Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 4
(2022): 755 - 765
SYNTHETIC
APPROACHES TOWARDS QUINOLACTACIN DERIVATIVES VIA DIELS-ALDER, ACYL MIGRATION
AND MULTICOMPONENT REACTIONS
(Pendekatan
Sintesis Ke Arah Terbitan Quinolaktasin Melalui Tindak Balas Diels-Alder,
Migrasi Asil dan Tindak Balas Pelbagai Komponen)
Ahmad
Zahir Hafiz Ismail1,2, Putri Nur Arina Mohd Arif 1,2,
Nurul Syafiqah Rezali3, Mohd Fazli Mohammat2, Zurina
Shaameri2*
1Organic Synthesis Laboratory, Institute
of Science,
Universiti Teknologi MARA Puncak Alam,
43200 Bandar Puncak Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
2Faculty of Applied Sciences,
Universiti Teknologi MARA, 40450 Shah
Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
3Chemical Sciences Programme,
School of Distance Education, Universiti
Sains Malaysia, 11800 Penang, Malaysia
*Corresponding author:
zurina@uitm.edu.my
Received: 18 September 2021; Accepted: 27 February 2022;
Published: 25 August 2022
Abstract
Quinolactacins
are rare fungal alkaloids extracted from the culture broth of Penicillium
species isolated from larvae mulberry pyralis (Margonia pyloalis Welker). The synthesis of the natural alkaloids
has gained interests among many researchers due to its unique 𝛾-lactam
conjugated ring quinolone skeleton. Furthermore, the alkaloids are also proven
to exhibited inhibitory activities against tumour necrosis factor (TNF)
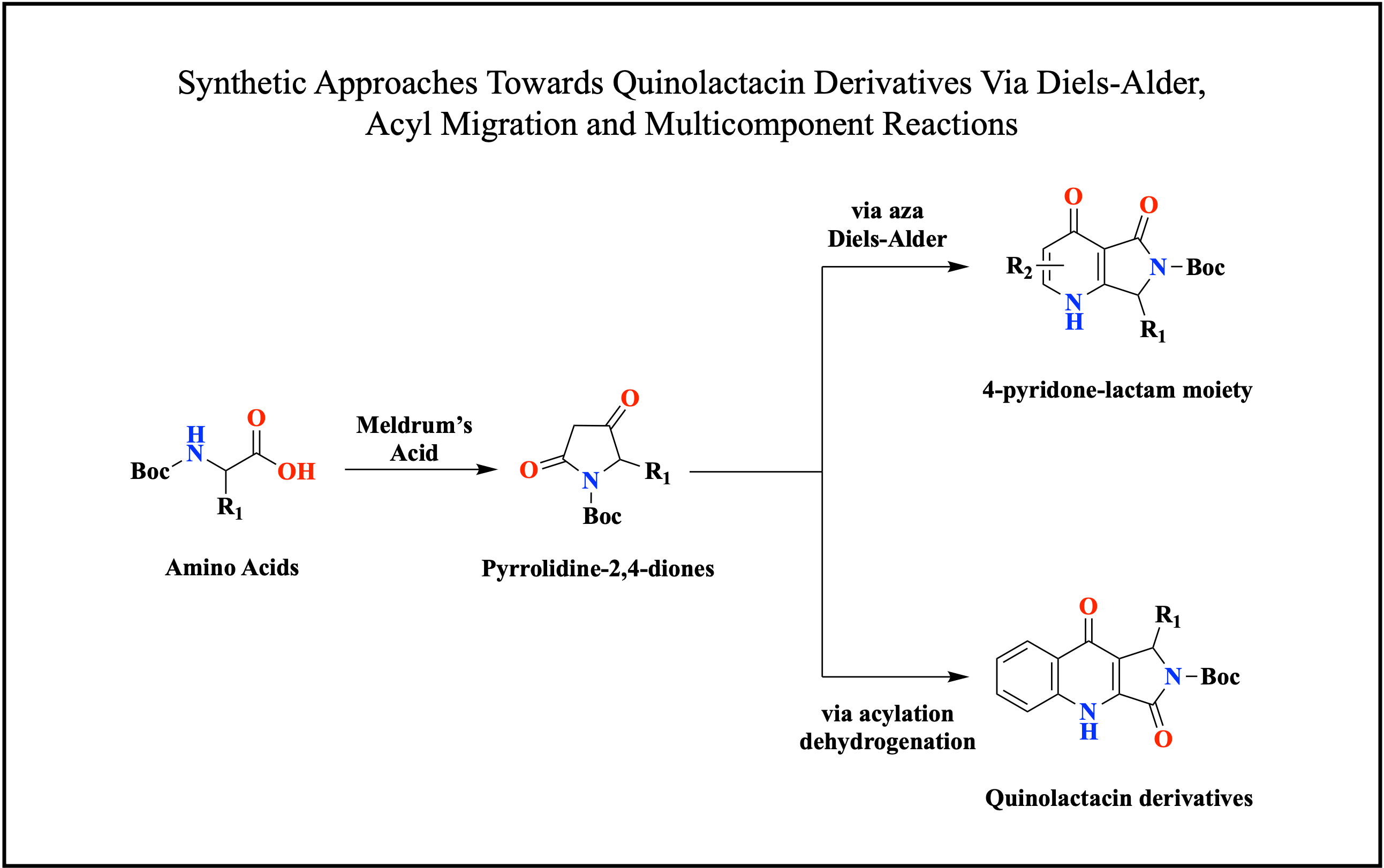
production. Synthesizing the alkaloids is initiated by forming the key
pyrrolidine-2,4-dione intermediates via the acid-mediated Meldrum reaction and tetramic acid
cyclisation of different amino acids. Subsequently, the diketo intermediates
are reduced and eliminated to form
hydroxy and enone analogues. The enone analogues are then reacted with an
amine-substituted diene by aza Diels-Alder reaction to form the anticipated
4-pyridone-lactam moiety with different substitutions. Nonetheless, the availability
of amine-substituted dienes is limited even though aza Diels-Alder reactions
shorten the formation of the tricyclic compounds. Consequently, the present
study synthesised quinolactacin derivatives through alternative routes,
including acylating the key pyrrolidine-2,4-dione with 2-nitrobenzoyl chloride
to obtain an acylated tetramic acid and hydrogenated and furnish the final
quinolactacin derivatives. The derivatives were also procured through a
multicomponent reaction of diethyl oxaloacetate salt with aldehydes and amines.
The synthesised compounds were analysed and confirmed with proton and carbon
nuclear magnetic resonance (1H- and 13C-NMR) and infrared
(IR) spectroscopy.
Keywords: Penicillium sp., Diels-Alder,
2,4-pyrrolidinone, quinolactacin
Abstrak
Quinolaktasin adalah kulat alkaloid
nadir yang terhasil daripada kultur kaldu Penicillium spesies, di ekstrak
daripada larva piralis mulberi (Marfonia pyloalis Welker).
Sintesis bahan alkaloid yang natural ini telah menarik minat ramai ahli
penyelidik oleh kerana keunikan struktur quinolone di mana ianya konjugat
bersama gegelang 𝛾-lactam. Alkaloid ini telah dibuktikan
bahawa ianya bersikap aktif terhadap aktiviti rencatan melawan penghasilan
faktor tumor nekrosis (TNF). Sintesis ini bermula dengan bahantara
pirolidina-2,4-dion melalui tindak balas asid Meldrum dan pengitaran asid
tetramik dari variasi asid amino. Bahantara diketo pula akan melalui
pengurangan berturutan dan tindak balas penyingkiran kumpulan hidroksi dan
variasi enon. Variasi enon ini bertindak balas dengan diena amina gantian
melalui reaksi aza Diels-Alder bagi menghasilkan sebatian 4-piridona-laktam
dengan variasi gantian. Walaupun reaksi kimia aza Diels-Alder dapat membantu
menghasilkan sebatian trisiklik dalam langkah yang pendek, tetapi variasi diena
amina gentian juga adalah terhad. Oleh itu, sintesis bagi penghasilan variasi
quinolaktasin dijalankan melalui cara alternatif di mana pirolidina-2,4-dion
menjalani pengasilan dengan 2-nitrobenzoil klorida untuk menghasilkan tetramik
asid terasilasi dan penghidrogenan bagi menghasilkan sebatian akhir
quinolaktasin. Reaksi pelbagai komponen oleh garam dietil oxaloasetat bersama
aldehid dan amina pula adalah alternatif lain bagi penghasilan variasi sebatian
quinolaktasin. Semua sebatian di dalam kajian ini dianalisa dan disahkan
menggunakan resonans magnet nucleus (1H- dan 13C-NMR) dan
spektroskopi infra merah (IR).
Kata kunci: Penicillium
sp., diels-alder, 2,4-pirolidina, quinolaktasin
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Sasaki, T., Takahashi, S., Uchida,
K., Funayama, S., Kainosho, M. and Nakagawa, A. (2006). Biosynthesis of
quinolactacin A, a TNF production inhibitor. Journal of Antibiotics,
59(7): 418-427.
2.
Kakinuma, N., Iwai, H., Takahashi,
S., Hamano, K., Yanagisawa, T., Nagai, K. and Nakagawa, A. (2000).
Quinolactacins A, B and C. novel quinolone compounds from Penicillium
sp. EPF-6. I. Taxonomy, production, isolation and biological properties. The
Journal of Antibiotics, 53(11): 1247-1251
3.
Abe, M., Imai, T., Ishii, N., Usui,
M., Okuda, T. and Oki, T. (2005). Quinolactacide, a new quinolone insecticide
from Penicillium citrinum Thom F 1539. Bioscience, Biotechnology and
Biochemistry, 69(6): 1202-1205.
4.
Čaplar, V., Raza, Z.,
Katalenić, D. and Žinić, M. (2003). Syntheses of amino alcohols and
chiral C2-symmetric bisoxazolines derived from O-alkylated
R-4-hydroxyphenylglycine and S-tyrosine. Croatica Chemica Acta, 76(1):
23-36.
5.
Yuan, Y., Li, X. and Ding, K. (2002).
Acid-free aza diels-alder reaction of Danishefsky’s diene with imines. Organic
Letters, 4(19), 3309-3311.
6.
Chemie, O. and Universit, T. (2005).
Imidazolinium salts as catalysts for the aza-Diels–Alder reaction. Organic
& Biomolecular Chemistry, 3(2):239-244.
7.
Abe, M., Imai, T., Ishii, N. and Usui, M. (2006). Synthesis
of quinolactacide via an acyl migration reaction and dehydrogenation with
manganese dioxide, and its insecticidal activities. Bioscience,
Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 70(1): 303-306.