Malaysian
Journal of Analytical Sciences, Vol 26 No 6 (2022): 1191 - 1204
DEVELOPMENT OF AN
ELECTROCHEMICAL IMMUNOSENSOR STRIP FOR EARLY DETECTION OF RICE BACTERIAL LEAF BLIGHT
(BLB) DISEASE AND ITS APPLICATION ON A PORTABLE DEVICE
(Pembangunan Strip
Imunosensor Elektrokimia Untuk Pengesanan Awal Penyakit Hawar Daun Bakteria
Padi dan Aplikasinya Pada Peranti Mudah Alih)
Hazana
Razali1, Norhafniza Awaludin1, Nurul Hidayah Husin1,
Sahira Akmar Zulkepli1, Rafidah Abd Rahman1, Mohammad
Rejab Ismail1, Kogeethavani Ramachandran2, Faridah Salam1,
Nur Azura Mohd Said1*
1Biotechnology
& Nanotechnology Research Centre,
MARDI
Headquarter, Persiaran MARDI-UPM, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
2Paddy&
Rice Research Centre,
MARDI
Seberang Perai, 13200 Seberang Perai, Pulau Pinang
*Corresponding
author : nazurams@mardi.gov.my
Received: 8 February 2022; Accepted:
27 April 2022 ; Published: 27 December
2022
Abstract
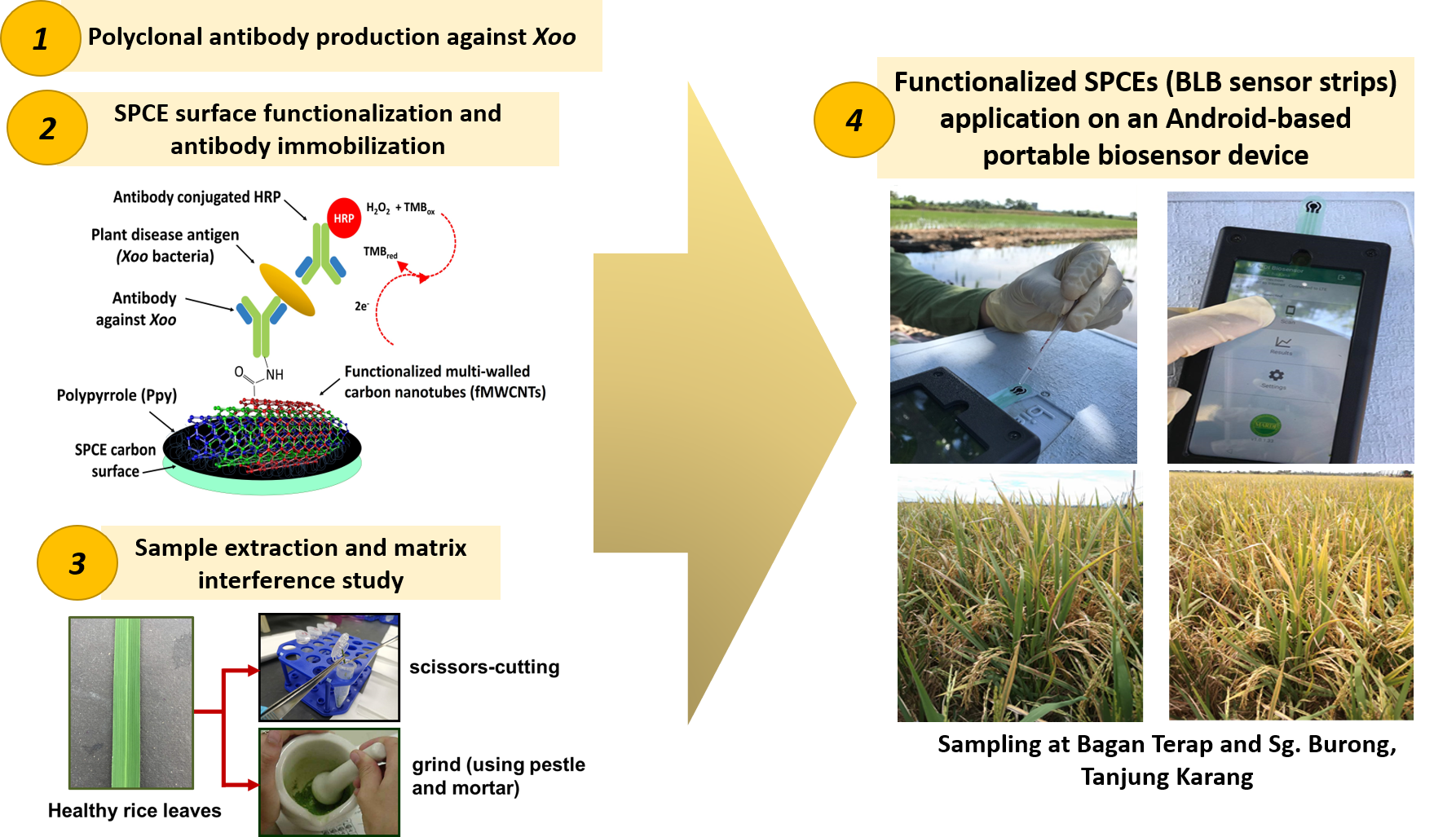
We described here an electrochemical
immunosensor strip based on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) for early
detection of rice bacterial leaf blight (BLB) disease. The causal agent for
this destructive disease has been identified as Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae
(Xoo). In order to circumvent the disease outbreak,
an early detection system is required. Polyclonal antibody against Xoo was employed
and immobilized on the SPCE strips modified with polypyrrole (PPy) and
functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube (fMWCNT) network. The anti-Xoo
antibody is conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) as an enzyme label and
used as the detection agent in the sensor development. Electrochemical
detection was carried out via the chronoamperometry technique at a set
potential of -200 mV. A fixed anti-Xoo antibody concentration at 0.03
mg/mL on the working electrode of the strip surface produced a standard linear
curve for Xoo detection (R2 = 0.9746). Two extraction
methods for rice leaves (scissors-cutting and grinding) were compared for real
samples application analysis. The scissors-cutting method had less matrix
interference effect and gave a higher recovery rate than the grinding method.
The optimal immunosensor configuration was then compared with the PCR technique
for Xoo detection in inoculated
leaves in a controlled environment. A good correlation of 92.7% was achieved
between the two methods. The immunosensor strips were then tested on an
Android-based portable biosensor device for on-site detection of BLB in hotspot areas
at Bagan Terap, Selangor Northwest and Sg. Burong, Tanjung Karang. On-field detection has indicated
that the immunosensor strips can detect BLB disease as early as 15 days after
transplant (DAT) before symptoms appear.
Keywords: bacterial leaf blight, early detection,
immunosensor, rice disease, Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae
Abstrak
Satu strip imunosensor elektrokimia berasaskan
elektrod karbon bercetak skrin (SPCE) untuk pengesanan awal penyakit hawar daun
bakteria (BLB) pada pokok padi dilaporkan dalam kajian ini. Agen penyakit padi
ini telah dikenalpasti disebabkan oleh bakteria Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzea
(Xoo). Bagi mengekang penyebaran
penyakit padi ini, satu sistem pengesanan awal penyakit padi adalah diperlukan.
Antibodi poliklonal terhadap Xoo digunakan
dalam kajian ini dan dipegunkan ke atas permukaan strip yang telah diubah suai
dengan jaringan polipirol (PPy) dan nanotiub karbon berbilang dinding berfungsi
(fMWCNT). Antibodi anti-Xoo dikonjugasikan
dengan horseradish peroxidase (HRP) sebagai label enzim; dan digunakan
sebagai agen pengesanan dalam pembangunan sensor. Pengesanan elektrokimia
dilakukan dengan menggunakan teknik kronoamperometri pada set potensi -200 mV.
Pada kepekatan antibodi 0.03 mg/mLyang dipegunkan pada permukaan elektrod
bekerja strip, satu graf piawai linear untuk pengesanan Xoo berjaya dibangunkan (R2
= 0.9746). Bagi aplikasi sampel sebenar, dua kaedah pengekstrakan daun padi
(menggunting daun dan pengisaran daun) telah dibandingkan. Kaedah menggunting
daun didapati memberikan kesan matriks yang lebih rendah dan kadar pulangan
yang lebih tinggi berbanding kaedah pengisaran daun. Kaedah sensor ini kemudian
dibandingkan dengan teknik PCR bagi analisis sampel daun teraruh dengan
bakteria Xoo dalam persekitaran yang
terkawal. Korelasi yang baik dengan nilai 92.7% telah dicapai bagi kedua-dua
kaedah tersebut. Strip imunosensor ini kemudiannya diuji pada satu peranti
biosensor mudah alih berasaskan Android untuk pengesanan BLB di lapangan di
kawasan titik panas Bagan Terap, Barat Laut Selangor dan Sg. Burong, Tanjung
Karang. Kajian lapangan menunjukkan bahawa strip pengesanan imunosensor ini
berupaya mengesan penyakit BLB seawal hari ke-15 selepas transplan (HLT)
sebelum kemunculan simptom penyakit.
Kata kunci: hawar daun
bakteria, pengesanan awal, imunosensor, penyakit padi, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo)
Graphical Abstract
References
1.
Nurul Nahar, E., Adam, P., Mazidah, M., Roslan,
I., and Rafii, Y. M. (2020). Rice blast disease in Malaysia: Options for its
control. Journal of Tropical Agriculture
& Food Science, 48(1): 11-23.
2.
Shamsudin, N. A. A., Swamy, B. P. M., Ratnam,
W., Cruz, M. T. S., Raman, A. and Kumar, A. (2016). Marker assisted pyramiding
of drought yield QTLs into a popular Malaysian Rice Cultivar, MR219. BMC Genet. 17: 30.
3.
Faizal Azizi, M. M. and Lau, H. Y. (2022).
Advanced diagnostic approaches developed for the global menace of rice disease:
A review. Canadian Journal of Plant
Pathology, 44(5): 627-651.
4.
Song, E.S., Noh, T.H. and Chae, S.C. (2014).
PCR-based
assay
for rapid
and specific
detection
of the new
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae K3a race
using an AFLP-derived
marker.
Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 24(6): 732-739.
5.
Thakur, M., Wang, B. and Verma, M. L. (2022).
Development and applications of nanobiosensors for sustainable agricultural and
food industries: Recent developments, challenges and perspectives. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 26:
102371.
6.
Perez-Fernandez, B. and
de la Escosura-Muniz, A. (2022). Electrochemical
biosensors based on nanomaterials for aflatoxins detection: A review
(2015-2021). .Analytica Chimica Acta,
1212: 339658.
7.
Fang, Y. and Ramasamy, R. P. (2015). Current and
prospective methods for plant disease detection. Biosensors, 5(3): 537-561.
8.
Felix, F. S. and Angnes,
L. (2018).
Electrochemical
immunosensors—a
powerful
tool
for analytical
applications. Biosensors & Bioelectronic,
102:
470-478.
9.
Wen, W., Yan, X.,
Zhu, C. Du, D. and Lin, Y. (2017). Recent advances in
electrochemical immunosensors. Analytical Chemistry, 89:
138-156.
10. Sireesha, M., Babu, V.
J., Kiran, A. S. K. and Ramakrishna, S. (2018). A review on carbon nanotubes in
biosensor devices and their applications in medicine. Nanocomposites, 4(2):
36-57.
11. Bianchi,
V., Boni, A., Bassoli, M., Giannetto, M., Fortunati, S., Careri, M. and Munari,
I. D. (2021). IoT and biosensors: A smart portable potentiostat with advanced
cloud-enabled features. IEEE Access,
9: 141544-141554.
12. Uda,
M. N. A., Hasfalina, C. M., Samsuzanaa, A. A., Faridah, S., Gopinath, S. C. and
Parmin, N. A. (2019). A disposable biosensor based on antibody-antigen
interaction for tungro disease detection. Nanobiosensors
for Biomolecular Targeting, 2019: 147-164.
13. Mohd
Said, N. A., Abu Bakar, N. and Lau, H. Y. (2020). Label‐free Detection of
Erwinia mallotivora DNA for papaya
dieback disease using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy approach. ASM Science Journal, 13(4): 1-8.
14. Awaludin,
N., Abdullah, J., Salam, F., Ramachandran, K., Yusof, N. A. and Wasoh, H.
(2020). Fluorescence-based immunoassay for the detection of Xanthomonas oryzaepv. oryzae in rice leaf. Analytical Biochemistry, 610: 113876.
15. Shi, J. and Marshall Porterfield, D. (2014). Surface
modification approaches for electrochemical biosensors. Biosensors-Emerging Materials and Applications, 2014: 642.
16. heikhzadeh, E.,Chamsaz, M.,
Turner, A. P. F., Jager, E. W. H. and Beni, V. (2016). Label-free
impedimetric
biosensor
for Salmonella typhimurium detection
based
on poly
[pyrrole-co-3-carboxyl-pyrrole] copolymer supported
aptamer. Biosensors &
Bioelectronics, 80: 194-200.
17. Ancuta, D. and Constantin, A. (2021). Development of
polypyrrole modified screen-printed carbon electrode based
sensors for determination of l-tyrosine in pharmaceutical products. International Journal Molecular Science,
22:7528.
18. Welch, N. G., Scoble, J. A., Muir, B. W., and Pigram,
P. J. (2017). Orientation and characterization of immobilized antibodies for
improved immunoassays. Biointerphases,
12(2): 301.
19. Li, W., Diao, K., Qiu, D., Zeng, Y., Tang, K. and Zhu,
Y. (2021). A highly-sensitive and selective antibody-like sensor based on
molecularly imprinted poly (L-arginine) on COOH-MWCNTs for electrochemical
recognition and detection of deoxynivalenol.
Food Chemistry, 350: 129229.
20. Hassanein, A., Salahuddin, N., Matsuda, A., Kawamura,
G. and Elfiky, M. (2017). Fabrication of biosensor based on Chitosan-ZnO/Polypyrrole
nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode for electroanalytical
application. Materials Science & Engineering: C, 80:
494-501.
21. Abd Rahman, R., Razali, H., Mohd Said, N. A., Masdor,
N. A. and Salam, F. (2020). Determination of immunosensor parameters for a
sensitive and rapid detection of Xanthomonas
oryzae pv. oryzae. Transactions of The Malaysian Society of
Plant Physiology, pp. 27.
22. Mohd Said, N. A., Razali, H., Abd Rahman, R., Masdor,
N. A., Ismail, M. R. and Salam, F. (2018). Sensor optimizations for
immunosensor development for the detection of
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzicola in rice bacterial leaf streak.
Proccedings of National Conference on Agricultural and Food Mechanization 2018 (NCAFM
2018), 17-19 April, Pullman Kuching, Sarawak, pp. 313-316.
23. Hazana, R., Nur Azura, M. S. and Faridah, S. (2019).
Immunosensor development for the detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola
in rice bacterial leaf streak. Transactions
of The Malaysian Society of Plant Physiology, 26: 315-319.
24. Guo, M., Lan, J., Mingli Guan, J. S., Shi, J., Guan,
M., Wei, J., Liu, L., Li, L., Dou, S. and Liu, G. (2015). Western Blot
detection of Xanthomonas oryzaepv. Oryzae in rice, Journal of Plant Pathology & Microbiology, 4:1-6.
25. Wu, X., Kong, D., Song, S., Liu, L., Kuang, H. and Xu,
C. (2015). Development of sandwich ELISA and immune chromatographic strip
methods for the detection of Xanthomonas
oryzae pv. Oryzae. Analytical Methods, 7: 6190-6197.