CHARACTERIZATION OF
CELLULOSE NANOCRYSTAL-GOLD NANOPARTICLES/CHITOSAN MODIFIED SCREEN-PRINTED CARBON
ELECTRODE AND ITS APPLICATION IN THE FABRICATION OF ELECTROCHEMICAL BIOSENSOR
FOR TETRACYCLINE DETECTION
(Percirian Elektrod Skrin Bercetak Karbon Terubahsuai
Nanokristal Selulosa-Partikel Nano Emas/Kitosan dan Aplikasinya dalam Fabrikasi
Penderia Bio Elektrokimia untuk
Pengesanan Tetrasiklin)
Nurul
Shahirah Hasim1, Nor Azah Yusof1.2, Ruzniza Mohd Zawawi1,
Noordiana Nordin3*
1Department of
Chemistry,
Faculty of
Science,
Universiti Putra
Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
2Functional
Nanotechnology Devices Laboratory,
Institute of
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,
Universiti
Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
3Laboratory of
Food Safety and Food Integrity,
Institute of
Tropical Agriculture and Food Security,
Universiti
Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
*Corresponding author: noordiana@upm.edu.my
Received: 10 February 2022; Accepted:
19 July 2022; Published: 27 December
2022
Abstract
Tetracycline is one of the antibiotics used
therapeutically and as a growth promoter in animals. Tetracycline residues in
food products of animal origin have raised concerns among consumers. Due to its
adverse effects on human health, it is critical to develop a reliable
analytical method for routine monitoring of tetracycline in foods. Biosensors
are among the rapid analytical devices that are reliable because of their
simple detection methodology, low cost, sensitivity and specificity. For an
effective signal transformation of tetracycline residues, it is critical to
completely attach the transducer to the biological component, so that a
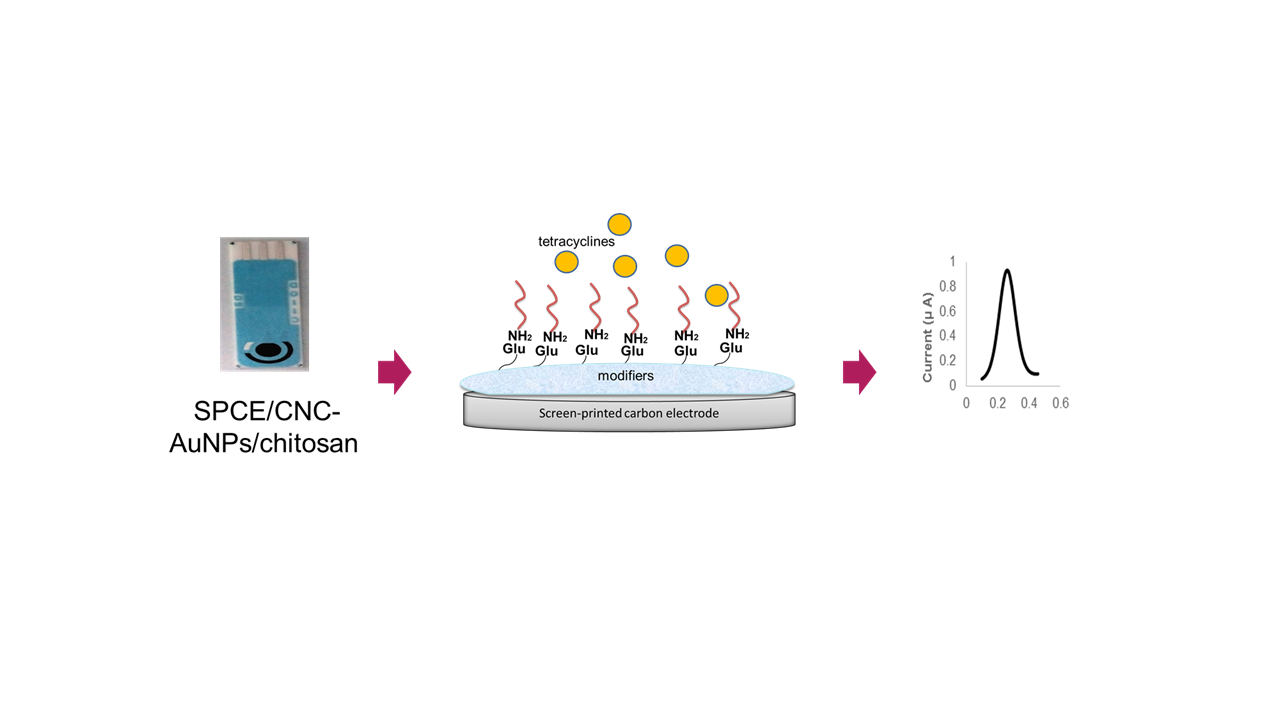
feasible biosensor can be constructed. In this study, the screen-printed carbon
electrode (SPCE) was modified with cellulose nanocrystal–gold
nanoparticles/chitosan composite (CNC–AuNPs/chitosan). The synthesized
CNC–AuNPs composite was characterized using UV–Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction,
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and high-resolution transmission
electron microscopy. In addition, the electrochemical behavior of the modified
SPCE was investigated by cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry
(DPV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy under optimized conditions.
DPV showed a linear calibration within the range of 0.01 to1000 µM
concentration of tetracycline with the detection limit of 0.07 µM. The
developed biosensor also resulted in different peak currents measured after
storage for 14 days at room temperature (53.07%) and under 4°C (89.28%).
Therefore, with acceptable sensitivity and selectivity, the fabricated
biosensor can be suggested as a potential detection method for tetracycline
residues.
Keywords: Cellulose nanocrystal, gold nanoparticles,
screen-printed carbon electrode, electrochemical biosensor, tetracycline
Abstrak
Tetrasiklin adalah salah satu
antibiotik yang digunakan secara terapeutik dan sebagai penyokong pertumbuhan
pada haiwan. Sisa tetrasiklin dalam produk makanan yang berasal dari haiwan
telah menimbulkan kebimbangan di kalangan pengguna. Oleh kerana kesan buruknya
terhadap kesihatan manusia, adalah sangat penting untuk membangunkan kaedah
analisis yang boleh dipercayai untuk pemantauan rutin tetrasiklin dalam
makanan. Penderia bio adalah antara peranti analisis pantas yang boleh
dipercayai kerana kaedah pengesanannya yang mudah, menjimatkan kos, kepekaan
dan kekhususannya. Untuk transformasi isyarat yang berkesan dari sisa tetrasiklin,
adalah sangat penting untuk melampirkan transduser sepenuhnya ke komponen
biologi, supaya penderia bio yang boleh dilaksanakan dapat dibina. Dalam kajian
ini, penderia bio dengan pengubahsuaian elektrod skrin bercetak karbon (SPCE)
telah melibatkan nanokristal selulosa-partikel nano emas/kitosan
(CNC-AuNPs/kitosan). Komposit CNC-AuNPs yang disintesis telah dicirikan dengan
menggunakan spektroskopi penglihatan-UV, pembelauan sinaran-X, spektroskopi
inframerah transformasi Fourier dan mikroskopi penghantaran elektron. Di
samping itu, tingkah laku elektrokimia SPCE yang diubahsuai telah disiasat oleh
voltammetri berkitar, voltammetri pembeza denyut (DPV) dan spektrometer
electrokimia impedans dibawah keadaan yang optima. DPV menunjukkan kalibrasi
linear dalam julat kepekatan tetrasiklin 0.01 hingga 1000 µM dengan had
pengesanan 0.07 µM. Penderia bio yang telah dibangunkan juga telah
menghasilkan perbezaan dalam arus puncak yang diukur setelah disimpan selama 14
hari pada suhu bilik (53.07%) dan di
bawah suhu 4°C (89.28%). Oleh itu, dengan sensitiviti dan selektiviti
yang telah diperoleh, penderia bio yang dibangunkan disyorkan berpotensi
sebagai kaedah pengesanan sisa tetrasiklin.
Kata kunci: nanokristal selulosa,
partikel nano emas, elektrod karbon tercetak, penderia bio elektrokimia,
tetrasiklin
Graphical
Abstract
References
1 . Ramchandani, M., Manges, A. R., DebRoy, C.,
Smith, S. P., Johnson, J. R. and Riley, L.W. (2005). Possible animal origin of
human-associated, multidrug-resistant, uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
Clinical Infectious Diseases, 40(2): 251-257.
2 . Landers, T. F., Cohen, B., Wittum, T. E.
and Larson, E .L. (2012). A review of antibiotic use in food animals:
Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Reports, 127(1): 4-22.
3 . Food Drug Administration (2014). 2012
summary report on antimicrobials sold or distributed for use in food-producing
animals. Washington DC: Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug
Administration, Center for Veterinary Medicine: pp. 1-56.
4 . Boyaci, I. H. and Mutlu, M. (2011).
Amperometric biosensors in food processing, safety, and quality control. Biosensors
in Food Processing, Safety, and Quality Control, 2011: 1-51.
5 . Codex Alimentarius (2018). Maximum residue
limits (MRLs) and risk management recommendations (RMRs) for residues of
veterinary drugs in food CX/MRL 2-2018. Access from
http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/codex-texts/dbs/vetdrugs/veterinary-drugs/en/.
6 . Mustafa, F. and Andreescu, S. (2018).
Chemical and biological sensors for food-quality monitoring and smart
packaging. Foods, 7(10): 168.
7 . Yan, W., Chen, C., Wang, L., Zhang, D., Li,
A.J., Yao, Z. and Shi, L.Y. (2016). Facile and green synthesis of cellulose
nanocrystal-supported gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic activity. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 140: 66-73.
8 . Guo, Y., Shen, G., Sun, X. and Wang, X.
(2015). Electrochemical aptasensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes and
graphene for tetracycline detection. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(3):
1951-1958.
9 . Ouyang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, Q., Guo, Z.,
Zhao, J., Li, H. and Hu, W. (2017). Rapid and specific sensing of tetracycline
in food using a novel upconversion aptasensor. Food Control, 81:156-163.
10 . Jahanbani, S. and Benvidi, A. (2016).
Comparison of two fabricated aptasensors based on modified carbon paste/oleic
acid and magnetic bar carbon paste/Fe3O4@oleic acid
nanoparticle electrodes for tetracycline detection. Biosensors and
Bioelectronics, 85:553-562.
11 . Le, T. H.,
Pham, V. P., La, T. H., Phan, T. B. and Le, Q. H. (2016). Electrochemical
aptasensor for detecting tetracycline in milk. Advances in Natural Sciences:
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 7(1): 015008.
12 . Brown, K. R., Walter, D. G. and Natan, M. J.
(2000). Seeding of colloidal Au nanoparticle solutions: Improved control of particle size and shape. Chemistry
of Materials, 12(2): 306-313.
13 . Zhao, H., Kwak, J. H., Conrad Zhang, Z.,
Brown, H. M., Arey, B.W. and Holladay, J. E. (2007). Studying cellulose fiber
structure by SEM, XRD, NMR and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydrate Polymers,
68(2): 235-241.
14
. Krishnamurthy, S., Esterle, A.,
Sharma, N. C. and Sahi, S. V. (2014). Yucca-derived synthesis of gold
nanomaterial and their catalytic potential. Nanoscale Research Letters,
9(1): 1-9.
15 . Lam, E., Hrapovic, S., Majid, E., Chong, J.
H. and Luong, J. H. T. (2012). Catalysis using gold nanoparticles decorated on
nanocrystalline cellulose. Nanoscale, 4(3): 997-1002.
16 . Kimling, J., Maier, M., Okenve, B., Kotaidis,
V., Ballot, H. and Plech, A. (2006). Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle
synthesis revisited. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110(32):
15700-15707.
17 . Jiang, Y. and Wu, J. (2019). Recent
development in chitosan nanocomposites for surface-based biosensor
applications. Electrophoresis, 40(16): 2084-2097.
18 . Zhou, L., Li, D.J., Gai, L., Wang, J. P. and
Li, Y. Bin. (2012). Electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of
tetracycline with multi-walled carbon nanotubes amplification. Sensors and
Actuators, B: Chemical, 162(1): 201-208.
19 . Benvidi, A., Tezerjani, M. D., Moshtaghiun,
S. M. and Mazloum-Ardakani, M. (2016). An aptasensor for tetracycline using a
glassy carbon modified with nanosheets of graphene oxide. Microchimica Acta, 183:
1797-1804.
20 . Tang, Y., Liu,
P., Xu, J., Li, L. Le, Yang, L., Liu, X., Liu, S. and Zhou, Y. (2018). Electrochemical
aptasensor based on a novel flower-like TiO2 nanocomposite for the
detection of tetracycline. Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical, 258:
906-912.
