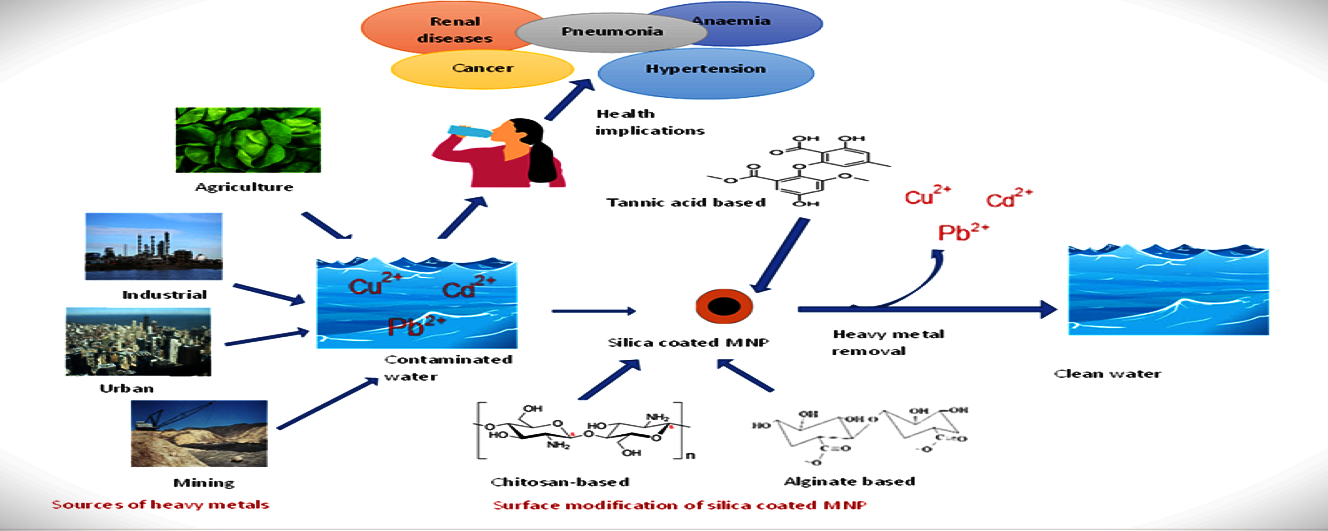
Graphical
Abstract
References
1. Sayato, Y.
(1989). WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. Eisei Kagaku, 35(5):
307-12.
2. WHO
(2003). Lead in drinking-water: background document for
development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO. Available from https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/75370.
3. WHO (2017).
Guidelines for drinking-water quality: first addendum to the fourth edition.
World Health Organisation. Available from:
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254636/9789241550017-eng.pdf
4. Ali, H., Khan,
E. and Ilahi, I. (2019), Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous
heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. Journal
of Chemistry, 2019: 6730305.
5. Zhang, Y. and
Duan, X. (2020). Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater by
using the synthetical magnesium hydroxy carbonate. Water Science Technology;
81(6):1130-1136.
6. Bashir, A.,
Malik, L. A., Ahad, S., Manzoor, T., Bhat, M. A., Dar, G. N., et al. (2019).
Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption
methods. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(2): 729-754.
7. Al-Shannag, M.,
Al-Qodah, Z., Bani-Melhem, K., Qtaishat, M. R. and Alkasrawi, M. (2015). Heavy
metal ions removal from metal plating wastewater using electrocoagulation:
Kinetic study and process performance. Chemical Engineering Journal,
260: 749-756.
8. Deliyanni, E.
A., Kyzas, G. Z., Matis, K. A., (2017). Various flotation techniques for metal
ions removal. Journal Molecular Liquids, 225: 260-264.
9. Yee, L. Y.,
Asrul, N. M., Kamarulzaman, F. F., Ali, T. G., Zulkifli, N. S. E., Kamaruddin,
A. F., et al. (2021). Recent advances in agricultural waste-based adsorbents
for the removal of pollutants in water (2017-2020). Malaysian Journal
Analytical Sciences, 25(3): 415-431.
10. Fouda-Mbanga, B.
G., Prabakaran, E. and Pillay, K., (2021). Carbohydrate biopolymers,
lignin-based adsorbents for removal of heavy metals (Cd2+, Pb2+,
Zn) from wastewater, regeneration, and
reuse for spent adsorbents including latent fingerprint detection: A review. Biotechnology
Reports, 30:e00609.
11. Cheng, T. H.,
Sankaran, R., Show, P. L., Ooi, C. W., Liu, B. L., Chai, W. S., et al. (2021).
Removal of protein wastes by cylinder-shaped NaY zeolite adsorbents decorated
with heavy metal wastes. International
Journal Biology Macromolecules, 185(May):761-772.
12. Khalfa, L.,
Sdiri, A., Bagane, M. and Cervera, M. L. (2021). A calcined clay fixed-bed
adsorption studies for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Journal Clean Production, 278:123935.
13. Zhang, Z., Wang,
T., Zhang, H., Liu, Y. and Xing, B. (2021). Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by
magnetic-activated carbon and its mechanism. Science Total
Environment, 757:143910.
14. Liu, Z. H. and
Yi, J. (2002), Falling film evaporation heat transfer of water/salt mixtures
from roll-worked enhanced tubes and tube bundle. Applied Thermal Engineering, 22(1): 83-95.
15. Yaacob, S. F. F.
S., Razak, N. S. A., Aun, T. T., Rozi, S. K. M., Jamil, A. K. M. and Mohamad,
S. (2018). Synthesis and characterizations of magnetic bio-material
sporopollenin for the removal of oil from aqueous environment. Industrial Crops Production,124(July):
442-448.
16. Abd Razak, N. F.,
Shamsuddin, M. and Lee, S. L. (2018). Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics
studies of gold(III) ions using thioctic acid-functionalized silica coated
magnetite nanoparticles. Chemical
Engineering Research Design, 130:18-28.
17. Ding, J., Gao,
Q., Luo, D., Shi, Z. G. and Feng, Y. Q. (2010). n-Octadecylphosphonic acid
grafted mesoporous magnetic nanoparticle: Preparation, characterization, and
application in magnetic solid-phase extraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217: 7351-7358.
18. Shen, Y., Zhao,
P. and Shao, Q., (2014). Porous silica and carbon derived materials from rice
husk pyrolysis char. Microporous
Mesoporous Materials, 188: 46-76.
19. Sutirman, Z. A., Sanagi, M. M.,
Abd Karim, K. J., Wan Ibrahim, W. A., Jume, B. H. (2018). Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies of
Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions adsorption by modified chitosan beads. International Journal Biology
Macromolecules,116: 255-263.
20. Poon, L., Wilson,
L. D. and Headley, J. V. (2014). Chitosan-glutaraldehyde copolymers and their
sorption properties. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 109: 92-101.
21. Song, X., Li, L.,
Zhou, L. and Chen, P., (2018). Magnetic thiolated/quaternized-chitosan
composites design and application for various heavy metal ions removal,
including cation and anion. Chemical
Engineering Research Design, 136: 581-592.
22. Sun, P., Zhang,
W., Zou, B., Zhou, L., Ye, Z. and Zhao, Q. (2021). Preparation of EDTA-modified
magnetic attapulgite chitosan gel bead adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II),
Pb(II), and Ni(II). International Journal
Biology Macromolecules, 182:1138-1149.
23. Chen, X., Huang,
Z., Luo, S. Y., Zong, M. H. and Lou, W. Y., (2021). Multi-functional magnetic
hydrogels based on Millettia speciosa
champ residue cellulose and chitosan: Highly efficient and reusable adsorbent
for Congo red and Cu2+ removal. Chemical
Engineering Journal, 423(5): 130198.
24. Elanchezhiyan, S.
S., Karthikeyan, P., Rathinam, K., Hasmath Farzana, M. and Park, C. M. (2021).
Magnetic kaolinite immobilized chitosan beads for the removal of Pb(II) and
Cd(II) ions from an aqueous environment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 261(3):117892.
25. Huang, Y., Hu,
C., An, Y., Xiong, Z., Hu, X., Zhang, G., et al. (2021). Magnetic phosphorylated chitosan
composite as a novel adsorbent for highly effective and selective capture of
lead from aqueous solution. Journal
Hazardous Materials, 405(7): 124195.
26. Liu, T., Han, X.,
Wang, Y., Yan, L., Du, B., Wei, Q., et al. (2017). Magnetic
chitosan/anaerobic granular sludge composite: Synthesis, characterization, and
application in heavy metal ions removal. Journal
Colloid Interface Sciences, 508:405-414.
27. Zhang, Q.,
Zhuang, S. and Wang, J. (2020). Biosorptive removal of cobalt(II) from aqueous
solutions using magnetic cyanoethyl chitosan beads. Journal Environmental
Chemical Engineering, 8(6):104531.
28 Sutirman, Z. A., Sanagi,
M. M., Abd Karim, K. J., Wan Ibrahim, W. A. and Jume, B. H. (2018).
Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions adsorption
by modified chitosan beads. International Journal of Biological
Macromolecules, 116:
255-263.
29. Pooladi, A. and
Bazargan-Lari, R. (2020). Simultaneous removal of copper and zinc ions by
Chitosan/hydroxyapatite/nano-magnetite composite. Journal
Materials Resesearch Technology, 9(6):14841-14852.
30. Feng, G., Ma, J.,
Zhang, X., Zhang, Q., Xiao, Y., Ma, Q., et al. (2019). Magnetic natural composite
Fe3O4-chitosan@bentonite for removal of heavy metals from
acid mine drainage. Journal Colloid
Interface Sciences,538:132-141.
31. Sun, H., Xia, N.,
Liu, Z., Kong, F. and Wang, S. (2019). Removal of copper and cadmium ions from
alkaline solutions using chitosan-tannin functional paper materials as
adsorbent. Chemosphere, 236:
124370.
32. Huang, H., Yang,
Q., Zhang, L., Huang, C. and Liang, Y., (2022). Polyacrylamide modified kaolin
enhances the adsorption of sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel
beads for copper ions. Chemical
Engineering Research Design, 180 :296-305.
33. Zhang, H., Li, R.
and Zhang, Z., (2022). A versatile EDTA and chitosan bi-functionalized magnetic
bamboo biochar for simultaneous removal of methyl orange and heavy metals from
complex wastewater. Environmental Pollution,
293(11):118517.
34. Karimi, F.,
Ayati, A., Tanhaei, B., Sanati, A. L., Afshar, S., Kardan, A., et al. (2022). Removal of metal ions using a new
magnetic chitosan nano-bio-adsorbent; A powerful approach in water treatment. Environmental
Research, 203(5): 111753.
36. Nasirimoghaddam, S., Zeinali, S. and Sabbaghi, S.,
(2015). Chitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbent for efficient
removal of mercury contents from industrial aqueous and oily samples. Journal
Industrial Engineering Chemistry, 27(2014): 79-87.
37. Jiang, Y.,
Cai, W., Tu, W. and Zhu, M., (2019). Facile cross-link method to synthesize magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-chitosan
with high adsorption capacity toward hexavalent chromium. Journal
Chemical Engineering Data, 64(1): 226-233.
38 Kim, H.
S., Lee, C. G. and Lee, E. Y. (2011). Alginate lyase: Structure, property, and
application. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 16(5): 843-851.
39. Ren, H., Gao, Z.,
Wu, D., Jiang, J., Sun, Y. and Luo, C. (2016). Efficient Pb(II) removal using sodium
alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and
adsorption mechanism. Carbohydrate Polymers, 137: 402-409.
40. Córdova, B. M.,
Venâncio, T., Olivera, M. and Huamani-Palomino, R. G. (2021). Xanthation of
alginate for heavy metal ions removal. Characterization of xanthate-modified
alginates and their metal derivatives. International Journal Biology
Macromoleclues, 169: 130-142.
41. Fuks, L.,
Herdzik-Koniecko, I., Polkowska-Motrenko, H. and Oszczak, A. (2018). Novel procedure
for removal of the radioactive metals from aqueous wastes by the magnetic
calcium alginate. International Journal Environmental Science Technology, 15(12):
2657-2668.
42. Lee, H. K., Choi,
J. W., Kim, J. H., Kim, C. R. and Choi, S. J. (2021). Simultaneous selective
removal of cesium and cobalt from water using calcium alginate-zinc
ferrocyanide-Cyanex 272 composite beads. Environmental Science Pollution
Ressearch, 28: 42014-42023.
43. Song, D., Park,
S., Kang, H. W., Park, S. and Bin Han, J. (2013). Recovery of lithium (I),
strontium (II), and lanthanum (III) using Ca-alginate beads. Journal
Chemical Engineering Data, 58: 2455-2464.
44. Dai, M., Liu, Y.,
Ju, B. and Tian, Y. (2019). Preparation of thermoresponsive alginate/starch
ether composite hydrogel and its application to the removal of Cu(II) from
aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 294(7):122192.
45. Ahmed, A.,
Mohamed, F., Elzanaty, A. M. and Abdel-Gawad, O. F. (2021). Synthesis and
characterization of diphenylamine grafted onto sodium alginate for metal
removal. International Journal Biology Macromolecules, 167:766-776.
46. Allouss, D.,
Essamlali, Y., Chakir, A., Khadhar, S. and Zahouily, M. (2020). Effective
removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution over graphene oxide encapsulated carboxymethylcellulose-alginate
hydrogel microspheres: towards real wastewater treatment plants. Environmental
Science Pollution Ressearch, 27(7):7476-7492.
47. Hassan, R. M. (2021).
Novel synthesis of natural cation exchange resin by crosslinking the sodium
alginate as a natural polymer with 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate in inert
solvents: Characteristics and application. International
Journal Biology Macromolecules, 184:926-935.
48. Córdova, B. M.,
Infantas, G. C., Mayta, S., Huamani-Palomino, R. G., Kock, F. V. C., Montes de
Oca, J., et al. (2021). Xanthate-modified alginates for the removal of Pb(II)
and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions: A brief analysis of alginate xanthation. International
Journal Biology Macromolecules, 179:557-566.
49. Ibrahim, W. A.
W., Hassan, A. A. M., Sutirman, Z. A. and Bakar, M. B. (2020). A mini review on
sporopollenin-based materials for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous
solution. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 24(3): 300-312.
50. Ahmad, N. F.,
Kamboh, M. A., Nodeh, H. R., Nadiah, S., Abd, B. and Mohamad, S. (2017). Synthesis
of piperazine functionalized magnetic sporopollenin: a new organic-inorganic
hybrid material for the removal of lead (II) and arsenic (III) from aqueous
solution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(27):
21846-21858.
51. Sayin, S., Gubbuk,
I. H. and Yilmaz, M. (2013). Preparation of calix[4]arene-based sporopollenin
and examination of its dichromate sorption ability. Journal of Inclusion
Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 75(12):111-118.
52. Ünlü, N. and
Ersoz, M., (2007). Removal of heavy metal ions by using
dithiocarbamate-sporopollenin. Separaction and Purification Technology,
52(3): 461-469.
53. Hassan, A. M.,
Wan Ibrahim, W. A., Bakar, M. B., Sanagi, M. M., Sutirman, Z. A., Nodeh, H. R.,
et al. (2020). New effective 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane functionalized
magnetic sporopollenin-based silica coated graphene oxide adsorbent for removal
of Pb(II) from aqueous environment. Journal Environental Management,
253(10):109658.
54 Ren, Y., Abbood,
H. A., He, F., Peng, H., Huang, K. (2013). Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4
adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal
adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226: 300-311.
55. Bilgic, A.,
Cimen, A., Bastug, E. and Kursunlu, A. N. (2022). Fluorescent sporopollenin
microcapsule modified by BODIPY for sensitive&selective recognition
and efficient removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Research Design,178: 61-72.
56. Ahmad, N. F.,
Kamboh, M. A., Nodeh, H. R., Halim, S. N. B. A. and Mohamad, S., (2017).
Synthesis of piperazine functionalized magnetic sporopollenin: a new
organic-inorganic hybrid material for the removal of lead(II) and arsenic(III)
from aqueous solution. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 24(27):
21846-21858.
57 Sargin
I, Arslan G. (2015). Chitosan/sporopollenin microcapsules: Preparation,
characterization, and application in heavy metal removal. International Journal Biology
Macromolecules, 75: 230-238.
58. Sargin, İ.
And Arslan, G., (2016). Effect of glutaraldehyde cross-linking degree of
chitosan/sporopollenin microcapsules on the removal of copper(II) from aqueous
solution. Desalination Water Treatment, 57(23): 10664-10676.
59. Şener, M.,
Reddy, D. H. K. and Kayan, B. (2014). Biosorption properties of pretreated
sporopollenin biomass for lead(II) and copper(II): Application of response
surface methodology. Ecological Engineering, 68: 200-208.
60. Ersoz, M.,
Pehlivan, E., Duncan, H. J., Yildiz, S. and Pehlivan, M. (1995), Ion exchange
equilibria of heavy metals in aqueous solution on new chelating resins of
sporopollenin. Reaction Polymers, 24(3): 195-202.
61. Bagtash, M.,
Yamini, Y., Tahmasebi, E., Zolgharnein, J. and Dalirnasab, Z., (2016).
Magnetite nanoparticles coated with tannic acid as a viable sorbent for
solid-phase extraction of Cd2+, Co2+, and Cr3+.
Microchimica Acta, 183(1): 449-456.
62. Makeswari, M.
(2013). Tannin gel derived from leaves of Ricinus communis as an adsorbent
for the removal of Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution. International
Journal of Modern Engineering Research, 3(5): 3255-3266.
63. Kavitha, V. U.
and Kandasubramanian, B. (2020). Tannins for wastewater treatment. SN
Applied Sciences, 2: 1081.
64. Zou, L., Shao,
P., Zhang, K., Yang, L., You, D., Shi, H., et al. (2018). Tannic acid-based
adsorbent with a superior selectivity for lead(II) capture: Adsorption site and
selective mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 364: 160-166.
65. Huang, L., Shuai,
Q. and Hu, S. (2019), Tannin-based magnetic porous organic polymers as robust
scavengers for methylene blue and lead ions. Journal Cleaner Production,
215: 280-289.
66. Huang, Q., Zhao,
J., Liu, M., Chen, J., Zhu, X., Wu, T., et al. (2018). Preparation of
polyethylene polyamine@tannic acid encapsulated MgAl-layered double hydroxide
for the efficient removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution. Journal
Taiwan Institute Chemical Engineering, 82:92-101.
67. Shi, P., Hu, X.,
Duan, M. (2021). A UIO-66/tannic acid/chitosan/polyethersulfone hybrid
membrane-like adsorbent for the dynamic removal of dye and Cr(VI) from water. Journal
Cleaner Production, 290: 125794.
68. Liu, Q., Liu, Q.,
Liu, B., Hu, T., Li,u W. and Yao, J., (2018), Green synthesis of
tannin-hexamethylenediamine based adsorbents for efficient removal of Cr(VI). Journal
Hazardous Materials, 352(3):27-35.
69. Gao, J., Lei, H.,
Han, Z., Shi, Q., Chen, Y. and Jiang, Y., (2017). Dopamine functionalized
tannic-acid-templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the
efficient removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Scientific
Reports, 7(7): 1-11.
70. Zhang, Y., He, F.
and Li, X. (2016). Three-dimensional composite hydrogel based on polyamine
zirconium oxide, alginate, and tannic acid with high performance for Pb(II),
Hg(II), and Cr(VI) trapping. Journal Taiwan Institute Chemical Engineering,
65: 304-311.
71. Deng, X., Wang,
L., Xiu, Q., Wang, Y., Han, H., Dai, D., et al. (2021). Adsorption performance
and physicochemical mechanism of MnO2-polyethyleneimine-tannic acid
composites for the removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Frontier
Chemical Science Engineering, 15(3): 538-551.
72. Zhu, Y. H.,
Zhang, Q., Sun, G. T., Chen, C. Z., Zhu, M. Q. and Huang, X. H. (2022), The
synthesis of tannin-based graphene aerogel by hydrothermal treatment for
removal of heavy metal ions. Industrial Crops and Production,
176:114304.
73. Üçer, A., Uyanik,
A. and Aygün, Ş. F. (2006). Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II), Zn(II), Mn(II),
and Fe(III) ions by tannic acid immobilized activated carbon. Separation
Purification Technology, 47(3): 113-118.
74. Fan, R., Min, H.,
Hong, X., Yi, Q., Liu, W., Zhang, Q., et al. (2019). Plant tannin immobilized
Fe3O4@SiO2 microspheres: A novel and green
magnetic bio-sorbent with superior adsorption capacities for gold and
palladium. Journal Hazardous Materials, 364:780-790.
75. Zhang, S., Zhang,
Y., Liu, J., Xu, Q., Xiao, H., Wang, X., et al. (2013). Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2
as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury
removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226: 30-38.
76 Egodawatte, S.,
Datt, A., Burns, E. A. and Larsen, S. C. ( 2015) Chemical insight into the adsorption of
chromium(III) on iron oxide/mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Langmuir,
31(27): 7553-7562.
77 Sabermahani F.,
Irannejad, L. and Mahani, N. M. (2018).
Using polyaniline/maghemit magnetic nanocomposite for removal of lead from
aqueous solutions. Iranian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 5(1): 33-38.
78. Lin, Y., Chen,
H., Lin, K., Chen, B. and Chiou, C., (2011). Application of magnetic particles
modified with amino groups to adsorb copper ions in aqueous solution. Journal
Environmental Sciences, 23(1):44-50.
79. Jin, S., Park, B.
C., Ham, W. S., Pan, L. and Kim, Y. K. (2017). Effect of the magnetic core size
of amino-functionalized Fe3O4-mesoporous SiO2
core-shell nanoparticles on the removal of heavy metal ions. Colloids
Surfaces A Physicochemical Engineering Aspects, 531(8):133-140.
80. Nodeh, H. R., Aini,
W., Ibrahim, W. and Sanagi, M. M. (2016). Development of magnetic graphene
oxide adsorbent for the removal and preconcentration of As (III) and As (V)
species from environmental water samples. Environmental Science Pollution
Research, 23: 9759-9773.
81. Purwanto, A.,
Putri, E. A. and Rosyidah, D. (2017). Adsorption of Pb (II) using silica gel
composite from rice husk ash modified 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) -
activated carbon from coconut shell. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1823:
020034.
82. Ahmad, N.,
Sereshti, H., Mousazadeh, M., Rashid Nodeh, H., Kamboh, M. A., Mohamad, S.
(2019), New magnetic silica-based hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposite for
the removal of lead(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Materials
Chemistry and Physics, 226: 73-81.
83. Wang Z, Xu J, Hu Y, Zhao H, Zhou J, Liu Y, et al. (2015).
Functional nanomaterials: Study on aqueous Hg(II) adsorption by magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-SH
nanoparticles. Journal Taiwan Institute Chemical Engineering, 60: 394-402.
84. Ghorbani, M., Shams, A., l Seyedin,
I. and Lahoori, O. N. (2018). Magnetic ethylene
diamine-functionalized graphene oxide as a novel sorbent for removal of lead
and cadmium ions from wastewater samples. Environmental Science and
Pollution Research, 25: 5655-5667.
85. Santhosh,
C., Daneshgar, E., Kollu,
P., Peräniemi, S.,
Nirmala, G., A., Bhatnagar, A.
(2017). Magnetic SiO2@CoFe2O4 nanoparticles
decorated on graphene oxide as efficient adsorbents for the removal of anionic
pollutants from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 322: 472-487.