Malaysian Journal of Analytical
Sciences, Vol 26
No 5 (2022): 1023 - 1036
(Templat Bio Bismut Ferit (BiFeO3) Nanopemangkin
untuk Fotodegradasi Ofloxacin Menggunakan Cahaya Suria Dibawah Pengaruh
Parameter Operasi)
Ahmad Fadhil Rithwan1,
Muhammad Alif Abdul Khani1, Noor Haida Mohd Kaus1*,
Rohana Adnan1,
Sirikanjana
Thongmee2, Siti Fairus Mohd Yusoff3, Takaomi Kobayashi4,
Mohd Amirul Ramlan5
1 School
of Chemical Sciences,
Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
2Physics
Department,
Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok 10900,
Thailand
3
Department of Chemical Sciences,
Faculty of Science and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malaysia,
Bangi 43600, Selangor, Malaysia
4Department
of Materials Science and Technology,
Nagaoka University of Technology Nagaoka, Japan
5Department
of Polytechnic & Community Colleges Education,
Ministry of Higher Education, Persiaran Perdana, Presint 4,
Putrajaya 62100, Malaysia
*Corresponding
author: noorhaida@usm.my
Received: 2 March 2022; Accepted: 3
July 2022; Published: 30 October2022
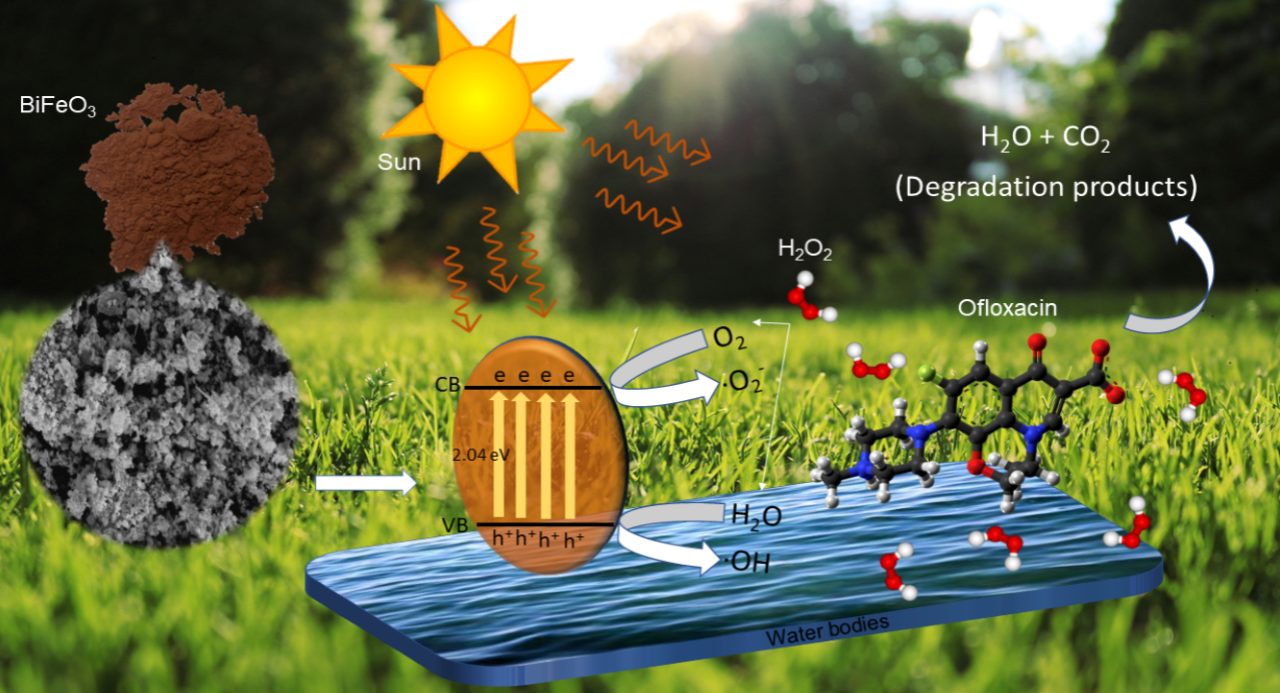
Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3)
has been demonstrated to be one of the most efficient perovskite-based
photocatalysts for pollutant degradation under direct sunlight. The focus of
this research was to study the photocatalytic activity of BiFeO3 in
relation to the degradation of the antibiotic ofloxacin. Different operational
parameters for the optimized system were determined, such as photocatalyst
dosage (0.05 g L-1 to 0.50 g L-1), pollutant
concentration (2.5 mg L-1 to 20 mg L-1), reaction
duration (2 hours), pH of solution (pH 2 to pH 12), and the effect of hydrogen
peroxide, H2O2 as an oxidant (0.1 M to 0.7 M). X-ray
Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope-Energy Dispersive X-ray
(SEM-EDX), and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses all
corroborated that the rhombohedral BiFeO3 has a high purity and
large surface area. The most efficient condition for all selected parameters
was 0.07 g L-1 BiFeO3 at pH 8 in 10 mg L-1 of
ofloxacin and the addition of 0.3 M H2O2 with 70.1%
degradation and the total organic carbon left in the solution was 9.36%. The
reaction obeyed pseudo-first order kinetics with R2 value obtained
is 0.9399, with decreasing k values as the initial concentration
increased. This demonstrated that the system performed best at low
concentrations. This discovery paves the way for future research into the
operational parameters that contribute to the photocatalyst efficacy in
removing antibiotics as a pollutant.
Keywords: photocatalysis,
photofunctional material, ofloxacin, visible light source, bismuth ferrite
Ferit bismut, BiFeO3 terbukti sebagai salah satu
daripada fotopemangkin berasaskan perovskit terbaik untuk degradasi pelbagai
pencemar di bawah cahaya matahari langsung. Kajian ini dijalankan untuk
mempelajari prestasi fotoaktiviti BiFeO3 terhadap degradasi
antibiotik ofloxacin. Parameter operasi yang berbeza telah ditentukan untuk
sistem yang dioptimumkan termasuk dos fotopemangkin (0.05 g L-1
hingga 0.50 g L-1), kepekatan bahan cemar (2.5 mg L-1
hingga 20 mg L-1), masa tindak balas (2 jam), pH (pH 2 hingga pH
12), dan kesan hidrogen peroksida (H2O2) sebagai agen
pengoksidaan (0.1 M hingga 0.7 M). Keputusan analisis pembelauan sinar-x (XRD),
spektroskopi inframerah-transformasi Fourier (FT-IR) dan mikroskop elektron
imbasan-spektroskopi sinar-x penyebaran tenaga (SEM-EDX) mengesahkan ketulenan
tinggi BiFeO3 rombohedral yang telah dihasilkan dengan luas
permukaan yang tinggi. Keadaan yang paling berkesan untuk semua parameter
terpilih adalah dos BiFeO3 0.07 g L-1 pada pH 8 di dalam
10 mg L-1 ofloxacin dengan penambahan 0.3 M H2O2
yang menghasilkan degradasi ofloxacin sebanyak 70.1% dan jumlah kesuluruhan
karbon yang tinggal didalam larutan adalah sebanyak 9.36 %. Tindak balas ini
tergolong di dalam urutan kinetik pseudo-pertama dengan nilai R2
tercapai sebanyak 0.9399, dengan nilai k menurun apabila kepekatan awal
meningkat. Ini menunjukkan bahawa sistem ini adalah lebih efisyen pada
kepekatan yang rendah. Penemuan ini telah membuka satu kajian berpotensi ke
arah penerokaan faktor yang meningkatkan kecekapan fotopemangkin bagi
penyingkiran pencemar antibiotik.
Kata
kunci: fotopemangkinan, bahan
fotofungsian, ofloxacin, sumber cahaya boleh lihat, bismut ferit

Reference
1. Siddique, M., Khan, N. M., & Saeed, M.
(2019). Photocatalytic activity of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles synthesized
via sol-gel route. Zeitschrift Fur Physikalische Chemie, 233(5):
595-607.
2. Huang, Q., Liu, Y., Cai, T. and Xia, X.
(2019). Simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions and organic pollutant by
BiOBr/Ti3C2 nanocomposite. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:
Chemistry, 375(December 2018): 201-208.
3. Boruah, P. K. and Das, M. R. (2020). Dual
responsive magnetic Fe3O4-TiO2/graphene
nanocomposite as an artificial nanozyme for the colorimetric detection and
photodegradation of pesticide in an aqueous medium. Journal of Hazardous
Materials, 385: 121516.
4. Sharma, P., Kumar, N., Chauhan, R., Singh,
V., Srivastava, V. C. and Bhatnagar, R. (2020). Growth of hierarchical ZnO nano
flower on large functionalized rGO sheet for superior photocatalytic
mineralization of antibiotic. Chemical Engineering Journal, 392: 123746.
5. Van Boeckel, T. P., Gandra, S., Ashok, A.,
Caudron, Q., Grenfell, B. T., Levin, S. A. and Laxminarayan, R. (2014). Global
antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: An analysis of national pharmaceutical
sales data. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 14(8): 742-750.
6. Ambrosetti, B., Campanella, L. and
Palmisano, R. (2015). Degradation of antibiotics in aqueous solution by
photocatalytic process: Comparing the efficiency in the use of ZnO or TiO2.
Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering A, 4(6): 273-281.
7. Manzetti, S. and Ghisi, R. (2014). The
environmental release and fate of antibiotics. Marine Pollution Bulletin,
79(1–2): 7-15.
8. Huang, J., Cao, J., Ding, Y., Hu, Y., Cen,
Y. and Tang, H. (2018). Variable-valence metals catalyzed solid NaBiO3
nanosheets for oxidative degradation of norfloxacin, ofloxacin and
ciprofloxacin: Efficiency and mechanism. Chemosphere, 205: 531-539.
9. Wang, J., Tsuzuki, T., Tang, B., Hou, X.,
Sun, L. and Wang, X. (2012). Reduced graphene oxide/ZnO composite: Reusable
adsorbent for pollutant management. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,
4(6), 3084-3090.
10. Nurchi, V. M., Crespo-Alonso, M., Pilo, M.
I., Spano, N., Sanna, G. and Toniolo, R. (2019). Sorption of ofloxacin and
chrysoidine by grape stalk. A representative case of biomass removal of
emerging pollutants from wastewater. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,
12(7): 1141-1147.
11. Bhatia, V., Ray, A. K. and Dhir, A. (2016).
Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin by co-doped titanium dioxide
under solar irradiation. Separation and Purification Technology, 161:
1-7.
12. Dai, J. F., Xian, T., Di, L. J. and Yang, H. (2013).
Preparation of BiFeO3 -graphene nanocomposites and their enhanced
photocatalytic activities. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2013: 1155.
13. Moussa, H., Girot, E., Mozet, K., Alem, H.,
Medjahdi, G. and Schneider, R. (2016). ZnO rods/reduced graphene oxide
composites prepared via a solvothermal reaction for efficient sunlight-driven
photocatalysis. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 185: 11-21.
14. Soltani, T. and Entezari, M. H. (2013).
Photolysis and photocatalysis of methylene blue by ferrite bismuth
nanoparticles under sunlight irradiation. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:
Chemical, 377(3): 197-203.
15. Gómez-Pastora, J., Dominguez, S., Bringas,
E., Rivero, M. J., Ortiz, I. and Dionysiou, D. D. (2017). Review and
perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water
treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 310: 407-427.
16. Hu, Z. T., Liu, J., Yan, X., Oh, W. Da and
Lim, T. T. (2015). Low-temperature synthesis of graphene/Bi2Fe4O9
composite for synergistic adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of hydrophobic
pollutant under solar irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 262:
1022-1032.
17. Liu, Y., Guo, H., Zhang, Y., Tang, W., Cheng,
X. and Li, W. (2018). Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by
sillenite Bi25FeO40: Singlet oxygen generation and
degradation for aquatic levofloxacin. Chemical Engineering Journal,
343(February): 128-137.
18. Rouhani, Z., Karimi-Sabet, J.,
Mehdipourghazi, M., Hadi, A. and Dastbaz, A. (2019). Response surface
optimization of hydrothermal synthesis of Bismuth ferrite nanoparticles under
supercritical water conditions: Application for photocatalytic degradation of
Tetracycline. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Management,
11: 100198.
19. Wang, X., Wan, X., Xu, X. and Chen X. (2014).
Facile fabrication of highly efficient AgI/ZnO heterojunction and its
application of methylene blue and rhodamine B solutions degradation under
natural sunlight. Applied Surface Sciences, 321:10-8.
20. Hapeshi, E., Achilleos, A., Vasquez, M. I.,
Michael, C., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Mantzavinos, D. (2014). Drugs degrading
photocatalytically: Kinetics and mechanisms of ofloxacin and atenolol removal
on titania suspensions. Water Research, 44(6):1737-1746
21. Satar, N. S. A., Aziz, A. W., Yaakob, M. K.,
Yahya, M. Z. A., Hassan, O. H., Kudin, T. I. T. and Kaus, N. H. M. (2016).
Experimental and first-principles investigations of lattice strain effect on
electronic and optical properties of biotemplated BiFeO3
nanoparticles. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(45): 26012-26020.
22. Lowell, S., Shields, J. E., Thomas., M. A.
(2004). Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size
and density. Molecularly Imprinted Materials: Science and Technology,
127(40): 14118-14120.
23. Sing, K. S. W., Everett, D. H., Haul, R. A.
W., Moscou, L., Pierotti, R. A., Rouquerol, J., & Siemieniewska, T. (1985).
Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to
the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry,
57(4): 603-619.
24. Huo, Y., Jin, Y. and Zhang, Y. (2010). Citric
acid assisted solvothermal synthesis of BiFeO3 microspheres with
high visible-light photocatalytic activity. Journal of Molecular Catalysis
A: Chemical, 331(1–2): 15-20.
25. Fiol, N. and Villaescusa, I. (2009).
Determination of sorbent point zero charge: Usefulness in sorption studies. Environmental
Chemistry Letters, 7(1): 79-84.
26. Xu, H. Y., Wu, L. C., Zhao, H., Jin, L. G.
and Qi, S. Y. (2015). Synergic effect between adsorption and photocatalysis of
metal-free g-C3N4 derived from different precursors. PLoS
One, 10(11): 1-20.
27. Crespo-Alonso, M., Nurchi, V. M., Biesuz, R.,
Alberti, G., Spano, N., Pilo, M. I. and Sanna, G. (2013). Biomass against
emerging pollution in wastewater: Ability of cork for the removal of ofloxacin
from aqueous solutions at different pH. Journal of Environmental Chemical
Engineering, 1(4), 1199–1204.
28. Peres, M. S., Maniero, M. G. and Guimarães,
J. R. (2015). Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin and evaluation of the
residual antimicrobial activity. Photochemical Photobiological Sciences;14(3):556-562.
29. Senasu, T., Chankhanittha, T., Hemavibool,
K. and Nanan, S. (2021). Visible-light-responsive photocatalyst based on
ZnO/CdS nanocomposite for photodegradation of reactive red azo dye and
ofloxacin antibiotic. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,
123: 105558.
30. Lescano, M. R., Lopez, A. O., Romero, R. L.
and Zalazar, C. S. (2021). Degradation of chlorpyrifos formulation in water by
the UV/H2O2 process: Lumped kinetic modelling of total
organic carbon removal. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:
Chemistry, 404: 112924.