes from
aqueous solution by iron oxide nanospheres. Journal of Industrial and
Engineering Chemistry, 20(4): 2561-2567.
45.
Zhu, C. S., Wang, L. P. and Chen, W. B. (2009). Removal of Cu (II) from
aqueous solution by agricultural by-product: peanut hull. Journal of
Hazardous Materials, 168(2-3): 739-746.
46.
Shin, H. S. and Kim, J. H. (2016). Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic
characteristics of adsorption of paclitaxel onto Diaion HP-20. Process
Biochemistry, 51(7): 917-924.
47.
Bedin, K. C., Martins, A. C., Cazetta, A. L., Pezoti, O. and Almeida, V.
C. (2016). KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon:
Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene Blue removal. Chemical
Engineering Journal, 286: 476-484.
48.
Ghani, Z. A., Yusoff, M. S., Zaman, N. Q., Andas, J. and Aziz, H. A.
(2017). Adsorptive removal of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in landfill
leachate by iron oxide nanoparticles (FeONPs). AIP Conference Proceedings,
1892: 040016.