Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 415 - 428
OPTIMISATION OF THE EXTRACTION METHOD OF RED Christia vespertilionis LEAVES TO YIELD BIOACTIVE PHTYOCHEMICALS AS MONITORED BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPCTROMETRY
(Pengoptimuman Kaedah Pengekstrakan Pada Daun Merah Christia vespertilionis untuk Menentukan Fotokimia Bioaktif Melalui
Kromatografi Gas-Spektrometri Jisim)
Izzah
Farhah Zambari1, Sitti Rahma Abdul Hafid2, Nur Airina
Muhamad1*
1Institute
of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science,
Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2Nutrition Unit, Product Development and Advisory Services
Division,
Malaysian Palm Oil Board, 43000 Kajang,
Selangor, Malaysia.
*Corresponding author: nurairina@um.edu.my
Received: 31 August 2021; Accepted: 30 December 2021; Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
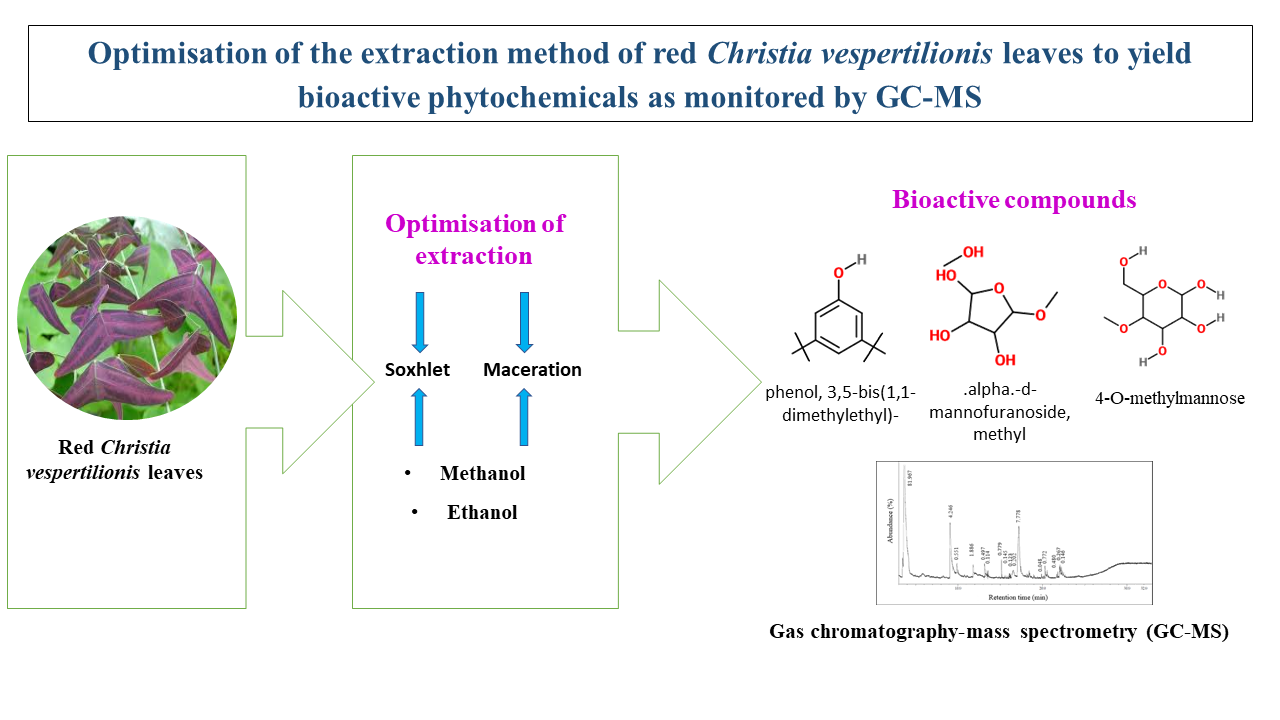
Christia vespertilionis (L. f.) Bakh. f. is well-known for treating
various contagious diseases. This plant has been recognised among researchers
and locals to have anti-inflammatory properties and has thus become popular for
treating cancer. Two types of C. vespertilionis
are acknowledged which are green and red. The green C. vespertilionis
has been widely studied by many researchers, however just a few have studied
the red type. This study was carried out to optimise the
extraction method of red C.
vespertilionis leaves by different extraction techniques (maceration and
Soxhlet extraction) and solvents (methanol and ethanol) to yield bioactive
phytochemicals using gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The
components were identified through GC-MS via comparisons as guided by the National Institute
of Standards and Technology Mass Spectral Library 2011 (NIST 11, version 2.0g). According to the four (4) samples of
red C. vespertilionis leaves using maceration of
methanol (RMM), maceration of ethanol (RME), Soxhlet extraction of methanol
(RSM), and Soxhlet extraction of ethanol (RSE), seventy-one (71) bioactive
phytochemicals were identified. Eleven (11) major
bioactive phytochemicals (abundance of > 4%) were identified namely, acetic acid, butyl ester; 1-butanol,
3-methyl-, acetate; heptanoic acid, propyl ester; hexanoic acid, 3-oxo-, ethyl
ester; phenol, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-; 1-octadecene; 4-O-methylmannose;
.alpha.-d-mannofuranoside, methyl; 2-undecene, 9-methyl-, (E)-; n-hexadecanoic
acid; and 1-octadecanol. Only seven (7) out of eleven (11) compounds were reported
to have biological activities. Among those samples, RSM was the most
effective using correlation coefficient between abundance (%) and retention
time (minute(s)) with a significant difference at P < 0.05.
Keywords: Christia
vespertilionis, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, phytochemicals,
maceration, Soxhlet extraction
Abstrak
Christia vespertilionis (L. f.) Bakh. f. dikenali secara meluas dalam merawat
pelbagai penyakit berjangkit. Tumbuhan ini diakui di kalangan penyelidik dan
penduduk tempatan tentang kelebihannya sebagai salah satu ubat tradisional yang
mempunyai sifat anti-radang serta digunakan secara meluas dalam merawat barah.
Terdapat dua jenis C. vespertilionis iaitu jenis hijau dan merah. C.
vespertilionis hijau telah banyak dikaji oleh penyelidik dan hanya sedikit
yang dikaji untuk jenis merah. Kajian ini dijalankan untuk mengoptimumkan
kaedah pengekstrakan daun C. vespertilionis merah dengan teknik
pengekstrakan yang berbeza (pengekstrakan maserasi dan Soxhlet) dan pelarut
(metanol dan etanol) untuk menentukan fitokimia bioaktif melalui kromatografi
gas-spektrometri jisim (GC-MS). Komponen tersebut dikenal pasti melalui GC-MS
dengan membuat perbandingan dari data rujukan Institut Piawaian dan Teknologi
Nasional 2011 (NIST11-MS, version 2.0g). Berdasarkan 4 sampel daun merah C.
vespertilionis melalui maserasi metanol (RMM), maserasi etanol (RME),
pengekstrakan Soxhlet methanol (RSM) dan pengekstrakan Soxhlet etanol (RSE),
tujuh puluh satu (71) sebatian fitokimia dikenal pasti. Sebelas (11) sebatian
fitokimia utama (> 4 % kawasan puncak) juga dikenalpasti seperti asid
asetik, butil ester; 1-butanol, 3-metil-, asetat; asid heptanoik, propil ester;
asid heksanoik, 3-okso-, etil ester; fenol, 3,5-bis (1,1-dimetiletil)-; 1-oktadekena;
4-O-metilmanos; .alpha.-d-manofurosida, metil; 2-undekena, 9-metil-, (E)-; asid
n-heksadekanoik dan 1-oktadekanol. Hanya tujuh (7) daripada sebelas (11)
sebatian yang dilaporkan mempunyai aktiviti biologi. Di antara sampel tersebut,
RSM adalah yang paling berkesan dengan menggunakan pekali korelasi antara
kebanyakan (%) dan masa pengekalan (min) dengan perbezaan yang signifikan pada P
< 0.05.
Kata kunci: Christia
vespertilionis, kromatografi gas-spektrometri jisim, fitokimia, maserasi,
pengekstrakan Soxhlet
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Nguyen-Pouplin,
J., Tran, H., Phan, T. A., Dolecek, C.,
Farrar, J., Tran, T. H., Caron, P., Bodo, B. and Grellier, P. (2007). Antimalarial and cytotoxic
activities of ethnopharmacologically selected medicinal plants from South
Vietnam. Journal Ethnopharmacology, 109: 417-427.
2. Hofer, D., Schwach, G.,
Tabrizi-Wizsy, N.G., Sadjak,
A., Sturm, S., Stuppner, H. and Pfragner, R.
(2013). Christia vespertilionis plant extracts as novel
antiproliferative agent against human neuroendocrine tumor cells. Oncology Reports, 6(29): 2219-2226.
3. Osman, M. S., Ghani, Z. A., Ismail, N. F., Razak, N.
A., Jaapar, J. and Ariff, M. A. (2017). Qualitative comparison of active
compounds between red and green Mariposa Christia vespertillonis leaves
extracts. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1885(020282): 1-6.
4. Sharma, A. and Cannoo, D.S. (2016). Effect
of extraction solvents/techniques on polyphenolic contents and antioxidant
potential of the aerial parts of Nepeta leucophylla and the analysis of
their phytoconstituents using RP-HPLC-DAD and GC-MS. RSC Advance, 6:
78151-78160.
5. Bunawan, H., Bunawan, S. N. and Baharum, S. N.
(2015). The red butterfly wing (Christia vespertilionis): A promising
cancer cure in Malaysia. International Journal of Pharmacy and
Pharmaceutical Sciences 7(8): 1.
6. Mohd Yasin, Z. N., Zakaria, M. A., Nik Mat Zin, N.
N. I., Ibrahim, N., Mohamad, F. S., Mat Desa, W. N. S., Sul’ain, M. D. and Abu
Bakar, N. (2020). Biological activities and GCMS analysis of the methanolic
extract of Christia vespertilionis (L.F.) Bakh. F. leaves. Asian
Journal of Medicine and Biomedicine 4(1): 1-11.
7. Haida, Z. and Hakiman, M. (2019). A review of
therapeutics potentials of Clinacanthus nutans as source for alternative
medicines. Sains Malaysiana, 48(12): 2683-2691.
8. Yusufzai, S. K., Khan, M. S., Hanry, E. L.,
Rafatullah, M. and Elison, B. (2019). GC-MS analysis of chemical constituents
and in vitro antioxidant activity of the organic extracts from the stem
of Bridelia stipularis. Sains Malaysiana, 48(5): 999-1009.
9. NIST/NIH/EPA Mass Spectral Library, Standard
Reference Database 1, NIST 11. (2011). Standard Reference Data
Program, National Institute of Standards and Technology. Gaithersburg, MD,
USA.
10.
Abd Rahim, E. N. A.,
Ismail, A., Omar, M. N., Rahmat, U. N. and Wan Ahmad, W. A. N. (2018). GC-MS
analysis of phytochemical compounds in Syzygium polyanthum leaves
extracted using ultrasound-assisted method. Pharmacognosy Journal,
10(1): 110-119.
11. Mohd Yasin, Z. N., Zakaria, M. A., Nik Mat Zin, N.
N.I., Ibrahim, N., Mohamad, F. S., Mat Desa, W. N. S., Sul’ain, M. D. and Abu
Bakar, N. (2020). Biological activities and chemical compositions of the
methanol extract of Christia vespertilionis leaves. Asian Journal of
Medicine and Biomedicine 4(2): 78-88.
12. Sidek, M. M., Ismail, N. Z., Zain, N. N. M. and
Arsad, H. (2019). Cytotoxicity activity of Christia vespertilionis
leaves extracts against Hela cells and the detection of compounds by GC-MS. Journal
of Biological & Scientific Opinion, 7(6): 71-78.
13. Gami, B. and Parabia, F. (2011). Screening of
methanol & acetone extract for antimicrobial activity of some medicinal
plants species of Indian folklore. International Journal Research
Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2(1): 69-75.
14. Truong, D-H., Nguyen, D-H., Ta, N.T.A., Bui, A.V.,
Do, T.H. and Nguyen, H.C. (2019). Evaluation of the use of different solvents
for phytochemical constituents, antioxidants, and in vitro anti-inflammatory
activities of Severinia buxifolia. Journal of Food Quality, 2019:
8178294.
15. Karunaratne, U. K. P. R. and Karunaratne, M. M. S.
C. (2012). Evaluation of methanol, ethanol and acetone extracts of four plant
species as repellents against Callosobruchus maculatus (Fab.). Vidyodaya
Journal of Science 17: 1-8.
16. Kalia, K., Sharma, K., Singh, H.P. and Singh, B.
(2008). Effects of extraction methods on phenolic contents and antioxidant
activity in aerial parts of Potentilla atrosanguinea L. and
quantification of its phenolic constituents by RP-HPLC. Journal Agriculture
Food Chemistry, 56: 10129-10134.
17. Aparna, V., Dileep, K. V., Mandal, P. K., Karthe,
P., Sadasivan, C. and Haridas, M. (2012). Antiinflammatory property of
n-hexadecanoic acid: Structural evidence and kinetic assessment. Chemical
Biology Drug Design, 80(3): 434-439.
18. Singab, A. N., El-Taher, E. M. M., Elgindi, M. R and
Kassem, M-S. (2015). Phoenix roebelenii O’Brien DNA profiling, bioactive
constituents, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities.
Asian Pacific Journal Tropical
Disease, 5(7): 552-558.
19. Mitchell, A. M., Strobel, G. A., Moore, E., Robison,
R. and Sears, J. (2010). Volatile antimicrobials from Muscodor crispans,
A novel endophytic fungus. Microbiology, 156: 270-277.
20. Chew, Y. L., Chan, E. W. L., Tan, P. L., Lim, Y. Y.,
Stanslas, J. and Goh, J. K. (2011). Assessment of phytochemical content,
polyphenolic composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of
Leguminosae medicinal plants in Peninsular Malaysia. BMC complementary and
Alternative Medicine, 11(1): 12.
21. Lee, J. J., Yazan, L. S., Kassim, N. K., Che
Abdullah, C. A., Esa, N., Lim, P. C. and Tan, D.C. (2020). Cytotoxic activity
of Christia vespertilionis root and leaf extracts and fractions against
breast cancer cell lines. Molecules, 25(2610):1-18.
22. Lee, Y. S., Kang, M. H., Cho, S. Y. and Jeong, C. S.
(2007). Effects of constituents of Amomum xanthioides on gastritis in
rats and on growth of gastric cancer cells. Achieve Pharmaceutical Research,
30(4): 436-443.
23.
Belakhdar, G., Benjouad,
A. and Abdennebi, E.H. (2015). Determination of some bioactive chemical
constituents from Thesium humile Vahl. Journal Materials
Environmental Sciences, 6(10): 2778-2783.
24.
Duke J. (2002).
American Agricultural Research Service-Phytochemical & Ethnobotanical
Database. Available at: http://www.ars-grin.gov/duke/index.html [accessed
on 09 December 2019].
25. Mutalib, N. A. and Latip, N. A. (2019). Synergistic
interactions between Christia vespertilionis leaves extract and
chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide on WRL-68 Cell Line. Asian Journal of
Pharmaceutical Research and Development, 7(3): 109-113.
26. Mishra, P. M. and Sree, A. (2007). Antibacterial
activity and GCMS analysis of the extract of leaves of Finlaysonia obovata
(a mangrove plant). Asian Journal Plant Sciences, 6(1): 168-172.
27. Kumar, P. R. Z. A. and Bhaskar, A. (2012).
Phytochemical evaluation by GC-MS and in vitro antioxidant activity of Punica
granatum fruit rind extract. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical
Research, 4(6): 2869-2873.
28.
Suman, T.,
Chakkaravarthi, K. and Elangomathavan, R. (2013). Phyto-chemical profiling of Cleistanthus
collinus leaf extracts using GC-MS analysis. Research Journal
Pharmaceutical and Technology, 6(11): 1173-1177.
29.
Igwe, K. K., Okafor, P.
N. and Ijeh, I. I. (2015). GC-MS analysis of phytocomponents in Vernonia
amygdalina. Del leaves and its contractile potential in mammary tissue in
female albino Wistar rats. Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science,
8(11): 25-30.
30. Johannes, E., Litaay, M. and Syahribulan. (2016).
The bioactivity of hexadecanoic acid compound isolated from hydroid Aglaophenia
cupressina lamoureoux as antibacterial agent against Salmonella
typhi. International Journal Biological Medicinal Research, 7(2):
5469-5472.
31.
Gavamukulya, Y.,
Abou-Elella, F., Wamunyokoli, F. and El-Shemy, H. A. (2015). GC-MS analysis of
bioactive phytochemicals present in ethanolic extracts of leaves of Annona
muricata: A further evidence for its medicinal diversity. Pharmacognosy
Journal, 7(5): 300-304.
32. Shukri, N. S. S. M., Perumal, V., Balan, T.,
Murugesu, S., Khatib, A., Saleh, M. S. M, Hin, L.W., Darus, K. A., Zailani,
I.A. and Zahidi, F. A. H. M. (2019). The screening of antioxidant activities
and FTIR analysis of Christia vespertilionis leaves extracts. International
Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10(1): 1713.
33. Guo, L., Wu, J., Han, T., Cao, T., Rahman, K. and
Qin, L. (2008). Chemical composition, antifungal and antitumor properties of
ether extracts of Scapania verrucosa Heeg. and its endophytic fungus Chaetomium
fusiforme. Molecules, 13: 2114-2125.
34. Wu, X. Y., Tang, A. C. and Lu, Q. Y. (2012). Study
on antitumor effect of the extract from Christia vespertilionis in
vivo. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,
8: 202-204.