Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences Vol 26 No 2
(2022): 334 - 346
Preparation of extracted magnetite from AN
industrial waste mill MODIFIed by CETYL TRIMETHYL ammonium bromide for Cadmium
ion removal from aqueous solution
(Penyediaan Magnetit daripada Sisa
Buangan Sisik Besi yang Dimodifikasikan oleh Setil Trimetil Ammonium Bromida
untuk Menyerap Kadmium Ion daripada Larutan Akues)
Nur Asyikin Ahmad
Nazri1,2* , Raba’ah Syahidah Azis2,3 , Hasfalina Che Man4,
Ismayadi Ismail2
1Centre
of Foundation Studies, Cawangan Selangor,
Universiti
Teknologi MARA, 43800 Dengkil, Selangor, Malaysia
2Material
Synthesis and Characterization Laboratory (MSCL), Institute of Advanced
Technology (ITMA)
3Department
of Physics, Faculty of Science
4Department
of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering
Universiti
Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: asyikin2750@uitm.edu.my
Received: 9 September 2021; Accepted: 18 December 2021;
Published: 28 April 2022
Abstract
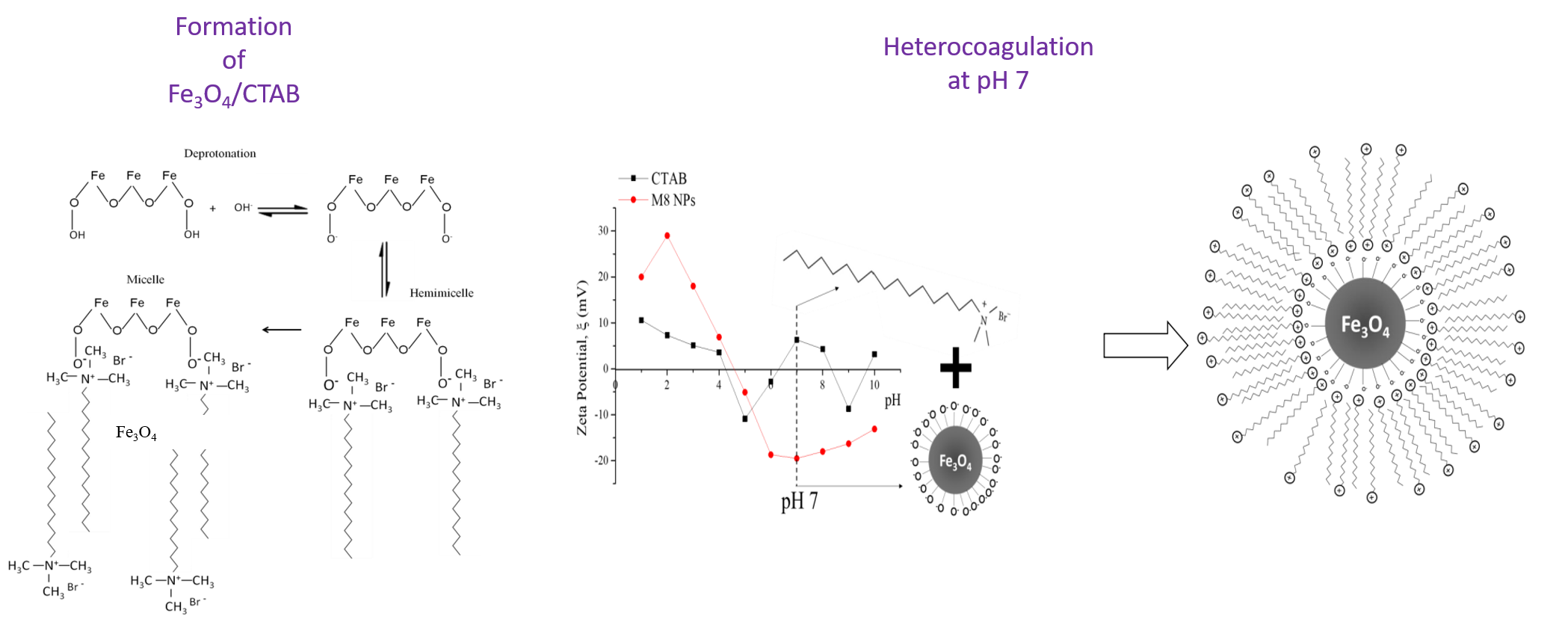
This work, using a batch study, revealed the
performance of modified magnetite millscales with a cationic surfactant [cetyl
trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB)] (Fe3O4/CTAB
MNS) in cadmium ion removal from aqueous solution. The self-assembly method was
employed to modify Fe3O4 with CTAB. As prepared Fe3O4
limited the modification method to ex situ. Therefore, a
heterocoagulation method was used to self-assemble CTAB on Fe3O4.
The prepared magnetic nanosorbents (MNSs) were used in batch adsorption to
optimize cadmium adsorption. In addition, characterization with Fourier
transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy
(TEM) revealed new characteristics of that modified Fe3O4
that contributed to the enhancement of the adsorption efficiency (Q) to
reach 21.6 mg/g. The higher removal percentage shown by Fe3O4/CTAB
MNS was 89%, which confirmed the successful modification. Therefore, Fe3O4
modified with CTAB has higher potential to be used as magnetic nanosorbent
owing to lower cost of production with compatible adsorption capacity.
Keywords: stabilized magnetite, magnetic nanosorbents,
cadmium solution, cation polymer, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
Abstrak
Kajian
ini mendedahkan prestasi skala magnetit yang diubah suai dengan surfaktan
kationik (setil trimetil ammonium bromida (CTAB))
(Fe3O4 / CTAB), digunakan sebagai penyingkiran ion
kadmium dari larutan akues melalui kajian kumpulan. Kaedah pemasangan diri
digunakan untuk mengubah Fe3O4 dengan CTAB. Fe3O4
yang telah disiapkan telah membatasi kaedah modifikasi menjadi ex situ.
Oleh itu, kaedah heterokoagulasi digunakan untuk memasang CTAB pada Fe3O4.
Penjerap nano magnetik yang disiapkan (MNS) digunakan dalam penjerapan kumpulan
untuk mengoptimumkan penjerapan kadmium. Selain itu, pencirian dengan
spektroskopi infra merah transformasi Fourier (FTIR), dan mikroskopi elektron
transmisi (TEM) telah mengungkapkan ciri-ciri baru Fe3O4
yang dimodifikasi yang menyumbang kepada peningkatan kecekapan penjerapan (Q)
menjadi 21.6 mg/g. Peratusan penyingkiran yang lebih tinggi yang ditunjukkan
oleh Fe3O4 / CTAB MNS adalah 89% yang membuktikan
pengubahsuaian berjaya. Oleh itu, dapat disimpulkan bahawa modifikasi dengan
CTAB berpotensi lebih tinggi untuk digunakan sebagai penjerap nano magnetik
kerana melibatkan kos pengeluaran yang lebih rendah dengan kapasiti penjerapan
yang serasi.
Kata
kunci: magnetit stabil, penjerap nano magnetik,
larutan kadmium, polimer kation, setil trimetil ammonium bromida
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Mahmood, Q., Asif, M., Shaheen, S., Hayat, M. T. and Ali, S. (2019).
Cadmium contamination in water and soil. In Cadmium toxicity and
tolerance in plants. Academic Press: pp. 141-161.
2.
Pyrzynska, K. (2019). Removal of cadmium from wastewaters with low-cost
adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(1):
102795.
3.
Ciesielczyk, F., Bartczak, P. and Jesionowski, T. (2016). Removal of
cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions from model aqueous solutions using
sol–gel-derived inorganic oxide adsorbent. Adsorption, 22(4):
445-458.
4.
Ali, A. H. (2013). Comparative study on removal of cadmium (II) from
simulated wastewater by adsorption onto GAC, DB, and PR. Desalination
and Water Treatment, 51(28-30): 5547-5558.
5.
Farhan, A. S. and Jasim, S. T. (2020). Cadmium toxicity and some target
organs: A review. Al-Anbar Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 13(2):
17-26.
6.
Riaz, U., Aslam, A., uz Zaman, Q., Javeid, S., Gul, R., Iqbal, S., ...
and Jamil, M. (2021). Cadmium contamination, bioavailability, uptake mechanism
and remediation strategies in soil-plant-environment system: a critical
review. Current Analytical Chemistry, 17(1): 49-60.
7.
Järup, L. and Åkesson, A. (2009). Current status of cadmium as an
environmental health problem. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 238(3):
201-208.
8.
Cui, L., Chen, T., Yin, C., Yan, J., Ippolito, J. A. and Hussain, Q.
(2019). Mechanism of adsorption of cadmium and lead ions by iron-activated
biochar. BioResources, 14(1): 842-857.
9.
Carolin, C. F., Kumar, P. S., Saravanan, A., Joshiba, G. J. and Naushad,
M. (2017). Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from
aquatic environment: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical
Engineering, 5(3): 2782-2799.
10.
Dubey, S., Banerjee, S., Upadhyay, S. N. and Sharma, Y. C. (2017).
Application of common nano-materials for removal of selected metallic species
from water and wastewaters: A critical review. Journal of Molecular
Liquids, 240: 656-677.
11.
Gaballah, N. M., Zikry, A. F., Khalifa, M. G., Farag, A. B., El-Hussiny,
N. A. and Shalabi, M. E. H. (2013). Production of iron from mill scale
industrial waste via hydrogen. Open Journal of Inorganic Non-metallic Materials, 3(3): 6.
12.
Hashim, M., Saiden, N. M., Daud, N. and Shahrani, N. M. M. (2015). Study
the iron environments of the steel waste product and its possible potential
applications in ferrites. In Advanced Materials Research, 1109:
295-299.
13.
Shahid, M. K., Phearom, S. and Choi, Y. G. (2018). Synthesis of
magnetite from raw mill scale and its application for arsenate adsorption from
contaminated water. Chemosphere, 203: 90-95.
14.
Shahid, M. K., Phearom, S. and Choi, Y. G. (2019). Adsorption of arsenic
(V) on magnetite-enriched particles separated from the mill scale. Environmental
Earth Sciences, 78(3): 1-11.
15.
Hosseinzadeh, M., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S. A., Raygan, S. and Masoudpanah, S.
M. (2016). Removal of cadmium and lead ions from aqueous solution by
nanocrystalline magnetite through mechanochemical activation. Journal
of Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, 49(2): 72-79.
16.
Elfeky, S. A., Mahmoud, S. E. and Youssef, A. F. (2017). Applications of
CTAB modified magnetic nanoparticles for removal of chromium (VI) from
contaminated water. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(4):
435-443.
17.
Saksornchai, E., Kavinchan, J., Thongtem, S. and Thongtem, T. (2018).
Simple wet-chemical synthesis of superparamagnetic CTAB-modified magnetite
nanoparticles using as adsorbents for anionic dye Congo red removal. Materials
Letters, 213: 138-142.
18.
Faraji, M., Yamini, Y., Tahmasebi, E., Saleh, A. and Nourmohammadian, F.
(2010). Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated magnetite nanoparticles as highly
efficient adsorbent for rapid removal of reactive dyes from the textile
companies’ wastewaters. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 7(2):
S130-S144.
19.
Elfeky, S. A., Mahmoud, S. E. and Youssef, A. F. (2017). Applications of
CTAB modified magnetic nanoparticles for removal of chromium (VI) from
contaminated water. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(4):
435-443.
20.
Chaki, S. H., Malek, T. J., Chaudhary, M. D., Tailor, J. P. and
Deshpande, M. P. (2015). Magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles
synthesis by wet chemical reduction and their characterization. Advances
in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 6(3): 035009.
21.
Xu, W., Liu, Z., Fang, J., Zhou, G., Hong, X., Wu, S., ... and Cen, C.
(2013). CTAB-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Bi2Sn2O7
photocatalyst and its highly efficient degradation of organic dye under
visible-light irradiation. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2013:
234806.
22.
Nikoobakht, B., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2001). Evidence for bilayer
assembly of cationic surfactants on the surface of gold nanorods. Langmuir, 17(20):
6368-6374.
23.
Ehrampoush, M. H., Miria, M., Salmani, M. H., & Mahvi, A. H. (2015).
Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by green synthesis iron oxide
nanoparticles with tangerine peel extract. Journal of Environmental Health
Science and Engineering, 13(1): 1-7.
24.
Taleb, K., Markovski, J., Veličković, Z., Rusmirović, J.,
Rančić, M., Pavlović, V and Marinković, A. (2019). Arsenic
removal by magnetite-loaded amino modified nano/microcellulose adsorbents:
Effect of functionalization and media size. Arabian Journal of
Chemistry, 12(8): 4675-4693.
25.
Aydın, H., Yerlikaya, Ç. and Uzan, S. (2012). Equilibrium and
kinetic studies of copper (II) ion uptake by modified wheat shells. Desalination
and Water Treatment, 44(1-3): 296-305.
26.
Hao, Y. M., Man, C. and Hu, Z. B. (2010). Effective removal of Cu (II)
ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic
nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184(1-3):
392-399.
27.
Cantu, Y. (2017). Remediation of trivalent and hexavalent chromium
ions from aqueous solutions using titanium dioxide polymorphs. The University
of Texas Rio Grande Valley: pp. 1576-1580.