Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 6 (2022): 1260 - 1273
Ferrocene
mediated amperometric biosensor for
L-glutamate based on L-glutamate oxidase
immobilized
in a photocurable methacrylic film
(Biosensor Amperometrik L-Glutamat berperantara Ferosena
berasaskan L-Glutamat Oksida Terpegun dalam Fotosalutan Filem Metakrilik)
Noor Zuhartini Md Muslim1*, Musa Ahmad2,
Lee Yook Heng3, Bahruddin Saad4
1School of Health
Sciences, Health Campus,
Universiti Sains
Malaysia, 16150 Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia
2Faculty of
Science & Technology,
Universiti Sains
Islam Malaysia, 71800 Bandar Baru Nilai, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia
3School of
Chemical Sciences and Food Technology,
Faculty of
Science & Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi,
Selangor, Malaysia
4Department of
Fundamental & Applied Scinces,
Universiti
Teknologi PETRONAS, Bandar Seri Iskandar, 32610 Perak, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: zuhartini@usm.my
Received: 24 May 2022; Accepted: 27
September 2022; Published: 27 December
2022
Abstract
L-glutamate is widely used as a flavour enhancer
in various foodstuffs and seasoning in the form of monosodium glutamate (MSG).
MSG has been linked to neurotoxic effects, metabolic disorders, headache,
numbness and palpitation. In this work, an amperometric
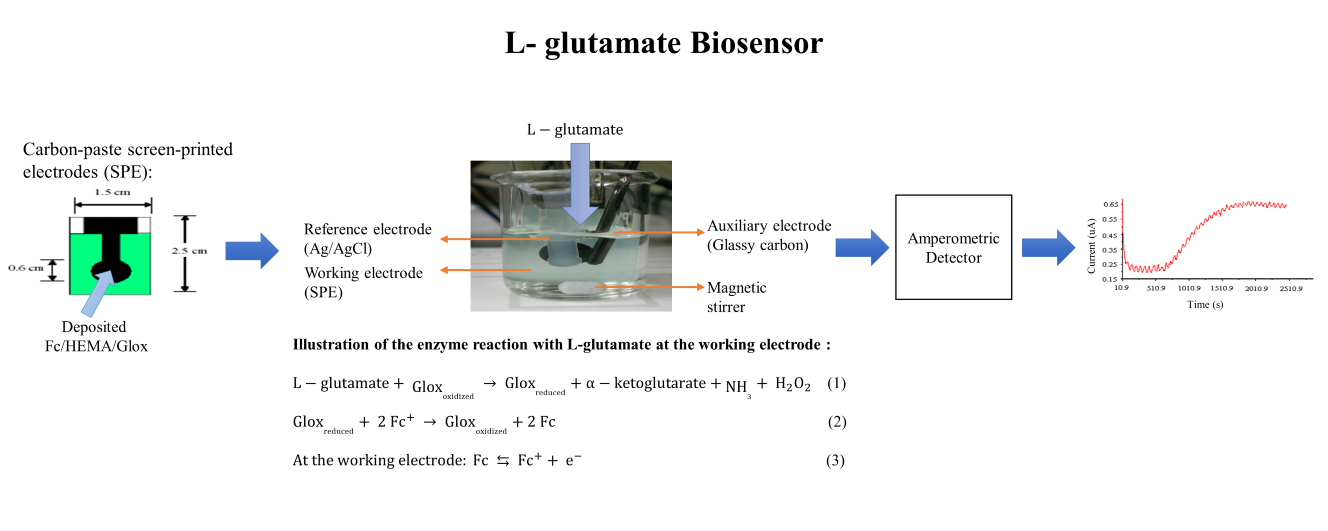
L-glutamate biosensor based on photocurable poly(2-hydroxylethyl
methacrylate)-containing ferrocene film for the determination of L-glutamate in
food samples is described. The sensor is fabricated based on simultaneous
immobilization of both L-glutamate oxidase and ferrocene as a mediator during
the deposition of poly(2-hydroxylethyl methacrylate) film via photocuring.
Ferrocene was used to shuttle the electrons directly between the reduced enzyme
and the electrode. From electrochemical studies, a linear response towards
L-glutamate in the concentration range of 10-30 mM was obtained at applied
potential of +0.25 V with the detection limit of 7.7 mM.
The storage stability of the biosensor is up to 4 months under storage
condition of 4 oC in refrigerator. The
performance of the biosensor was applied to the determination of L-glutamate in
food stocks from local supermarkets. Results from amperometric
L-glutamate biosensor were further validated with HPLC method.
Keywords: photocurable, methacrylate polymers, ferrocene,
L-glutamate biosensor
Abstrak
L-glutamat digunakan secara meluas
dalam pelbagai bahan makanan dan perasa dalam bentuk mononatrium glutamat (MSG).
MSG telah dikaitkan dengan kesan neurotoksik, gangguan metabolik, sakit kepala,
rasa kebas dan berdebar-debar. Biosensor amperomerik L-glutamat berasaskan
fotosalutan poli(2-hidroksiletil matakrilat)-mengandungi filem ferosena
dihuraikan untuk penentuan L-glutamat di dalam sampel makanan. Sensor ini
direka berasaskan pemegunan secara serentak bagi L-glutamat oksida dan ferosena
sebagai perantara semasa pemendapan filem poli(2-hidroksiletil metakrilat)
menerusi fotosalutan. Ferosena digunakan sebagai perantara ulang-alik elektron
secara langsung antara penurunan enzim dengan elektrod. Berdasarkan kajian
elektrokimia, rangsangan linear terhadap L-glutamat diperoleh dalam julat
kepekatan 10-30 mM pada keupayaan +0.25 V dengan had pengesanan 7.7 mM. Jangka
hayat kestabilan biosensor penyimpanan dalam peti sejuk adalah mencapai
sehingga 4 bulan pada suhu 4oC. Prestasi biosensor diaplikasikan
untuk penentuan L-glutamat dalam stok makanan daripada pasar raya tempatan.
Keputusan daripada biosensor L-glutamat seterusnya disahkan dengan kaedah HPLC.
Kata kunci: fotosalutan,
polimer metakrilat, ferosena, biosensor L-glutamat
Graphical Absract
References
1.
Borisova, T., Kucherenko, D.,
Soldatkin, O., Kucherenko, I., Pastukhov, A., Nazarova, A., Galkin, M.,
Borysov, A., Krisanova, N., Soldatkin, A. and El`skaya, A. (2018). An
amperometric glutamate biosensor for monitoring glutamate release from brain
nerve terminals and in blood plasma. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1022:
113-123.
2.
Isoaho, N., Peltola, E., Sainio, S., Koskinen, J. and
Laurila, T. (2018). Pt-grown carbon nanofibers for enzymatic glutamate
biosensors and assessment of their biocompatibility. Royal Society of
Chemistry Advance, 8, 35802-35812.
3.
Malaysia and International Law Book Services (2015).
Food act 1983 (Act 281) & regulations. International Law Book Services,
Petaling Jaya.
4.
EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added
to Food. (2017). Re-evaluation of glutamic acid (E 620), sodium glutamate (E
621), potassium glutamate (E 622), calcium glutamate (E 623), ammonium
glutamate (E 624) and magnesium glutamate (E 625) as food additives. EFSA
Journal, 15: 4910-4999.
5.
Lateef, M., Siddiqui, K.,
Saleem, M and Iqbal, L. (2012). Estimation of monosodium glutamate by modified
HPLC method in various pakistani spices formula. Journal- Chemical Society
of Pakistan, 34: 39-42.
6.
Soyseven, M. and Arli, G. (2021). Method validation and
rapid determination of monosodium glutamate in various food products by
HPLC–fluorescence detection and method optimization of HPLC–evaporative light
scattering detection approach without derivatization. Journal of
Chromatographic Science, 122: 60(8):760-769.
7.
Mustafa, S., Saleem, Y. and Hameed, S. (2015).
Determination of monosodium glutamate content in selected traditional meat
dishes. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research,
6: 569-572.
8.
Krishna Veni, N., Karthika, D., Surya Devi, M., Rubini,
M. F., Vishalini, M. and Pradeepa, Y. J. (2010). Analysis of monosodium
l-glutamate in food products by high-performance thin layer chromatography. Journal
of Young Pharmacists, 2: 297-300.
9.
Ambusaidi, M. M. S. K., Pandian, S. B. S., Swaminathan,
S. and Sudhakar, M. S. (2020). A survey on the monosodium glutamate occurrence
in food products and it’s analysis by thin layer chromatography and liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry from sultanate of Oman. International
Journal of Analytical and Bioanalytical Methods, 2: 1-11.
10.
Camila, D. M. C., Felix, G. R. R., Andreas, M. and
José, A. F. (2019). On-line electroextraction in capillary electrophoresis:
application on the determination of glutamic acid in soy sauces. Electrophoresis,
40: 323-329.
11.
Nuradi and Widarti (2018). Analysis of monosodium glutamat level on
meatballs snacks (BAKSO) sold in the Makassar and Parepare City of South
Sulawesi Province with visible spectrophotometer. International Journal of
Sciences: Basic and Applied Research, 38: 34-41.
12.
Ali, H. M., Hammad, S. F. and El-Malla, S. F. (2021).
Green spectrophotometric methods for
determination of a monosodium glutamate in different matrices. Microchemical
Journal, 169: 1-9.
13.
Rachma, F. A. and Saptawati, T. (2021). Analysis
tolerance of monosodium glutamate (MSG) in instant noodles with uv-vis
spectrophotometry. Journal of Science and Technology Research for Farmacy,
1: 20-24.
14.
Alonge, P. O., Idemudia, O. S. and Odokuma-Alonge, O. (2019). Direct
assay of monosodium glutamate in multi-sourced bouillon cubes by first
derivative potentiometric titration. Journal of Applied Sciences and
Environmental Management, 23: 299-304.
15.
Cui, Y., Barford, J. P. and Renneberg, R. (2007).
Development of an interference-free biosensor for l-glutamate using a bienzyme
salicylate hydoxylase/l-glutamate dehydrogenase system. Enzyme and Microbial
Technology, 41: 689-693.
16.
Lioe, H. N., Dyahpakarti, G. C., Zakaria, N. A.,
Sudrajat, H. R., and Rahayu, I. (2019). Exposure assessment of monosodium
glutamate in prepared foods with frying, sautéing, grilling or baking process. Proceedings
of the 2nd SEAFAST International Seminar, pp. 49-56.
17.
Zhang, M., Mullens, C. and Gorski, W. (2006).
Amperometric glutamate biosensor based on chitosan enzyme film.
Electrochimica Acta, 51: 4528-4532.
18.
Chang, K. –S, Chang, C. –K, Chou, S. –F., Han, H. –C. and
Chen, C. –Y. (2007). Characterization of a planar l-glutamate amperometric
biosensor immobilized with a photo-crosslinkable polymer membrane. Sensors
and Actuators B, 122: 195-203.
19.
Alnokkari, A., Ataie, M. and Alasaf, Z. (2013).
Colorimetric determination of monosodium glutamate in food samples using l-glutamate oxidase. Chinese
Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 19: 1069-1072.
20.
Yılmaz, D. and Karakus, E. (2011). Construction of
a potentiometric glutamate biosensor for determination of glutamate in some
real samples. Artificial Cells, Blood Substitutes, and Biotechnology,
39: 385-391.
21.
Mizutani, S., Okumura, Y., Horio, T., Iwata, T.,
Okumura, K., Takahashi, K., Murakami, Y., Dasai, F., Ishida, M. and Sawada, K.
(2017). Development of glutamate sensor for neurotransmitter imaging. Sensors
and Materials, 29: 253-260.
22.
Soldatkina, O. V., Soldatkin, O.
O., Ozansoy Kasap, B., Kucherenko, D. Yu., Kucherenko, I. S., Akata Kurc, B.
and Dzyadevych, S. V. (2017). A novel amperometric glutamate biosensor based on
glutamate oxidase adsorbed on silicalite. Nanoscale Research Letters, 12:
1-8.
23.
Liu, J., Fan, Y., Chen, G. and Liu, Y. (2021). Highly
sensitive glutamate biosensor based on platinum nanoparticles decorated
MXene-Ti3C2Tx for l-glutamate determination in
foodstuffs. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 148: 1-8.
24.
Sim Bean, L., Yook Heng, L., Yamin, B. M. and Ahmad, M.
(2005). Photocurable ferrocene-containing poly(2-hydroxyl ethyl methacrylate)
films for mediated amperometric glucose biosensor. Thin solid Films, 477: 104-110.
25.
Sarika, C., Rekha, K. and Narasimha Murthy, B. (2015).
Studies on enhancing operational stability of a reusable laccase-based biosensor
probe for detection of ortho-substituted phenolic derivatives. 3 Biotech,
5: 911-924.
26.
Ryth-Rinder, M.,
Kerekes, N., Svensson, M. and Hökfelt, T. (2001). Glutamate release from adult
primary sensory neurons in culture is modulated by growth factors. Regulatory Peptides, 102: 69-79.
27.
Wachiratianchai, S., Bhumiratana, A.
and Udomsopagit, S. (2004). Isolation, purification, and characterization of
l-glutamate oxidase from Streptomyces
sp. 18G. Journal of Biotechnology, 7: 277-284.
28.
Haymond, S., Babcock, G. T. and Swain, G. M. (2003).
Electron transfer kinetics of ferrocene at microcryctalline boron-doped diamond
electrodes: Effects of solvent and electrolytes. Electroanalysis, 15:
249-253.
29.
Maalouf, R., Chebib, H., Saïkali, Y., Vittori, O.,
Sigaud, M. and Jaffrezic-Renault, N. (2007). Amperometric and impedimetric
characterization of a glutamate biosensor based on Nafion® and a
methyl viologen modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 22: 2682-2688.
30.
Wang, H.-S., Pan, Q.-X. and Wang, G. -X. (2005). A
biosensor based on immobilization of horseradish peroxide in chitosan matrix
cross-linked with glyoxal for amperometric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Sensors,
5: 266 -276.
31.
Lim, P. E. and Ang, T. T. (1990). Enzim dan ilmu
energetik sel. Pusat Pengajian Luar Kampus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Pulau
Pinang.
32.
Deng, Q., Guo, Y. and Dong, S. (1996). Cyro-hydrogel
for the construction of a tyrosinase-based biosensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 319: 71-77.
33.
Seidel, J. M. and Malmonge, S. M. (2000). Synthesis of
polyHEMA hydrogels for using as biomaterials. bulk and solution
radical-initiated polymerization techniques. Material Research, 3:
79-83.
34.
Neumann, M. G., Schmitta, C. C., Catalina, F. and Goi,
B. E. (2007). Material behaviour: The relation between the polymerization rates
and swelling coefficients for copolymers obtained by photoinitiation. Polymer
Testing, 26: 189-194.
35.
Miller, J. N. and Miller, J. C. (2000). Statistics and
chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 4th Edition, Pearson
Education.
36.
Janarthanan, C. and Mottola, H. A. (1998). Enzymatic
determinations with rotating bioreactors: Determination of glutamate in food
products. Analytical Chimica Acta,
369: 147-155.
37.
Isa, I. M. and Ghani, S. A. (2009). A non-plasticized
chitosan based solid state electrode for flow injection analysis of glutamate
in food samples. Food Chemistry, 112: 756-759.
38.
Upadhyay, S., Ohgami, N., Kusakabe, H., Mizuno, H.,
Arima, J., Tamura, T., Inagaki, K. and Suzuki, H. (2006). Performance
characterization of recombinant l-glutamate oxidase in a micro GOT/GPT sensing
system. Sensors and Actuators B, 119: 570 – 576.
39.
Karyakin, A. A., Karyakina, E. E. and Lo Gorton. (2000).
Amperometric biosensor for glutamat using prussion blue-based “artificial
peroxidase” as a transducer for hydrogen peroxide. Analytical Chemistry,
72: 1720-172.